Chapter 29 Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection, Paramedian Approach
Note: Please see page ii for a list of anatomical terms/abbreviations used in this book.
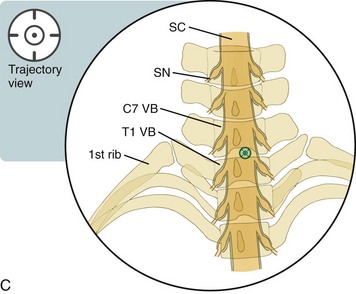
With the approach described in this chapter, the needle is placed with the use of a trajectory view. It is then advanced using multiplanar imaging, with an emphasis on safety that results from the use of the lateral and/or contralateral oblique views6 to confirm needle depth as the spinolaminar line and epidural space are approached. Because it is common for the patient’s shoulders to obscure the needle image in the lateral view, the 60-degree contralateral oblique view may be the only view available for safely identifying needle depth by visualizing the line. If the needle tip is midline, the oblique may be in either direction (i.e., right or left.) When the lateral or contralateral oblique view is used to assess depth, one need not “step off” of the lamina, as is often recommended.
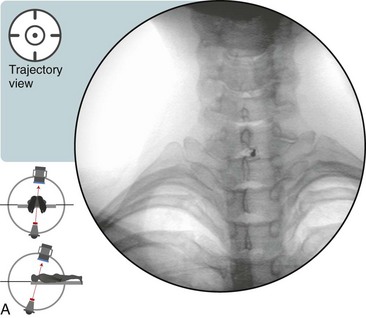
 Trajectory View (Figure 29–1)
Trajectory View (Figure 29–1)
 Confirm the level (with the anteroposterior [AP] view).
Confirm the level (with the anteroposterior [AP] view).
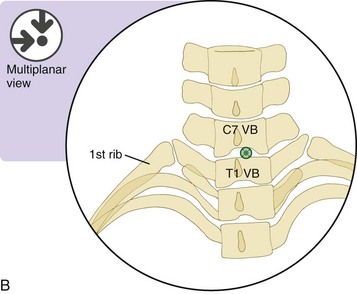
 Maximize the radiolucent size of the targeted interlaminar space (usually C7-T1) with the use of a caudad tilt.
Maximize the radiolucent size of the targeted interlaminar space (usually C7-T1) with the use of a caudad tilt.
 Oblique slightly to symptomatic side about 5 to 10 degrees.
Oblique slightly to symptomatic side about 5 to 10 degrees.
 The needle is placed directly midline or just ipsilateral to midline on the painful side in the target radiolucent interlaminar space.
The needle is placed directly midline or just ipsilateral to midline on the painful side in the target radiolucent interlaminar space.