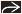Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma
Nayela Keen, MD
Christine M. Glastonbury, MBBS
Key Facts
Terminology
Cutaneous tumor, the cells of which resemble basal cells of epidermis
Most common skin cancer
75% of all nonmelanoma skin cancer in USA
90% in sun-exposed head and neck region
Imaging
Most lesions superficial and not imaged
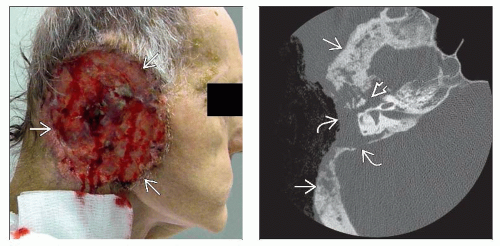
Ulcerative lesion with heaped-up tumor margins
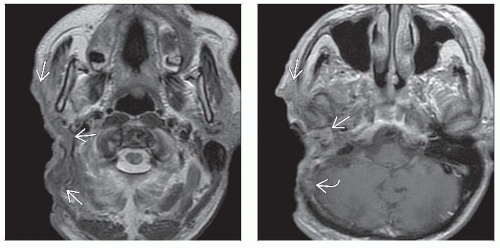
MR generally preferred for superior definition of tumor infiltration and perineural spread
Noncontrast CT if concern for bony invasion
Top Differential Diagnoses
Cutaneous SCCa
Cutaneous melanoma
Merkel cell carcinoma
Pathology
Ultraviolet radiation-induced skin tumor
Other predisposing factors: Immunosuppression, ionizing radiation, arsenic, burn scars, genetic syndromes
Clinical Issues
Slow growing, tends to invade local tissues
Nodal or distant metastases rare
Treated primarily by complete resection
Diagnostic Checklist
MR best if invasive disease suspected
Imaging often underestimates extent of tumor
Look for extension into deep structures and surrounding tissues
Look for perineural spread along cranial nerves 5 & 7
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Basal cell carcinoma (BCCa)
Synonyms
Also referred to as a “rodent ulcer”
Definitions
Cutaneous slow growing tumor, the cells of which resemble basal cells of epidermis (outer skin layer)
Tendency for local tissue invasion; metastases rare
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Enhancing cutaneous/subcutaneous mass ± deeper invasion
Location
90% occur in sun-exposed head and neck
Size
Variable, both in superficial and deep extent
Morphology
Ulcerative lesion with heaped-up tumor margins
CT Findings
Soft tissue mass or skin thickening depending on size of primary tumor
Invasion of normal tissues, including bone erosion with more aggressive lesions
MR Findings
T1WI
Isointense to muscle; can see tumor infiltration within subcutaneous fat
T2WI FS
Heterogeneous, generally hyperintense to muscle
T1WI C+ FS
Moderate to marked enhancement
Nuclear Medicine Findings
PET
Moderately increased FDG uptake
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool
If imaging obtained prior to resection, MR preferred
Superior soft tissue definition of tumor infiltration and perineural spread
Noncontrast CT if concern for bony invasion
Protocol advice
MR: T2 FS and T1 C+ FS improve tissue contrast
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree