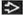Diffuse Interstitial Pneumonitis
Tan-Lucien H. Mohammed, MD, FCCP
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Chronic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia characterized by macrophage filling of alveolar spaces, probably related to cigarette smoking
Continuum of smoking-related lung injury: Respiratory bronchiolitis → respiratory bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD) → DIP
Imaging Findings
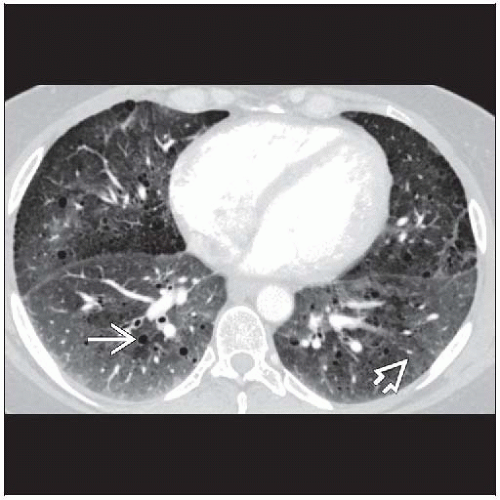
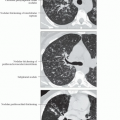
Best diagnostic clue: Diffuse ground-glass opacities with scattered cysts in heavy smoker
Ground-glass attenuation predominant abnormality
Extent of ground-glass opacities directly correlated with pack-years of smoking
Small well-defined cysts: Round, thin-walled, < 2 cm in diameter, typically occur within ground-glass opacities
Nodules: Uncommon, consider superimposed Langerhans cell histiocytosis or respiratory bronchiolitis
Top Differential Diagnoses
RB-ILD
Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonitis
Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Pathology
Concept that DIP evolves to UIP now discredited
Clinical Issues
Decreased diffusion capacity (DLCO): Most common and striking abnormality
Smoking cessation most important
10 year survival (90%)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP), alveolar macrophage pneumonia
Definitions
Chronic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia characterized by macrophage filling of alveolar spaces, probably related to cigarette smoking
Term “desquamative” is misnomer: Cells filling alveoli initially thought to represent desquamated alveolar lining cells
Continuum of smoking related lung injury: Respiratory bronchiolitis → respiratory bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD) → DIP
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Diffuse ground-glass opacities with scattered cysts in heavy smoker
Patient position/location
Lower lung predominance (70%)
Peripheral subpleural distribution (60%)
Morphology: Ground-glass attenuation predominant abnormality
CT Findings
Morphology
Ground-glass pattern (100%)
Predominant abnormality, bilateral and symmetric
Mean extent of pulmonary involvement (30%)
Typically ground-glass pattern panlobular, sharply demarcated from normal lung by interlobular septa, producing geometric pattern
Extent of ground-glass opacities directly correlated with pack-years of smoking
Distribution ground-glass pattern
Lower lung zones predominance (70%)
Peripheral predominance (60%)
Random distribution (25%)
Diffuse (20%)
Mid and upper lungs may be affected preferentially (15%)
Small well-defined cysts (80%)
Round, thin-walled, < 2 cm in diameter, typically occur within ground-glass opacities
Similar to cysts in lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP), may resolve with treatment
Superimposed emphysema common (60%) in older patients and also may produce small cystic spaces
Reticular pattern (60%)
Irregular linear opacities predominately in periphery lower lung zones
Usually intralobular (80%) and mild
Honeycombing (10%), uncommon and if present usually mild
Nodules
Uncommon, consider superimposed Langerhans cell histiocytosis or respiratory bronchiolitis
DIP, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, and respiratory bronchiolitis can be seen simultaneously
Adenopathy
Mild mediastinal adenopathy in 70% (short axis diameter > 10 mm)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree