Abstract
Campomelic dysplasia (CD) is skeletal dysplasia associated with abnormal facies and multiple congenital anomalies, with characteristic skeletal anomalies. Newborns with CD often die due to respiratory insufficiency and congenital anomalies. CD results from mutations in the gene that encodes SOX9 gene. Ultrasound findings include midshaft bending of the femora and tibiae, micrognathia, and usual normal chest size and head circumference.
Keywords
skeletal dysplasia, SOX9 , campomelic dysplasia
Introduction
Campomelic dysplasia (CD) is a skeletal dysplasia characterized by abnormal facies, multiple congenital anomalies, a typical pattern of skeletal abnormalities, and frequent male-to-female sex reversal. Newborns with CD often die as a result of respiratory insufficiency and congenital anomalies. A small subset of individuals with clinical features of CD lack characteristic long bone bowing and are classified as having acampomelic campomelic dysplasia.
CD results from mutations in the gene that encodes SOX9 gene. SOX9 is a transcription factor and is involved in testis development and in development of the skeleton. It is a master regulator of endochondral ossification. CD is an autosomal dominant condition, and germline mosaicism has been reported. Affected neonates often die in infancy because of respiratory insufficiency secondary to cervical spine instability or airway instability (laryngotracheomalacia). Despite these immediate risks, there are several reports of infants affected with CD who survived the neonatal period, although the prognosis is guarded.
Disorder
Definition
The term campomelic dysplasia is based on the Greek word campomelic, meaning “bent limb.” CD commonly causes skeletal abnormalities, Pierre Robin sequence, and can cause XY sex reversal in 75% of cases. The diagnosis is suspected by skeletal findings often seen on routine prenatal ultrasound (US) and can be confirmed with prenatal or postnatal molecular genetic testing or radiologic findings.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
CD is rare, and specific prevalence data are unavailable. CD does not have specific ethnicity or sex preponderance.
Infants with CD generally die shortly after birth as a result of respiratory insufficiency secondary to airway compromise or cervical spine instability. Interestingly, newborns with CD die of respiratory compromise, yet their chest size is frequently normal, suggesting underlying lung pathology.
Etiology, Pathophysiology, and Embryology
CD is an autosomal dominant disorder resulting from de novo mutations in the SOX9 gene. Most affected individuals have an identifiable mutation. Heterozygosity for mutations involving missense mutations, nonsense mutations, deletion of the coding region, and occasionally chromosomal rearrangements that disrupt the regulatory regions of SOX9 have been reported.
If a parent has gonadal mosaicism for a mutation, the recurrence risk is increased and is higher if the parent has somatic mosaicism. There is evidence that mildly affected individuals can have children with classic features of campomelic dysplasia. Unbalanced chromosomal rearrangements within the chromosomal region encoding SOX9 inherited from a parent can also confer an increased recurrence risk.
Manifestations of Disease
Clinical Presentation
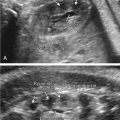
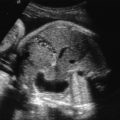
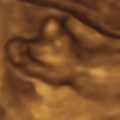
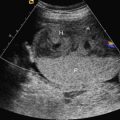
CD manifests with characteristic skeletal findings, pretibial skin dimples, dysmorphic facies, dolichocephaly, low set ears, laryngotracheomalacia, dislocated hips, and a high incidence of sex reversal in males. Skeletal abnormalities include hypoplastic scapulae ( Fig. 47.1 ), underdeveloped pubic bones, short and often bowed long bones in the midshaft ( Fig. 47.2 ), hip dislocations (see Fig. 47.2 ), cervical spine instability ( Fig. 47.3 ) due to hypoplastic cervical vertebrae, and bell-shaped thorax with 11 pairs of ribs. Facial features commonly seen with CD include a relative macrocephaly, flattened midface, long philtrum and micrognathia ( Fig. 47.4 ), and cleft palate.