Arthrogryposis |
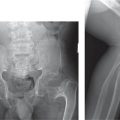
Bones are not dysplastic. Bone demineralization and dislocation of large joints. |
Heterogeneous group of diseases that are all characterized clinically by joint contractures already evident at birth. Muscle weakness and fibrosis. |
Spinal muscular atrophy |
Slender long bones, increased height of vertebral bodies, and bell-shaped chest. |
Cardinal feature is proximal muscle weakness due to degeneration of motor neurons. Childhood and adult onset forms. Molecular characterization has led to subtypes (e.g., 1–4). |
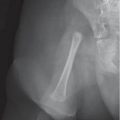
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
Slender long bones and osteopenia with frequent fractures. |
Defect in connective tissue usually due to deficiency of type-1 collagen. Types I through VIII have different age of onset and severity. Type II fatal, type IV normal color of sclera. |
Marfan syndrome |
Scoliosis is common. Ascending aortic aneurysm and dissection are major findings |
Long fingers and toes (arachnodactyly). |
Caudal regression sequence |
Aplasia-hypoplasia of the sacrum with hypoplasia of the lower extremities, at the extreme sirenomelia. |
|
Homocystinuria |
|
Autosomal recessive trait; cystathionine beta synthase deficiency. |
Schwartz-Jampel syndrome |
|
Short stature, myotonic myopathy, and dystrophy of epiphyseal cartilage. |
Cockayne syndrome |
Decreased intramedullary space of the long bones, vertebrae, skull, and pelvis. Disproportionately long limbs and joint contractures. |
Short stature, mental retardation, retinal atrophy, cataracts, and hearing loss. Shows overlap with xeroderma pigmentosum, another disorder caused by defective deoxyribonucleic acid repair. |
Hallermann-Streiff syndrome |
|
Birdlike facies with hypoplastic mandible and beaked nose, proportionate dwarfism, hypotrichosis, microphthalmia, and congenital cataracts. |
Diaphyseal tubular narrowing (Kenny-Caffey syndrome) |
Characteristic cortical thickening and intramedullary stenosis of the long bones. |
Hypocalcemia and hypoparathyroidism. |