Female Pelvis Axial 4

Normal Anatomy
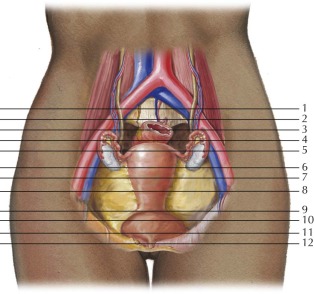
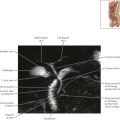
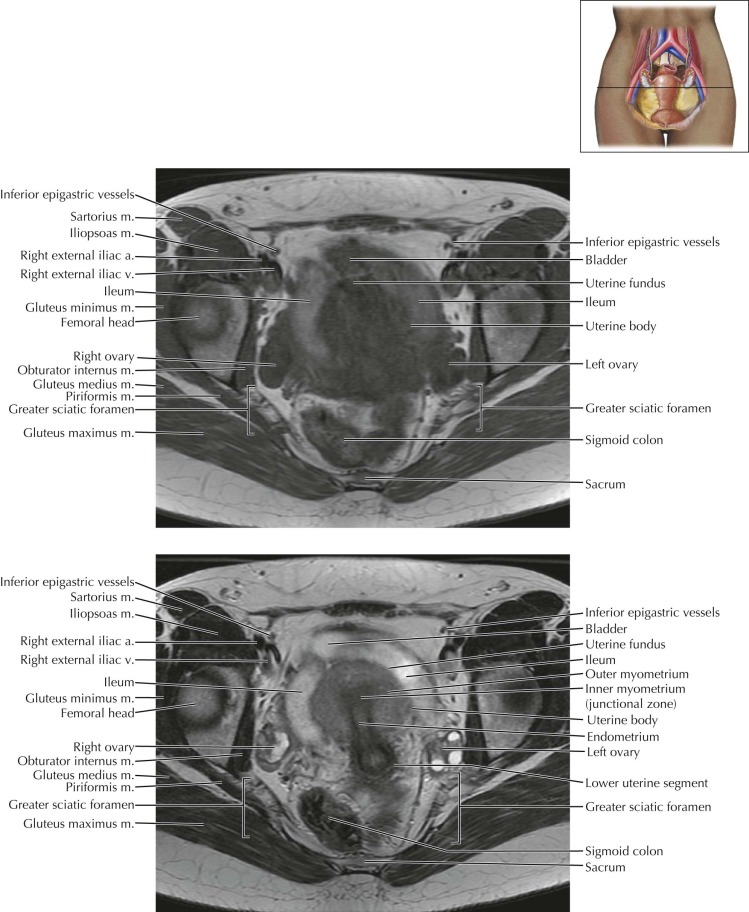
The piriformis muscle occupies most of the greater sciatic foramen. On this image, the superior gluteal vessels are seen exiting the pelvic through the greater sciatic foramen just superior to the piriformis muscle. The inferior gluteal vessels, internal pudendal vessels, and sciatic nerve also traverse the greater sciatic foramen just inferior to the piriformis muscle (see Female Pelvis Axials 6 and 7 and Sagittals 1 and 2 ).

Female Pelvis Axial 5

Normal anatomy
The paired round ligaments extend from the anterior uterine fundus, traverse the broad ligament, course anterolaterally along the pelvic wall, and travel through the inguinal canal to insert on the labia majora. The round ligament is the embryologic homologue to the gubernaculum in males.

Female Pelvis Axial 6

Normal Anatomy
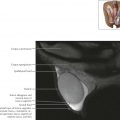
Magnetic resonance T2-weighted images clearly delineate the three uterine zones: a high signal intensity endometrium, a low signal intensity inner myometrium (also known as the junctional zone), and an intermediate–slightly high signal intensity outer myometrium. In some cases a very-high signal intensity endometrial canal can also be seen.
Diagnostic Consideration
Note the change in positioning of the pelvic organs as the bladder fills with urine throughout the examination. The postcontrast axial sequence was the last obtained in this MR study, and thus the urinary bladder is most distended on this sequence.
Female Pelvis Axial 7

Normal Anatomy
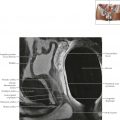
Cervical zonal anatomy is also well-demonstrated on T2-weighted MR images: the very high signal intensity fluid-filled endocervical canal is surrounded by the intermediate–slightly high signal intensity endocervical glands, followed by the low signal intensity inner cervical stroma, then the intermediate–slightly high signal intensity outer cervical stroma.

Female Pelvis Axial 10