• These are classified into 33 groups (1–33) • Conditions referenced elsewhere • These are classified into 3 groups (A–C) • They are due to altered blastogenesis occurring during the 1st 6 weeks of life • This results from defective endochondral bone formation • Limb shortening: rhizomelic (proximal) • A decreasing interpedicular distance within the lumbar spine (travelling caudally) • Sporadic, autosomal dominant mutation • Autosomal recessive (often lethal) • Small thorax with short ribs (horizontally orientated) • The development of dwarfism changes over time – the trunk gradually shortens relative to the limbs (due to the developing kyphoscoliosis) • Severe short-limbed dwarfism • Schmid type: more common • Jansen type: less common • Metaphyseal flaring • Autosomal recessive • Short ribs in infancy
Congenital skeletal anomalies
DEVELOPMENTAL SKELETAL ANOMALIES
OSTEOCHONDRODYSPLASIAS
 abnormalities are intrinsic to bone and cartilage and will continue to evolve throughout life
abnormalities are intrinsic to bone and cartilage and will continue to evolve throughout life
DYSOTOSES (LOCALIZED DISORDERS WITH PREDOMINANT CRANIAL AND FACIAL INVOLVEMENT)
 previously normal bones will remain so (unlike an osteochondrodysplasia)
previously normal bones will remain so (unlike an osteochondrodysplasia)  more than 1 bone may be involved
more than 1 bone may be involved
SELECTED OSTEOCHONDRODYSPLASIAS
ACHONDROPLASIA (GROUP 1)
DEFINITION
 mesomelic (medial)
mesomelic (medial)  acromelic (distal)
acromelic (distal)
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
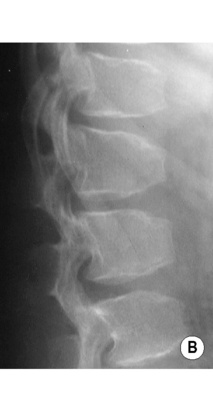
 short vertebral pedicles
short vertebral pedicles  posterior vertebral body scalloping
posterior vertebral body scalloping  flat acetabular roofs
flat acetabular roofs  short ribs and short wide tubular bones
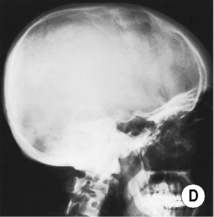
short ribs and short wide tubular bones  a large skull vault and a small foramen magnum
a large skull vault and a small foramen magnum 
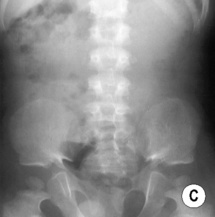
 ‘Bullet-shaped’ vertebral bodies: with an antero-inferior anterior beak
‘Bullet-shaped’ vertebral bodies: with an antero-inferior anterior beak
 ‘Tombstone’ appearance: squared small iliac wings with a small sciatic notch
‘Tombstone’ appearance: squared small iliac wings with a small sciatic notch
 ‘Champagne glass’ pelvis: the pelvic inlet resembles a champagne glass
‘Champagne glass’ pelvis: the pelvic inlet resembles a champagne glass
 ‘Chevron’ deformity: V-shaped growth plate notches
‘Chevron’ deformity: V-shaped growth plate notches
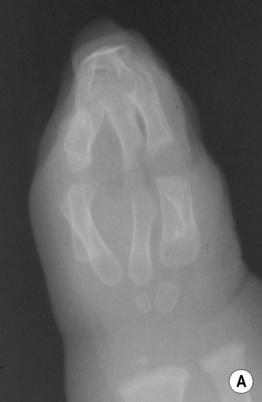
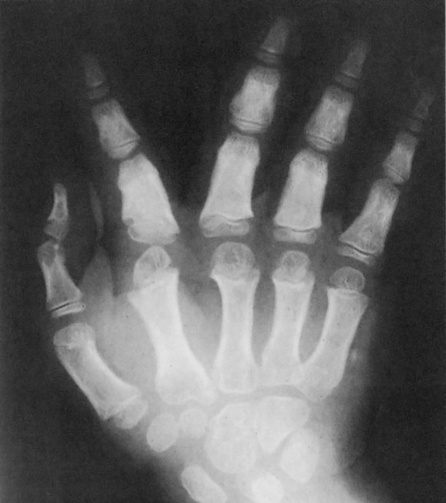
 ‘Trident hand’: the fingers are all the same length and diverge into 2 pairs
‘Trident hand’: the fingers are all the same length and diverge into 2 pairs
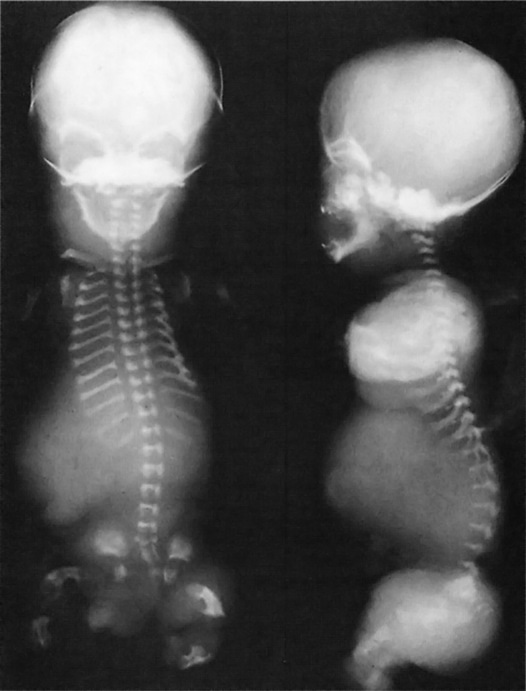
THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA (GROUP 1)
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 this is the most common lethal neonatal skeletal dysplasia
this is the most common lethal neonatal skeletal dysplasia  short markedly curved limbs
short markedly curved limbs  respiratory distress due to a (small thoracic cage)
respiratory distress due to a (small thoracic cage)
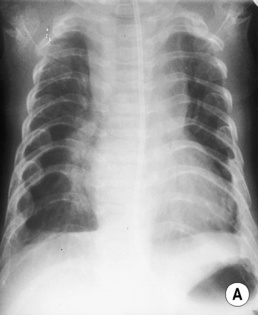
ASPHYXIATING THORACIC DYSPLASIA (JEUNE’S) (GROUP 4)
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 respiratory problems with a long narrow thorax
respiratory problems with a long narrow thorax  short hands and feet
short hands and feet  nephronophthisis in later-life survivors
nephronophthisis in later-life survivors
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
 widened costochondral junctions
widened costochondral junctions  high clavicles
high clavicles  short iliac bones
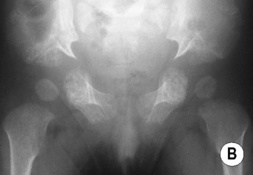
short iliac bones  horizontal acetabula with medial and lateral ‘spurs’ (‘trident’ appearance)
horizontal acetabula with medial and lateral ‘spurs’ (‘trident’ appearance)  ‘wineglass’ pelvis
‘wineglass’ pelvis  premature appearance of the proximal femoral ossification centres
premature appearance of the proximal femoral ossification centres  cone-shaped phalangeal epiphyses
cone-shaped phalangeal epiphyses  may have polydactyly
may have polydactyly
METATROPIC DYSPLASIA (GROUP 3)
DEFINITION
METAPHYSEAL CHONDRODYSPLASIA (GROUP 13)
DEFINITION
 mild
mild  predominantly involves the lower limbs
predominantly involves the lower limbs
 more severe
more severe  symmetrical involvement of all tubular bones
symmetrical involvement of all tubular bones
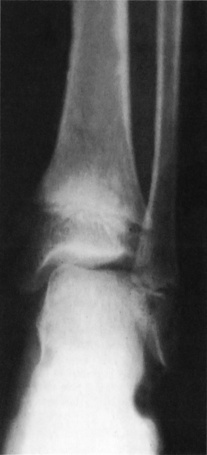
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
 irregular widened growth plates (most marked at the hips)
irregular widened growth plates (most marked at the hips)  increased density and unevenness of the metaphyses (particularly the upper femora and around the knees)
increased density and unevenness of the metaphyses (particularly the upper femora and around the knees)  large femoral capital epiphyses
large femoral capital epiphyses  coxa vara
coxa vara  femoral bowing
femoral bowing  anterior cupping of the ribs
anterior cupping of the ribs  normal spine
normal spine
ELLIS–VAN CREVELD (CHONDROECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA) (GROUP 4)
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 short stature
short stature  short limbs (more marked distally)
short limbs (more marked distally)  polydactyly
polydactyly  hypoplasia of the nails and teeth
hypoplasia of the nails and teeth  ectodermal dysplasia with sparse hair
ectodermal dysplasia with sparse hair  congenital cardiac defects (e.g. ASD)
congenital cardiac defects (e.g. ASD)
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
 short iliac wings
short iliac wings  ‘trident’ appearance – the pelvis becomes more normal in childhood
‘trident’ appearance – the pelvis becomes more normal in childhood  premature ossification of the femoral capital epiphyses
premature ossification of the femoral capital epiphyses  laterally sloping proximal tibial metaphysis
laterally sloping proximal tibial metaphysis  exostosis of the medial upper tibial shaft
exostosis of the medial upper tibial shaft  carpal fusions
carpal fusions  cone-shaped epiphyses (middle phalanges)
cone-shaped epiphyses (middle phalanges)  polydactyly of the hands and feet
polydactyly of the hands and feet
Congenital skeletal anomalies





 multiple skeletal abnormalities (dysplastic knees and elbows)
multiple skeletal abnormalities (dysplastic knees and elbows)  dysplastic fingernails
dysplastic fingernails  clinodactyly (curving of the 5th finger towards the 4th finger)
clinodactyly (curving of the 5th finger towards the 4th finger)  renal disease
renal disease absent or hypoplastic patellae
absent or hypoplastic patellae  hypoplastic lateral femoral condyles
hypoplastic lateral femoral condyles  genu valgum
genu valgum  hypoplastic capitellum
hypoplastic capitellum  radial head dislocation
radial head dislocation  short 5th metacarpals
short 5th metacarpals abnormalities are present from birth
abnormalities are present from birth  malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet
malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet  proptosis
proptosis  high arched or cleft palate
high arched or cleft palate  bifid uvula
bifid uvula progressive ankylosis of the phalangeal joints
progressive ankylosis of the phalangeal joints  dislocated radial heads
dislocated radial heads  progressive fusion within the cervical spine (commonly C5/C6)
progressive fusion within the cervical spine (commonly C5/C6)  progressive fusion of the large joints
progressive fusion of the large joints  hypoplasia of the glenoid fossae
hypoplasia of the glenoid fossae ear deformities
ear deformities  deafness
deafness  downslanting eyes
downslanting eyes  lateral coloboma of the lower eyelid
lateral coloboma of the lower eyelid  hypoplastic malar bone
hypoplastic malar bone  cleft palate
cleft palate maxillary hypoplasia
maxillary hypoplasia  mandibular hypoplasia
mandibular hypoplasia  hypoplastic paranasal sinuses
hypoplastic paranasal sinuses frequently there are 11 pairs of gracile ribs
frequently there are 11 pairs of gracile ribs  there are often two ossification centres within the manubrium sterni (normally only one)
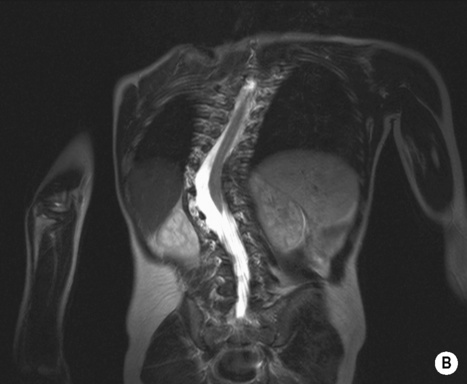
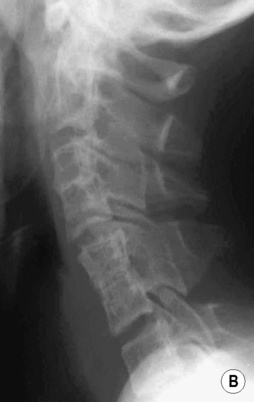
there are often two ossification centres within the manubrium sterni (normally only one)  atlantoaxial subluxation and instability with hypoplasia of the odontoid process (which is frequently a cause of myelopathy)
atlantoaxial subluxation and instability with hypoplasia of the odontoid process (which is frequently a cause of myelopathy)  generalized joint laxity
generalized joint laxity  relatively tall vertebral bodies
relatively tall vertebral bodies  short hands with clinodactyly of the little finger due to a hypoplastic middle phalanx
short hands with clinodactyly of the little finger due to a hypoplastic middle phalanx duodenal atresia and stenosis
duodenal atresia and stenosis  Hirschsprung’s disease
Hirschsprung’s disease  anorectal anomalies
anorectal anomalies cubitus valgus
cubitus valgus  webbed neck
webbed neck  widely spaced nipples
widely spaced nipples  lymphoedema
lymphoedema a 25% incidence of associated ovarian tumours such as a dysgerminoma (occurring up to the age of 20 years)
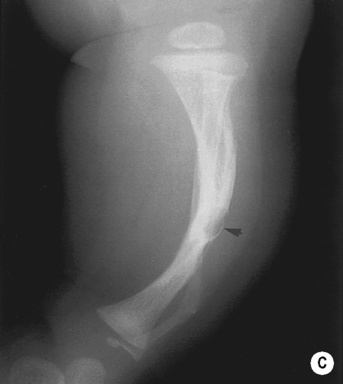
a 25% incidence of associated ovarian tumours such as a dysgerminoma (occurring up to the age of 20 years) flattening of the medial tibial condyle with a transitory exostosis
flattening of the medial tibial condyle with a transitory exostosis  beaked vertebral bodies
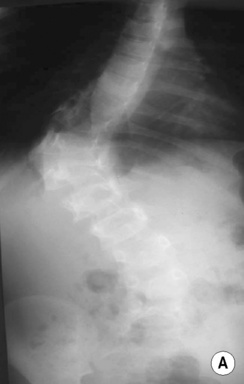
beaked vertebral bodies  osteoporosis
osteoporosis  scoliosis
scoliosis  coarctation of the aorta
coarctation of the aorta  increased occurrence of urinary tract anomalies (e.g. a horseshoe kidney)
increased occurrence of urinary tract anomalies (e.g. a horseshoe kidney)  delayed skeletal maturation
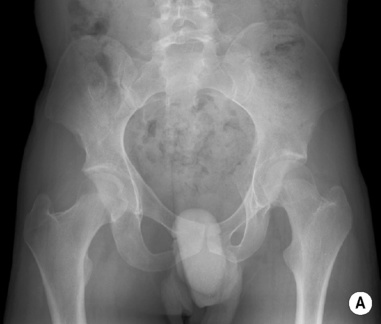
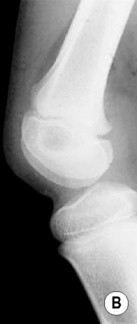
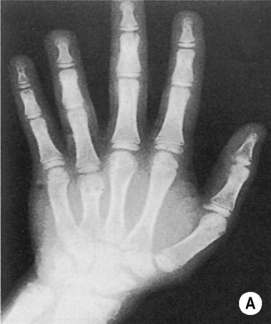
delayed skeletal maturation multiple neurofibromas and schwannomas
multiple neurofibromas and schwannomas  axillary freckling, café au lait spots and molluscum fibrosum
axillary freckling, café au lait spots and molluscum fibrosum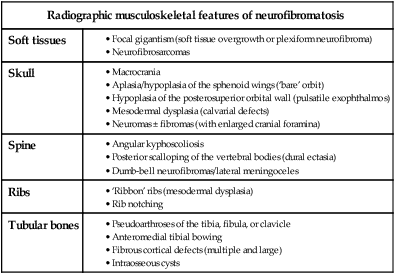
 short limbs and trunk
short limbs and trunk  narrowed thorax with respiratory distress in infancy
narrowed thorax with respiratory distress in infancy  bowed legs
bowed legs  lumbar lordosis
lumbar lordosis  prominent forehead with a depressed nasal bridge
prominent forehead with a depressed nasal bridge  hydrocephalus, brainstem and spinal cord compression
hydrocephalus, brainstem and spinal cord compression unossified vertebral bodies
unossified vertebral bodies  a large head with normal or reduced ossification
a large head with normal or reduced ossification it is caused by type II collagen abnormalities leading to abnormal bone and cartilage formation
it is caused by type II collagen abnormalities leading to abnormal bone and cartilage formation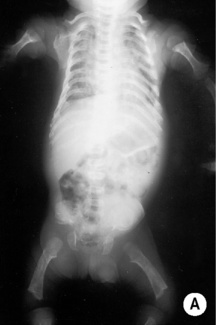
 variable short stature and a prominent forehead
variable short stature and a prominent forehead short and relatively broad long bones
short and relatively broad long bones  elongation of the distal fibula and ulnar styloid process
elongation of the distal fibula and ulnar styloid process  variable brachydactyly
variable brachydactyly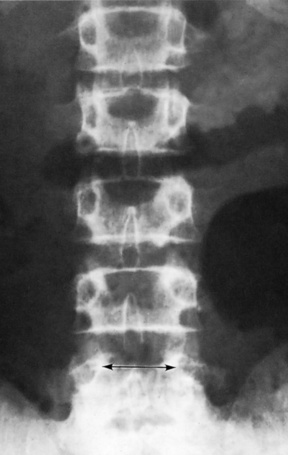
 severe platyspondyly
severe platyspondyly  horizontal acetabular roofs with medial spikes
horizontal acetabular roofs with medial spikes  small sacroiliac notches
small sacroiliac notches  marked shortness and bowing of the long bones
marked shortness and bowing of the long bones  irregular metaphyses
irregular metaphyses  short broad tubular bones in the hands and feet
short broad tubular bones in the hands and feet  small scapulae
small scapulae

 short limbs
short limbs  relatively narrow chest
relatively narrow chest  small appendage in the coccygeal region (tail)
small appendage in the coccygeal region (tail)  progressive kyphoscoliosis
progressive kyphoscoliosis platyspondyly
platyspondyly  relatively large intervertebral discs
relatively large intervertebral discs  flat acetabular roofs
flat acetabular roofs  short iliac bones
short iliac bones  short ribs with anterior widening
short ribs with anterior widening  hypoplastic odontoid process
hypoplastic odontoid process
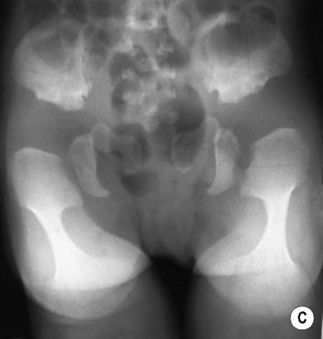
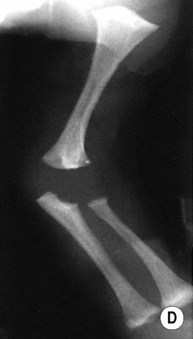
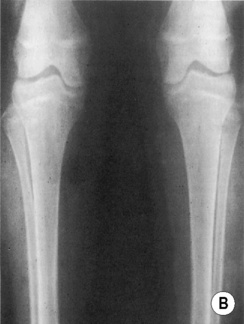
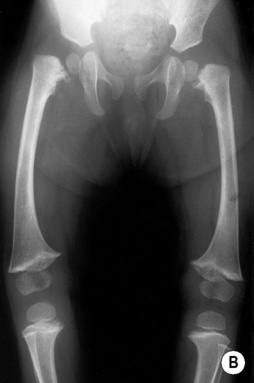
 shortened long bones. ©24
shortened long bones. ©24 short limbs, short stature, presenting in early childhood
short limbs, short stature, presenting in early childhood  genu varum (bow legs)
genu varum (bow legs)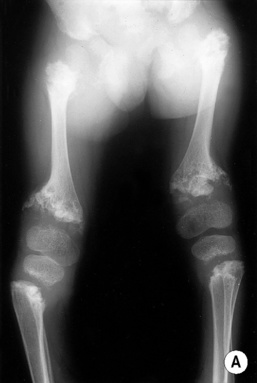
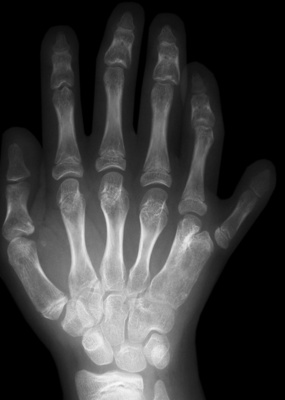
 short stature
short stature  cleft palate
cleft palate  myopia
myopia  maxillary hypoplasia
maxillary hypoplasia  thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis
thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis  barrel-shaped chest
barrel-shaped chest