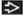Emphysema, Centrilobular
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
CLE: Enlargement and destruction of respiratory bronchioles within secondary pulmonary lobule
CLE most common form of emphysema associated with symptomatic or fatal chronic airway obstruction
Imaging Findings
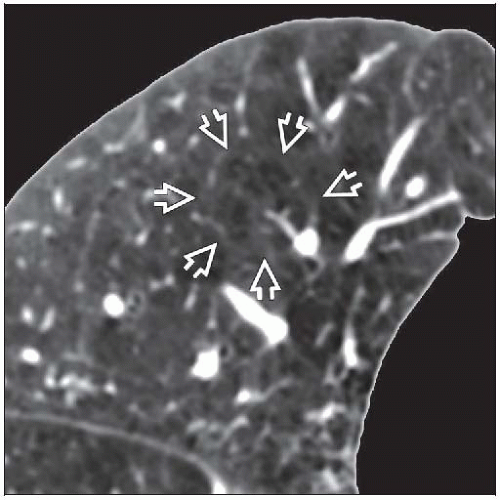
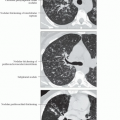
Small localized rounded areas of low attenuation within centrilobular region of secondary pulmonary lobule
Predominantly involves upper lung zones
Emphysematous areas tend to enlarge over time
Abnormality of diffusion capacity associated with upper zone emphysema
Top Differential Diagnoses
Panlobular Emphysema
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Asthma
Athletic Hyperinflation
Pathology
CLE strongly associated with cigarette smoking, both time- and dose-related
Precursor lesion may be respiratory bronchiolitis
Patients may have anatomic emphysema without alteration of pulmonary function
Approximately 30% of normal lung must be destroyed before pulmonary function deteriorates
Destruction of 2nd order respiratory bronchioles in secondary lobule
Clinical Issues
Progressive decline in ventilatory function
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Centrilobular emphysema (CLE), centriacinar emphysema (CAE), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), proximal acinar emphysema, vanishing lung
Definitions
Emphysema: Abnormal permanent enlargement of any or all parts of acinus, accompanied by destruction of alveolar tissue but without fibrosis
CLE: Enlargement and destruction of respiratory bronchioles within secondary pulmonary lobule (SPL)
COPD: Presence of airflow obstruction caused by chronic bronchitis or emphysema
Airflow obstruction is generally progressive; may be accompanied by airway hyper-reactivity and may be partially reversible
Includes asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and bronchiectasis
CLE most common form of emphysema associated with symptomatic or fatal chronic airway obstruction
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Well-defined holes in centrilobular portion of SPL
Patient position/location: Predominantly involves upper lung zones
CT Findings
Morphology
Small localized rounded areas of low attenuation within centrilobular region of SPL
Centrilobular artery may be identified in emphysematous lung
Wall is indiscernible; thin walls may be seen in larger emphysematous spaces, probably secondary to relaxation atelectasis of adjacent lung
Borders of SPL are preserved in mild disease
Bulla: Emphysematous space, commonly subpleural, > 1 cm diameter
Distribution
Upper lung zones show predominant disease
Axial plane: CLE more severe centrally than in peripheral lung
Quantification of extent of emphysema either subjective or objective
Subjective usually sufficient for clinical practice
Subjective visual grading
Normal, trivial (< 5% lung affected)
Mild emphysema (5-25%), moderate (26-50%), marked (51-75%), severe (> 75%)
Objective: Pixel density (density mask)
Normal lung density at full inspiration between -750 to -850 Hounsfield unit (HU)
Emphysema defined > 2 SD below normal average (˜ -900 HU)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree