Chapter 10 Congenital Heart Disease
Over one million adults have congenital heart disease (CHD) in the United States. For the first time, there are now more adults living with CHD than children. The reported incidence of CHD varies widely because of differences in counting minor lesions at birth (such as bicuspid aortic valve, small ventricular septal defects, silent patent ductus arteriosus, and anomalous pulmonary veins), and increasingly better diagnostic methods. The incidence of severe CHD requiring surgery is about 3 per 1000 live births. More accurate diagnosis at presentation and improved medical, surgical, and postoperative care have greatly improved survival so that 90% of children born today with CHD will reach adulthood.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS OF CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS
The steps for the segmental diagnostic approach to cardiac malformations are:
Cardiac Axis and Visceral Situs
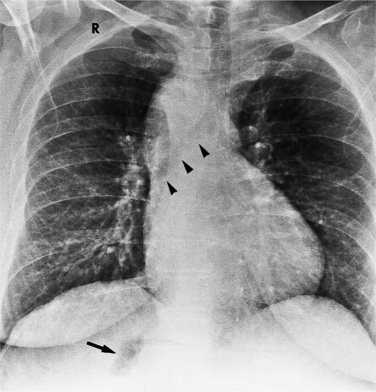
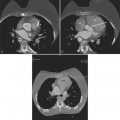
The situs is determined by chest and abdominal radiographs. Situs solitus and situs inversus are recognized by the asymmetry of the tracheobronchial tree and by the positions of the abdominal organs. Symmetrically lobed lungs (Fig. 10-10), midline liver, gastrointestinal malrotations, asplenia, and polysplenia denote the heterotaxy syndrome (Fig. 10-11), which can also be recognized by isomerism of the atria. Isomerism means that both atria have features of the right atrium or of the left atrium. The visceral-atrial rule is that the right and left atria develop on the same side as the thoracic and abdominal viscera do. In situs solitus, the right atrium is on the right side of the mediastinum and the left atrium is on the left side. In situs inversus, the morphologic right atrium is on the left side and the left atrium lies on the right side. In situs ambiguus, right and left sides cannot be determined because the lungs and abdomen are symmetric. For example, in asplenia there are two right (trilobed) lungs and both atria are morphologically right atria. In polysplenia there are two (bilobed) left lungs and both atria are morphologic left atria.
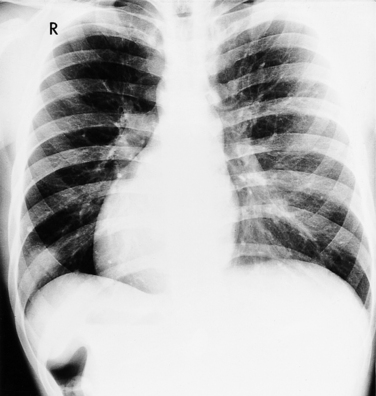
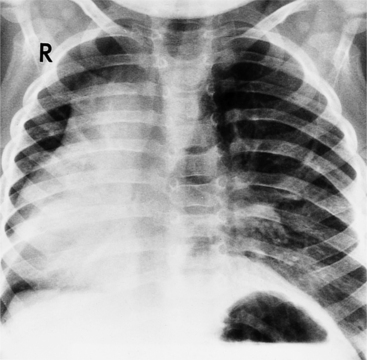
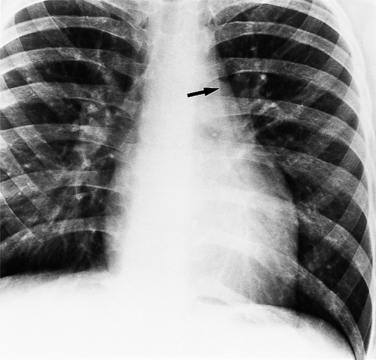
In most people, the major portion of the heart lies slightly to the left of midline. The cardiac apex denotes the location of the heart within the thorax. Dextrocardia (Fig. 10-12), levocardia (Fig. 10-13), and mesocardia then indicate the possible positions of the heart. Using this terminology, a cardiac malposition is any heart that does not have a leftward cardiac axis in situs solitus. A malposition includes dextrocardia in situs solitus and levocardia in situs inversus (Fig. 10-14), as well as dextrocardia in situs inversus. All these positions represent deviation from normal embryologic development without necessarily implying any hemodynamic or morphologic derangement.
In primary dextrocardia, the main defect is in the heart. There are two types of primary dextrocardia: (1) dextroversion, in which the heart is rotated or pivoted so that its apex lies on the right side with the atria as a fulcrum; and (2) mirror-image dextrocardia. In secondary dextrocardia, the heart is normal but the mediastinum is shifted to the right because of extracardiac abnormalities that involve the lungs, pleura, or skeleton (Box 10-1). Examples of the latter include pneumothorax, congenital herniation of the gastrointestinal tract into the thorax, and thoracolumbar scoliosis (Fig. 10-15).
Box 10-1 Types of dextrocardia
PRIMARY DEXTROCARDIA
Atrial Morphology
With rare exceptions, the morphology of the atria corresponds closely with the situs of the tracheobronchial tree and the abdominal viscera. Of the various criteria for distinguishing between right and left atria, the most reliable are the shape of the atrial appendage (see Figure 10-1) and the connection to the inferior vena cava (Box 10-2). The right atrial appendage is broad and pyramidal, whereas the left atrial appendage is thin with a narrow neck. The inferior vena cava almost always connects with the right atrium. This is true even in the “absence” of the inferior vena cava and azygos continuation. In this entity, there is no intrahepatic portion of the cava but the hepatic veins connect to the subdiaphragmatic portion of the inferior vena cava, which joins the right atrium.
Box 10-2 Normal atria
| Right Atrium | Left Atrium |
Ventricular Morphology
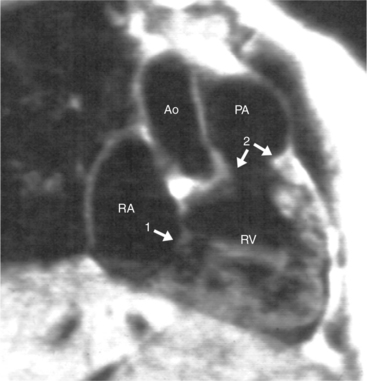
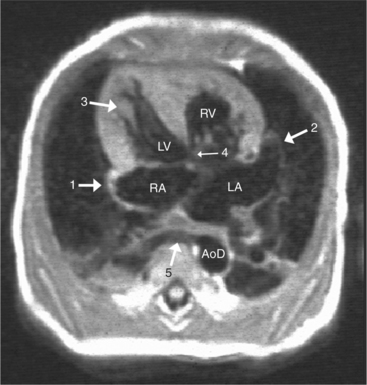
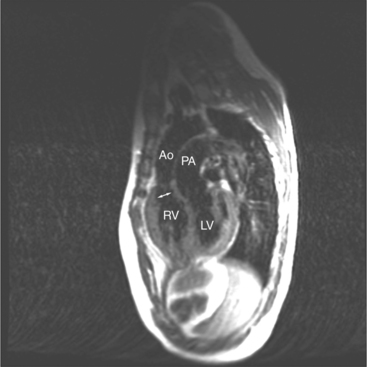
When the right and left ventricles are normal, identification of the two ventricles is relatively simple (Box 10-3). The normal right ventricle has coarse, trabeculated walls when compared with the smooth-walled left ventricle. The right ventricle has a contractile muscle called the conus or infundibulum between the tricuspid and pulmonary valves (see Figure 10-2), whereas the left ventricle has mitral-aortic continuity with no intervening muscle (Fig. 10-16). The right ventricle has trabeculations and papillary muscles on its septum, whereas in the left ventricle these structures are not present on the septum. A bicuspid (mitral) atrioventricular valve is a part of the left ventricle, whereas a tricuspid atrioventricular valve is part of the right ventricle, although either of these valves may have a cleft or be absent.
Box 10-3 Normal ventricles
| Right Ventricle | Left Ventricle |
|---|---|
| Coarse, trabeculated walls | Smooth walls |
| Contractile muscle (conus, infundibulum between tricuspid and pulmonary valves) | Mitral aortic continuity with no intervening muscle |
| Trabeculation and papillary muscles on septum | Septum free from trabeculations and papillary muscles |
| Tricuspid atrioventricular valve | Bicuspid (mitral) atrioventricular valve |
| Complex triangular shape | Spheroidal shape |
There is general agreement that an inflow tract must be present for a chamber to be considered a ventricle. The trabecular portion determines whether the chamber is of the right or left ventricular type. In these instances, the single ventricle consists of one large chamber that receives both atrioventricular valves. (Note that this definition excludes mitral or tricuspid atresia.) If only the trabecular and outflow segments are present, this structure is called an outlet chamber. Examples of such hearts are the univentricular heart of the left ventricular type, with or without a rudimentary outflow chamber.
Atrioventricular Connections
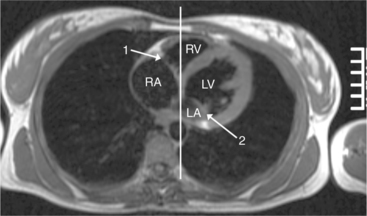
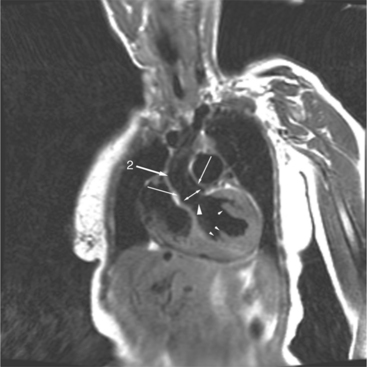
The atrioventricular connections are called concordant when the right atrium connects to the right ventricle (see Figure 10-4) and the left atrium connects to the left ventricle. When the right atrium connects to the left ventricle and the left atrium connects to the right ventricle, the ventricles are discordant in relation to the atria (see Figure 10-5). In the heterotaxy syndrome, in which either two right atria or two left atria may exist, the atrioventricular connection is ambiguous. This schema is less clear when either atresia of one of the atrioventricular valves exists or when one of the atrioventricular valves straddles the interventricular septum. When there is a double-inlet or a straddling atrioventricular valve, the tensor apparatus (the attachments of the chordae tendineae) may connect to either side of the interventricular septum.
Relations of the Great Arteries
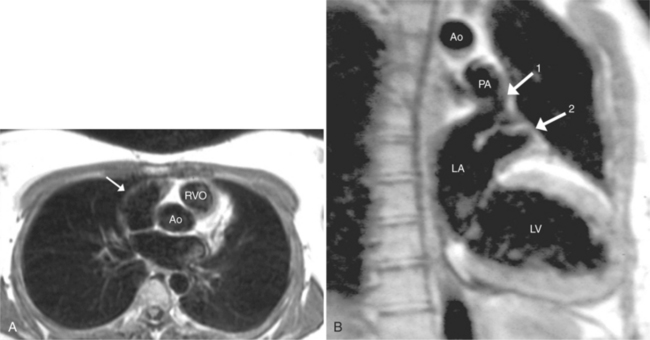
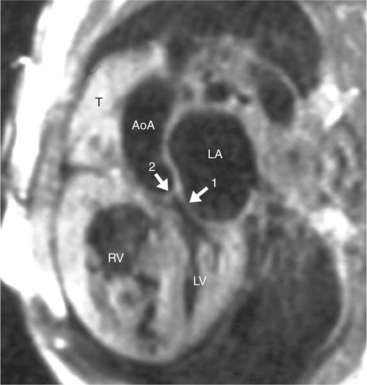
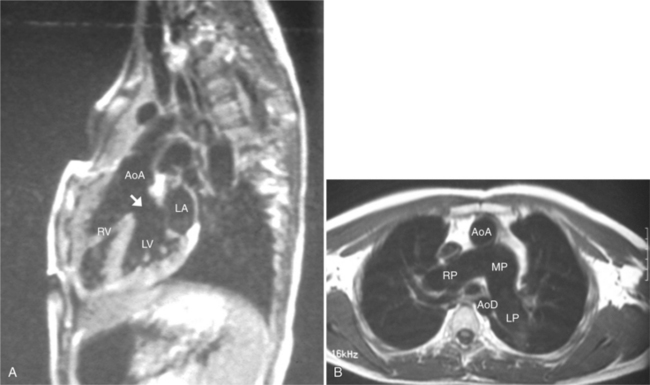
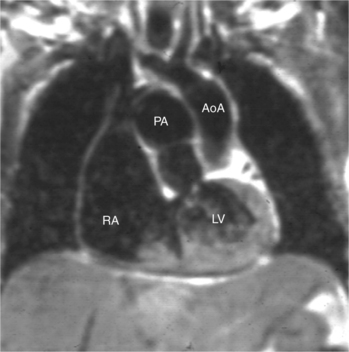
The position of the aorta is described relative to the pulmonary artery in both the anteroposterior and lateral planes (Fig. 10-17). In the normal heart, the aorta is to the right of and posterior to the pulmonary artery (see Figure 10-6). An anterior aorta to the right of the pulmonary artery is common in transposition of the great arteries (TGA; see Figures 10-7, 10-9). An aorta to the left of and anterior to the pulmonary artery is typical in, but not diagnostic of, corrected transposition (Fig. 10-18). Then there is a characteristic leftward convexity of the aorta (Fig. 10-19).
Ventriculoarterial Connections
The pulmonary valve is part of the pulmonary artery (not part of the right ventricle) and the aortic valve is part of the aorta. When the pulmonary artery or the aorta is related to, or overrides more than 50% of, a particular ventricle, it is defined as being connected to that ventricle. This association is particularly strong when there is a continuity between an atrioventricular valve and the semilunar valve. Concordant connections exist when the left ventricle is connected to the aorta and the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery (see Figures 10-2, 10-8). Discordant connections result when the left ventricle is connected to the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle to the aorta (see Figure 10-9). This latter connection is also called transposition. When both great arteries arise predominantly from one ventricle, there is a double-outlet right ventricle or double-outlet left ventricle. The final type of arterial connection is a single-outlet heart, of which there are three varieties:
The ventricular outflow tracts may be one of four distinct types:
Certain types of conus are associated with particular malformations:
Associated Malformations
Cardiotyping
At this point in the segmental analysis of the heart, the atrial and ventricular situs, the atrioventricular connections, the ventriculoarterial connections, and the position of the aorta are known. This data can be expressed in a notation developed by Van Praagh to categorize all possible types of hearts (Box 10-4). The situs of the atria, as indicated by the position of the abdominal viscera and the trachea and lungs, is designated as solitus (S), inversus (I), or ambiguus (A). The ventricular situs is characterized as a D-loop (D), L-loop (L), or undiagnosed loop (X). The position of the aorta in relation to the pulmonary valve is to the right (D), to the left (L), or directly anterior (A). These three letters are written in sequence (atrial situs, ventricular situs, and aortic situs). Examples are a normal heart (S,D,D), a dextrotransposition of the great arteries (S,D,D), and a congenitally corrected TGA or levotransposition (S,L,L) in which the D- and L- indicate the aortic position.
Box 10-4 Cardiotypes
DETERMINE ATRIAL SITUS BY ANALYZING ABDOMEN AND TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TREE
| S | solitus |
| I | inversus |
| A | ambiguus |
DETERMINE VENTRICULAR SITUS
| D | D-loop or solitus |
| L | L-loop or inverted |
| X | X-loop or undiagnosed |
DETERMINE AORTIC SITUS IN RELATIONS TO PULMONARY VALVE
| D | Normally related great arteries with aorta to the right of the pulmonary artery |
| L | Inverted great arteries with aorta to left of pulmonary artery |
| A | Aortic valve is directly anterior to pulmonary valve |
NOTATION (ATRIA, VENTRICLES, GREAT ARTERIES)
| Normal | (S,D,D) |
| D-transportation of great arteries | (S,D,D) |
| L-transportation of great arteries | (S,L,L) |
| Situs inversus | (I,L,L) |
| Asplenia, dextrocardia, transposition of great arteries | (A,L,L) |
MALPOSITIONS AND ABNORMAL CONNECTIONS
Cardiac Connections and Positions
Dextrocardia
Dextrocardia signifies that the apex of the heart is directed toward the right. Primary dextrocardia exists because of an embryologic abnormality. This type of dextrocardia can exist with any type of situs position (Fig. 10-21). When dextrocardia exists with situs inversus, the atrial and ventricular relations are a mirror image of their positions in the usual situs solitus. When the dextrocardia exists in situs solitus, the term isolated dextrocardia is frequently applied. It is clear then that dextrocardia can occur in situs solitus, inversus, and ambiguus. Many associated cardiac anomalies exist in primary dextrocardia. Frequent conditions include ventricular septal defect, TGA, corrected TGA, double-outlet right ventricle, and juxtaposition of the atrial appendages.
The goal of echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and angiography is to define the position and location of each chamber of the heart and their connections and relations with one another and with the great arteries. In those malpositioned hearts in which the location of the interventricular septum is not known before angiography, posteroanterior and lateral projections serve as initial guidelines. Frequently, the projections can be reversed for a malposition; that is, those structures that are normally best seen in the left anterior oblique projection in the normal heart would be studied in the right anterior oblique projection in dextrocardia. As a rule, the dextrocardia itself does not cause clinical problems but rather the associated malformations mandate medical or surgical alleviation.
Levocardia
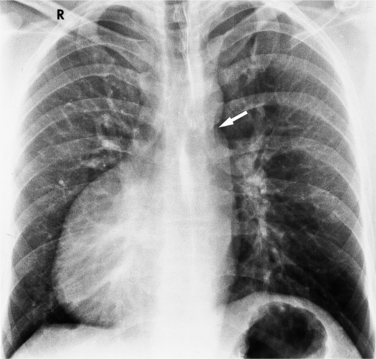
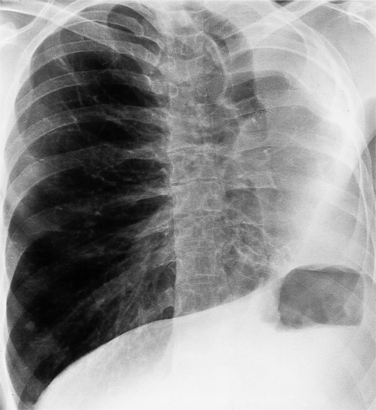
Strictly speaking, levocardia means that the cardiac apex is left sided. Isolated levocardias are those hearts that are left sided when situs inversus is present. This anomaly occurs in less than 1% of all patients with congenital cardiac malformation compared with a 2% incidence of dextrocardia in patients with CHD. With levocardia, the position of the thoracic and abdominal organs ranges from partial to complete situs inversus and also to heterotaxy (Fig. 10-22). Severe malformations are always associated with levocardia and frequently include ventricular septal defect, complete atrioventricular canal defects, and pulmonary stenosis or atresia. Isolated levocardia may be suspected on the chest film with a right-sided stomach bubble and left-sided liver shadow and a left cardiac apex. In contrast, in extrinsic levocardia the heart is intrinsically normal but the mediastinum is shifted from skeletal or pulmonary abnormalities (Fig. 10-23).
Heterotaxy and the Syndromes of Asplenia and Polysplenia
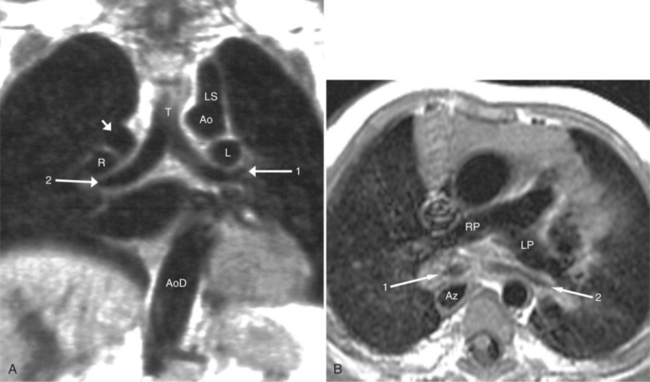
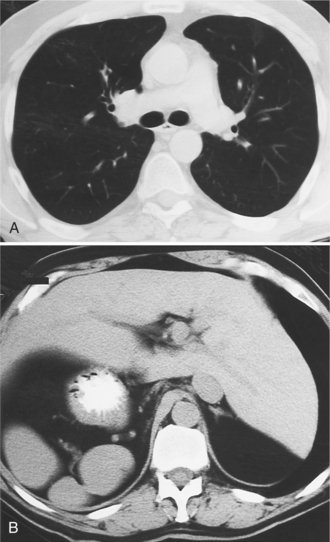
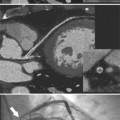
Heterotaxy is the failure of the developing embryo to establish normal left-right asymmetry. Asplenia and polysplenia are part of this spectrum. In these patients the thoracic and abdominal contents have a degree of symmetry, unlike those in situs solitus or inversus in which right- and left-sided organs exist together. In the thorax, both lungs may be trilobed with bilateral epiarterial bronchi, or both lungs may be bilobed with bilateral hypoarterial bronchi. In the abdomen, the asymmetry is also frequently lost. The liver may be midline. The attachment of the mesentery, which usually runs from the left upper quadrant to the right lower quadrant, may have a midline attachment. The spleen may be absent (asplenia), bilobed with multiple accessory spleens, or multiple small spleens (Fig. 10-24) may be found throughout the mesentery (polysplenia). Situs ambiguus exists either when the right and left sides of the lungs, heart, and abdomen are similar or where a right-left relationship is difficult to identify. Boxes 10-5 and 10-6 summarize the characteristics of asplenia and polysplenia.)
Splenic anomalies with malpositions and malformations in multiple organ systems have been recognized since 1826 when Martin and later Ivemark described the absence of the spleen in cyanotic CHD. Complex cardiac malformations are typical when the type of thoracic and abdominal situs abnormality is uncertain or has features of both situs solitus and situs inversus (Table 10-1).
TABLE 10-1 Cardiovascular abnormalities in asplenia and polysplenia
| Abnormality | Asplenia (%) | Polysplenia (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SUPERIOR VENA CAVA | ||
| Bilateral | 53 | 33 |
| Right | 34 | 33 |
| Left | 10 | 33 |
| Uncertain | 3 | — |
| INFERIOR VENA CAVA | ||
| Right sided | 60 | — |
| Left sided | 28 | — |
| Uncertain | 12 | — |
| Azygos continuation | — | 84 |
| Anomalous pulmonary veins | 84 | 50 |
| Total anomalous connection | 72 | — |
| Partial anomalous connection | 12 | — |
| CARDIAC APEX | ||
| Left | 56 | 58 |
| Right | 41 | 42 |
| Uncertain | 3 | — |
| AORTIC ARCH | ||
| Left | 56 | 33 |
| Right | 38 | 67 |
| Unknown | 6 | — |
| Great vessels | ||
| Normally related | 19 | 84 |
| Transposition of great arteries | 72 | 8 |
| Double-outlet right ventricle | 9 | 8 |
| PULMONARY VALVE | ||
| Normal | 22 | 58 |
| Stenosis | 34 | 33 |
| Atresia | 44 | 9 |
| Patent ductus arteriosus | 56 | 50 |
| Absent coronary sinus | 85 | 42 |
| Single ventricle | 44 | 8 |
| Ventricular septal defects | 90* | 67 |
* Of the ventricular septal defects in asplenia, 84% were of the atrioventricular canal type.
Modified from Rose V, Izukawa T, Moes CAF: Syndromes of asplenia and polysplenia; a review of cardiac and non-cardiac malformations in 60 cases with special reference to diagnosis and prognosis. Br Heart J 37:840-852, 1975.
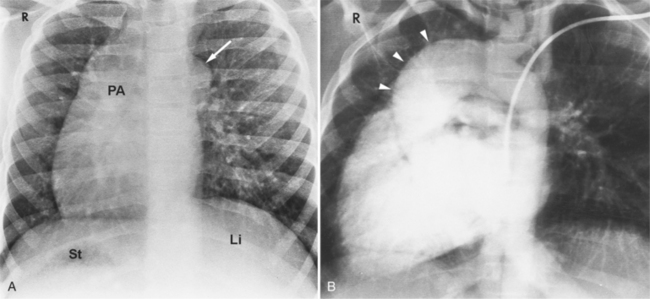
Segmental analysis of the defects in hearts associated with asplenia begins with the atria and the atrial septum. On the chest film, the external contours of the heart frequently do not conform to the expected heart chambers (Fig. 10-25). Almost all these hearts show a common atrioventricular valve, frequently associated with separate, large atrial septal defects in the primum and secundum location. The size and location of these atrial defects are such that the malformation is called a common atrium. The ventricles also almost invariably have major malformations. About one fourth of the ventricles are inverted (as seen in corrected transposition), and half of the hearts have a univentricular chamber with a rudimentary outflow tract.
Anomalies of the great vessels, including TGA and double-outlet right ventricle, have an incidence of 3% to 30%. Angiographically, the posteroanterior and lateral projections are best to allow identification of their right-left relationships. Anomalies in the ventricular septum and semilunar valve stenosis are common, so that filming is also done with the x-ray beam parallel to the interventricular septum with cranial angulation. Because two thirds of persons with asplenia have anomalous systemic venous or pulmonary venous connections, or both, these malformations frequently complicate catheterization.
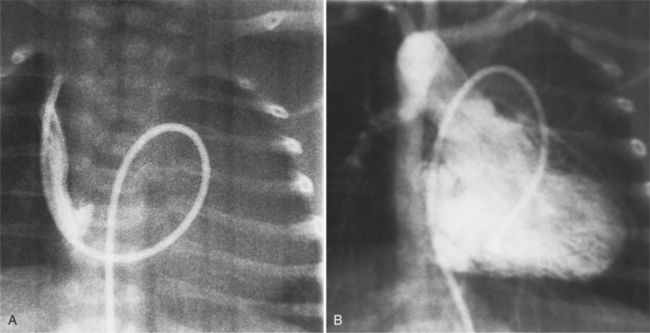
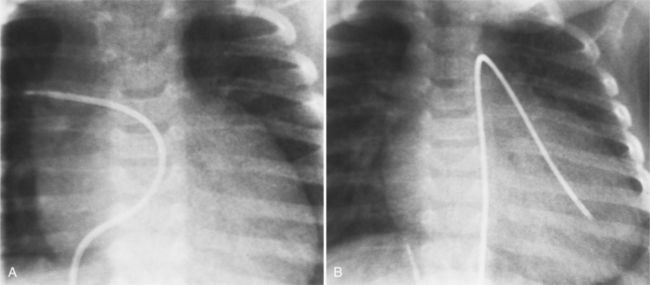
The features of the heart in polysplenia are quite variable, and in fact, there is occasionally no cardiac malformation. With a femoral vein approach, you can recognize azygos continuation by the course of the catheter around the azygos arch (Figures 10-10A, 10-26). You should not make the diagnosis of tricuspid atresia if the catheter tip fails to pass leftward through the heart above the diaphragm but instead should continue advancing the catheter superiorly until it goes around the azygos arch.
Atrioventricular Discordance
In the schema of segmental cardiac analysis, after recognition of the atria and ventricles, the next step is to determine whether the connections between them are concordant or discordant. Atrioventricular discordance means that the right atrium is connected to the left ventricle and the left atrium is connected to the right ventricle (see Figures 10-4, 10-5). Implicit in this definition is the presence of two atria, two atrioventricular valves, and two ventricles. This diagnosis is not appropriate when atrial identification is indeterminate in situs ambiguus or when there is a single common atrioventricular valve. Similarly, distinct right and left ventricles are necessary for this definition, although a ventricular septal defect may exist.
Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the Great Vessels (Levotransposition of the Great Arteries)
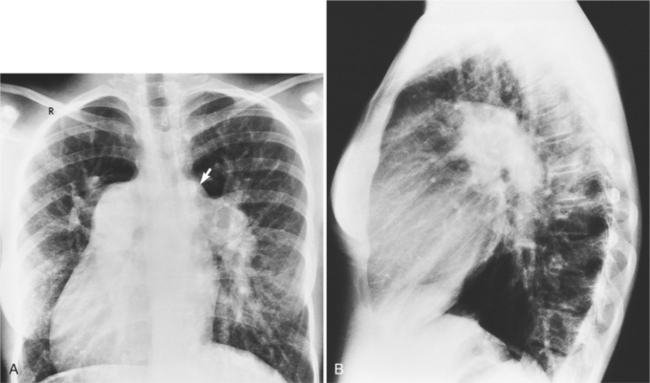
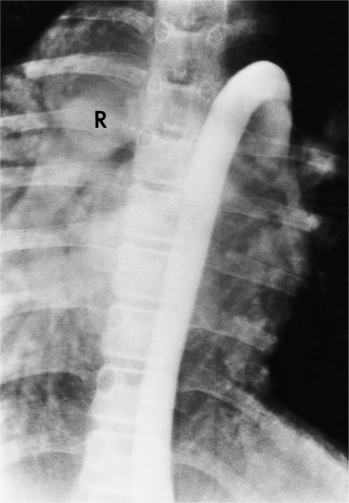
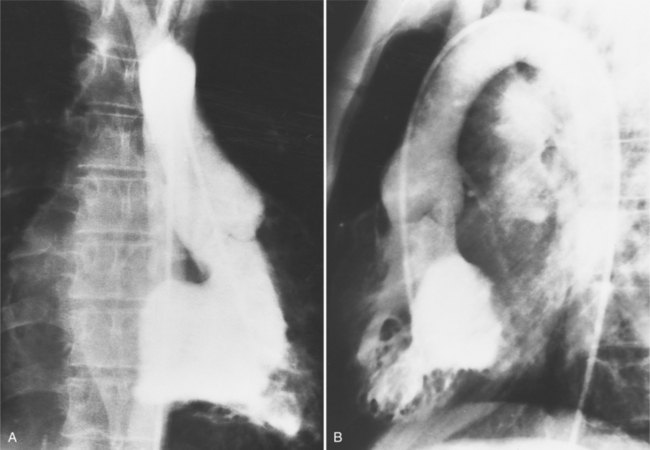
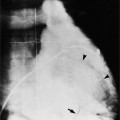
In 1875 Rokitansky reported a form of transposition in which blood passed in normal serial fashion through the pulmonary and systemic circuits. The right atrium was connected to the left ventricle, which was connected to the pulmonary artery. On the oxygenated side of the lungs, the left atrium was connected to the right ventricle, which was connected to the aorta. The atrioventricular valves always correspond with their ventricles, even when there is atrioventricular discordance. That is, the mitral valve is a left ventricular structure, and the tricuspid valve is a right ventricular structure. In congenitally corrected transposition of the great vessels, the aorta lies to the left of and anterior to the pulmonary artery, whereas the pulmonary valve lies to the right and posterior. The aortic valve is usually somewhat anterior to the pulmonary valve, although the two great vessels may be exactly lateral to each other. The ascending aorta frequently has an unusual course, passing in a direction toward the left shoulder so that occasionally a distinctive contour in the left side of the mediastinum is visible on the chest film.
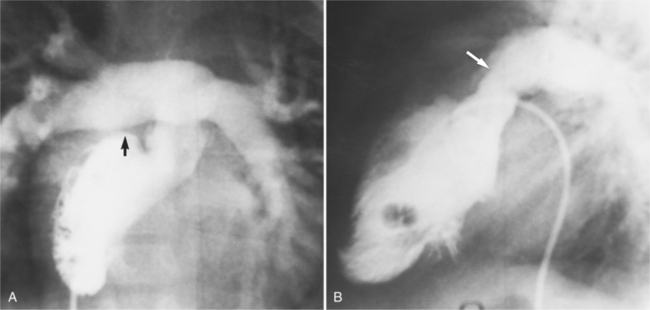
If there are no other defects, this malformation causes no hemodynamic problems and may go undetected during a normal life span. Unfortunately, associated malformations are the rule, and their site and severity determine the clinical course. Ventricular septal defects are frequent (Figures 10-27, 10-28) and may be large enough to cause pulmonary arterial hypertension. These defects are usually in the membranous septum adjacent to the pulmonary valve; muscular defects and supracristal defects are less common. Generally, the left-sided atrioventricular valve (i.e., the valve between the left atrium and the right ventricle) is displaced slightly into the ventricle in a manner resembling Ebstein anomaly. If the displacement is more than a few millimeters (because the tricuspid valve is usually displaced to the apex by that amount), the diagnosis of Ebstein anomaly is quite likely. Pulmonary stenosis is frequently associated with ventricular septal defect and may be caused by a malformed valve, a subpulmonary membrane, aneurysms of the membranous ventricular septum, or rarely, accessory tissue in the atrioventricular valve or a muscular bar in the subpulmonary region.
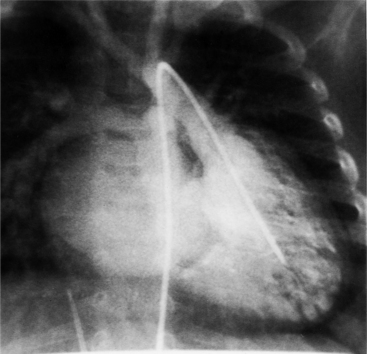
Imaging establishes the atrioventricular connections, the morphology of the ventricles, and the position of the aorta and pulmonary artery. The position of the venous and arterial catheters frequently give the first clue to a corrected transposition (Fig. 10-29). In situs solitus and levocardia, the venous catheter passes through the heart in the midline to reach the pulmonary arteries. The catheter in the pulmonary artery is posterior to its usual location, which is where the aorta should be in normal hearts. The retrograde arterial catheter has a distinctive curve in the ascending aorta as its course becomes convex medially and to the left before entering the heart (see Figure 10-18). On the lateral view, the aortic catheter is anterior and superior to the venous catheter. The venous and arterial catheters indicate the fundamental relationship between the aorta and the pulmonary artery in corrected transposition with situs solitus and levocardia; the pulmonary artery lies to the right and posterior, whereas the aorta is anterior and to the left.
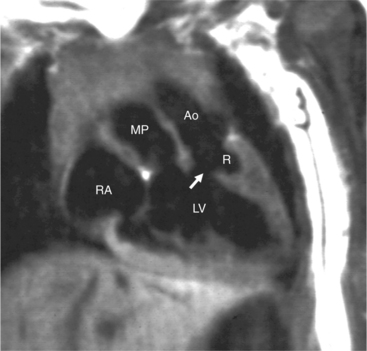
In the sagittal view, the left ventricle appears to “stand on its apex” with a conical shape whose apex is in the diaphragmatic-sternal angle. The anterior wall of the left ventricle extends superiorly into a distinctive pouch that is characteristic of inverted ventricles, namely the anteriorly placed left ventricle (Fig. 10-30). This recess is separate from both the mitral and pulmonary valves and is the most anterior and superior structure of either ventricle. The outflow portion of the left ventricle in the lateral projection is posterior and connects to a pulmonary artery, which is beside or posterior to the aorta. The posterior wall of the left ventricle beneath the pulmonary valve is the membranous septum, and the anterior wall forms a neck above the blind recess and below the pulmonary valve.
In the frontal view, the right ventricle is to the left of and slightly superior to the left ventricle (Fig. 10-31). In this position, the right ventricle has an oval to triangular shape and the usual coarse trabeculations. The tricuspid annulus is in the posteroanterior plane separated from the aortic valve by the muscular infundibulum. This morphologic right ventricle connects with the left atrium. The crista supraventricularis in this projection is the medial wall of the infundibulum above the tricuspid valve. In the lateral projection, the crista is the posterior wall of the infundibulum and separates the tricuspid from the aortic valve.
About one third of patients with corrected transposition have tricuspid regurgitation (i.e., from the right ventricle connected to the left atrium). The apically displaced tricuspid leaflets of Ebstein anomaly are usually the cause of the regurgitation, but there are occasionally other leaflet abnormalities. When there is severe regurgitation in infants, the details of the leaflets and the origin of their insertion are frequently difficult to identify. If technical factors such as arrhythmia and catheter position can be excluded, it should be presumed that severe regurgitation into the left atrium is associated with a “left-sided” Ebstein anomaly (Fig. 10-32). The tricuspid annulus is adjacent to the right coronary artery, which may be opacified during the ventriculogram.
Coronary Artery Patterns
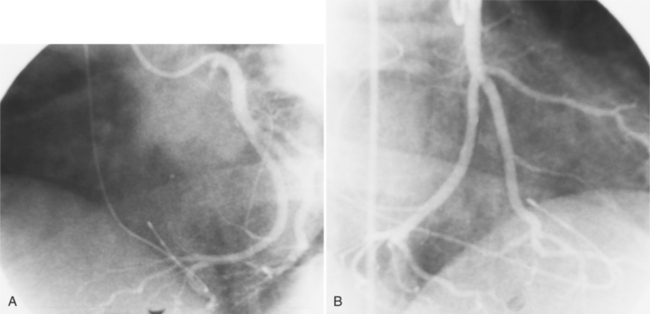
The coronary anatomy in congenitally corrected transposition of the great vessels is unique to inverted ventricles. The right coronary artery supplies the morphologic right ventricle and the left coronary artery provides an anterior descending branch in the interventricular sulcus and a variable circumflex branch over the morphologic left ventricle (Fig. 10-33). In congenitally corrected TGA, the right coronary artery passes to the left and inferior in the atrioventricular groove between the left atrium and right ventricle. Distally, this artery branches into the atrioventricular nodal branch, the posterior descending artery, and a variable set of branches to the inferior portion of the left ventricle (Fig. 10-34). The marginal branches over the right ventricular epicardial surface tend to be large with numerous branches. In contrast, the left coronary artery lies anterior and to the right of the right coronary artery. The left main coronary artery continues mainly as the anterior descending branch, which has numerous septal and diagonal branches. The circumflex artery in the atrioventricular groove between the right atrium and left ventricle tends to be vestigial. The position of the coronary arteries within the thorax may be different because of dextrocardia or other relative rotations, but the coronary distribution corresponds uniquely to the respective ventricle. When confusing ventricular morphology does not allow identification of the right or left ventricle, visualization of the coronary arteries permits accurate identification of the ventricles.
Isolated Ventricular Inversion
Atrioventricular discordance with ventriculoarterial concordance is termed isolated ventricular inversion. The segmental connections for the venous side of the heart are right atrium to left ventricle to aorta, and for the systemic side left atrium to right ventricle to pulmonary artery. As originally reported by the Van Praaghs (1966), the pulmonary artery arises anteriorly and to the left of the aorta. A large subaortic ventricular septal defect is adjacent to the septal leaf of the tricuspid valve. The aorta may also originate anterior to the pulmonary artery.
Ventriculoarterial Discordance
Complete Dextrotransposition of the Great Arteries
In 1797 Baillie described the heart of an infant in which the aorta connected to the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery to the left ventricle. The term transposition of the aorta and pulmonary artery is ascribed to Farre in 1814. Since that time, there has been controversy about whether it should be defined by the abnormal anteroposterior position of the great arteries or by the abnormal connections to the ventricles. TGA is a ventriculoarterial abnormality in which the aorta originates above the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery originates over the left ventricle.
Ventricular septal defects occur in about one third of babies with transposition (see Figure 10-7A), and when present, may result in congestive heart failure from the large blood flow. Extracardiac shunts may occur, as in patent ductus arteriosus or with bronchopulmonary connections to the pulmonary vascular bed. The ductus arteriosus remains patent in one fourth to one half of infants who do not receive prostaglandin E1 and allows blood to flow from the pulmonary artery to the aorta if the pulmonary vascular resistance is high and from the aorta to the pulmonary artery when the high fetal pulmonary artery pressures fall below the systemic blood pressure.
Besides the ventricular septal defect, the other major associated malformation is obstruction to blood entering the pulmonary arteries. About one fourth of those with TGA have some form of pulmonary stenosis (Fig. 10-35). The site of obstruction is usually in the subpulmonary region and it has a variety of causes: