Current Trends in Sinonasal Imaging 507
Benjamin Y. Huang, Brent A. Senior, and Mauricio Castillo
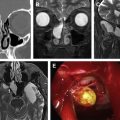
As endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) has evolved since its introduction to the United States, so has technology for imaging the sinonasal cavities. Although imaging is most frequently performed for evaluating chronic sinusitis refractory to medical therapy, its uses have expanded beyond inflammatory sinus disease. Multidetector Computed Tomography is the current workhorse for both diagnosis and preoperative planning in prospective ESS patients, while MR imaging remains a complementary tool for evaluating suspected tumors or intracranial and orbital complications of rhinosinusitis. In this article, the authors review current trends and potential future directions in the use of these modalities for sinus imaging.
Normal Anatomy and Anatomic Variants of the Paranasal Sinuses on Computed Tomography 527
Sanjay Vaid and Neelam Vaid
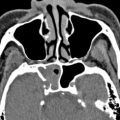
It is imperative for all imaging specialists to be familiar with detailed multiplanar CT anatomy of the paranasal sinuses and adjacent structures. This article reviews the radiologically relevant embryology of this complex region and discusses the region-specific CT anatomy of the paranasal sinuses and surrounding structures. Radiologists also need to know the clinical implications of identifying preoperatively the numerous anatomic variations encountered in this region and prepare a structured report according to the expectations of the referring clinician.
Imaging in Sinonasal Inflammatory Disease 549
Varsha M. Joshi and Rima Sansi
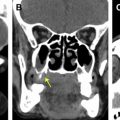
While most patients with inflammatory rhinosinusitis are successfully diagnosed clinically, imaging is indicated in patients with recurrent or chronic sinusitis, atypical symptoms and complicated acute sinusitis. Non-enhanced high resolution, thin section computed tomography (CT) is the reference standard in evaluating such patients. It provides superb anatomical details and enables a fairly accurate diagnosis and delineation of the disease, addressing all concerns of the endoscopic surgeon prior to intervention. Contrast MR imaging is preferred for assessing intraorbital or intracranial complications. The radiologist must have a systematic approach to sinonasal CT and generate a clinically relevant report that impacts patient management.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree