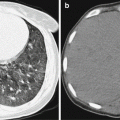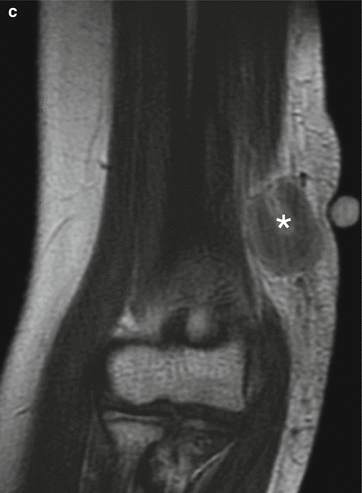
Fig. 4.1
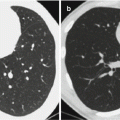
CSD lymphadenitis in the right armpit. (a) MR imaging demonstrates oval nodules in the right armpit, with surrounding edema. T1WI signals are equal (indicated by arrows). (b) T2WI fat-suppression sequence demonstrates high signals. (c) After the injection of contrast agent, centers of the lesions are enhanced (indicated by asterisk) (Reproduced with permission from Wang CW, et al. Clin Imaging, 2009, 33 (4):318)
For case detail and figures, please refer to Wang CW, et al. Clin Imaging, 2009, 33 (4): 318.
Case Study 4
A female patient aged 18 years was hospitalized due to a lump in her left elbow for 1 week. She denied histories of upper limb infection, trauma, as well as skin wound and bleeding at the location of the lump. By physical examination, the lump was moderately hard and mobile, with slight tenderness and a smooth surface. There was no distal radiating pain when it was pressed. Preoperatively, she was misdiagnosed with angioma. The following pathological examination defined the diagnosis of CSD lymphadenitis.
For case detail and figures, please refer to Zhang WQ, et al. Practice of Radiology, 2008, 23 (7): 789.
Case Study 5
A male patient aged 48 years complained of general upset, fatigue, epigastric pain, and no enlarged lymph nodes. He denied a history of contact to cat. Ultrasound indicated multiple nodules in the liver. His liver function is normal. The pathological examination after surgery defined the diagnosis of hepatic CSD.
For case detail and figures, please refer to Marsilia GM, et al. Int J Surg Pathol, 2006, 14 (4): 349.
Case Study 6
A girl aged 13 years was hospitalized due to systemic tonic convulsion and unconsciousness. Since day 10 after the hospitalization, she began to experience enlarged lymph nodes in the left groin and fever, with response to pain stimulations. It was reported that she raised a pet dog and cat at home. On day 1 of her hospitalization, she experienced nine episodes of convulsion, which was relieved after intravenous infusion of diazepam and was further improved after intravenous medication of midazolam and phenytoinum natricum. The patient gradually regained her consciousness. On day 2 of her hospitalization, she began to receive oral medication of carbamazepine. By cerebrospinal fluid examination, WBC count was 2 cells/μl, protein 0.22 g/L, bacterial culture negative, and herpes simplex virus negative. By immunofluorescence, IgG antibody titer was 1:512. The blood samples collected from the dog and cat at her home were detected, with Bartonella positive in the cat and Bartonella negative in the dog. The clinical diagnosis was defined to be cerebral CSD. The patient was cured after 3 months.
For case detail and figures, please refer to Ogura K, et al. Eur Neurol, 2004, 51 (2): 109.
4.8 Diagnostic Basis
4.8.1 Clinical Diagnosis
Item 1. The patient has a history of contact to animals, commonly dogs and cats, and has a history of animal scratch or bite.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree