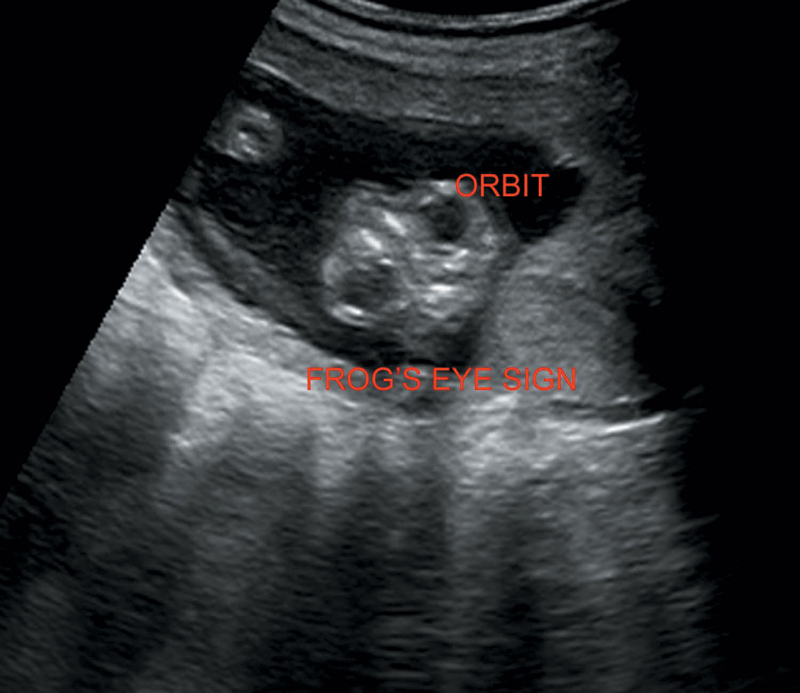
1. Anencephaly: Absence of fetal calvaria, no parenchymal tissue seen above the orbit (bulging orbits, mimicking frog’s eyes), and incompatible with life. Elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) (Figure 20.1).
2. Microcephaly: Fetal head and brain are smaller than normal.
3. Macrocephaly: Enlarged fetal head d/t severe hydrocephalus or presence of intracranial masses (tumors/cysts).
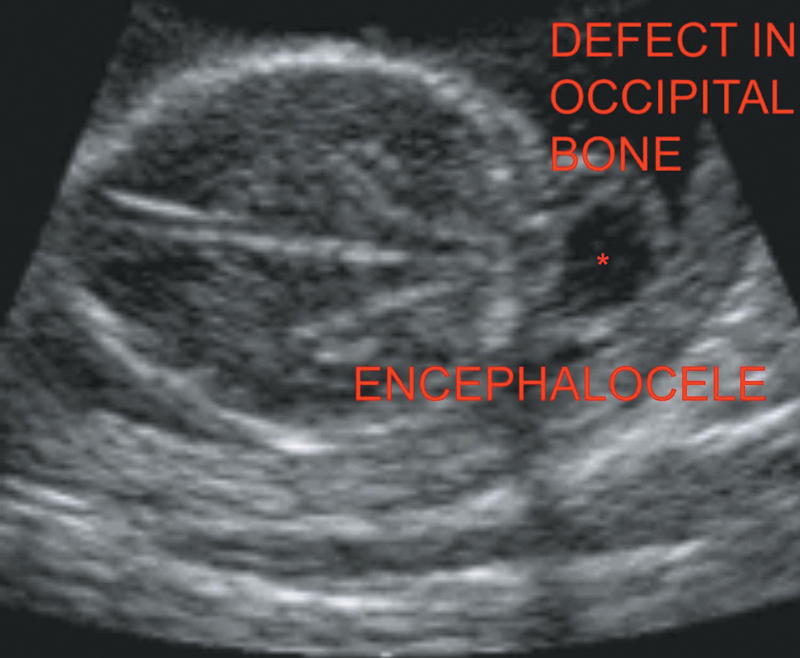
4. Cephalocele: Protrusion of meninges alone—Meningocele.
Of meninges and brain tissue—Encephalo meningocele through a bony defect located in the occipital pole usually (Figure 20.2).
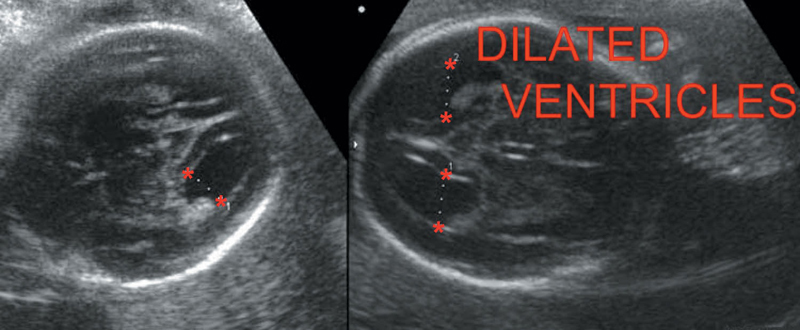
5. Ventriculomegaly (Hydrocephalus) (Figure 20.3).
Atrial width <10 millimeters—normal
10–15 millimeters—Borderline
>15 millimeters—Severe ventriculomegaly.
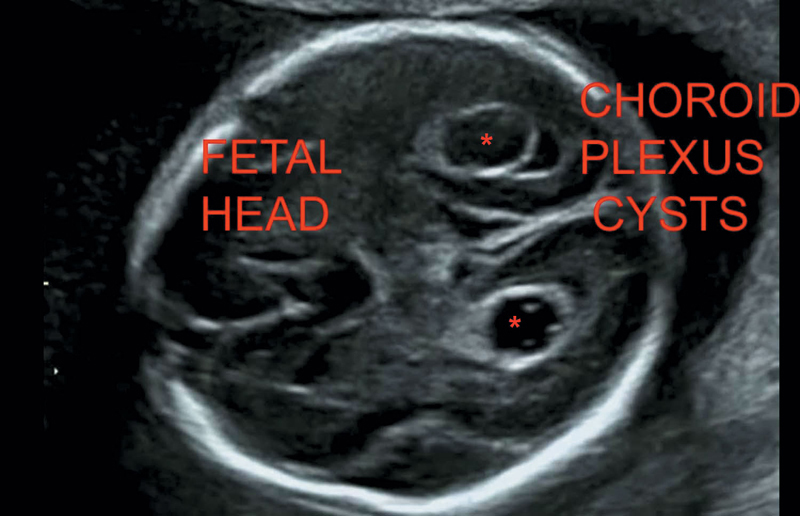
6. Choroid plexus cysts: Usually B/L (Figure 20.4)
Transient and disappears by the end of second trimester (TM). Cystic collection in B/L ventricles.
7. Holoprosencephaly
Alobar: Horseshoe shape of single ventricle with fused thalami.
Semilobar: Frontal horns are fused with abnormal occipital horns.
Lobar: Difficult to diagnose.
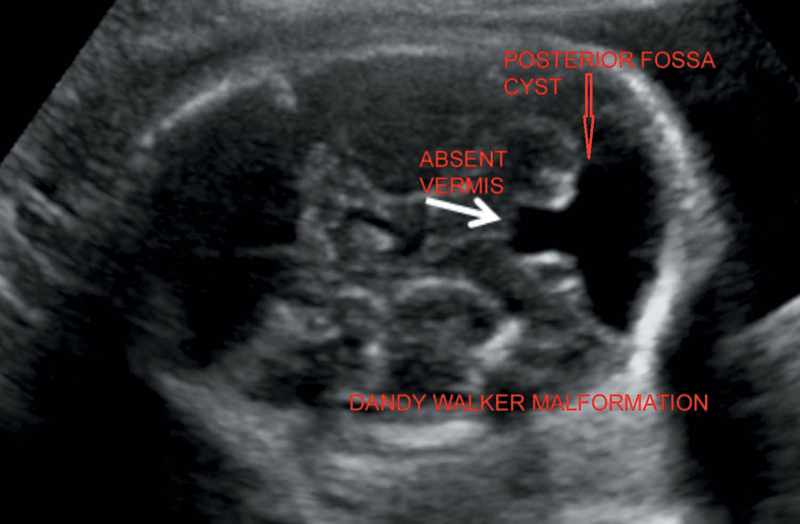
8. Dandy–Walker complex (DWC) (Figure 20.5)
DWC (Complex) classic
Severe hypoplasia of vermis
Enlarged fourth ventricle a/w hydrocephalus
Dandy walker variant (DWV) (variant) Mild hypoplasia of vermis
Enlarged fourth ventricle with key-hole appearance
D/D Blake pouch cyst—Normal vermis.
9. Mega cisterna magna: Anteroposterior (AP) diameter at the level of cerebellar vermis >10 millimeters.
10. Chiari II: Small posterior fossa, effaced cisterna magna, and banana-shaped cerebellum.
Lemon-shaped calvaria.
11. At the level of orbits →
a. Hypotelorism
b. Cyclopia
c. Hypertelorism
d. Microphthalmia
e. Anophthalmia
Figure 20.1 Illustrates frog’s eye sign of anencephaly.
Figure 20.2 Depicting occipital encephalocele.
Figure 20.3 Illustrating hydrocephalus.
Figure 20.4 Illustrating bilateral choroid plexus cysts.
Figure 20.5 Illustrating Dandy–Walker malformation with posterior fossa cyst and absence of vermis.
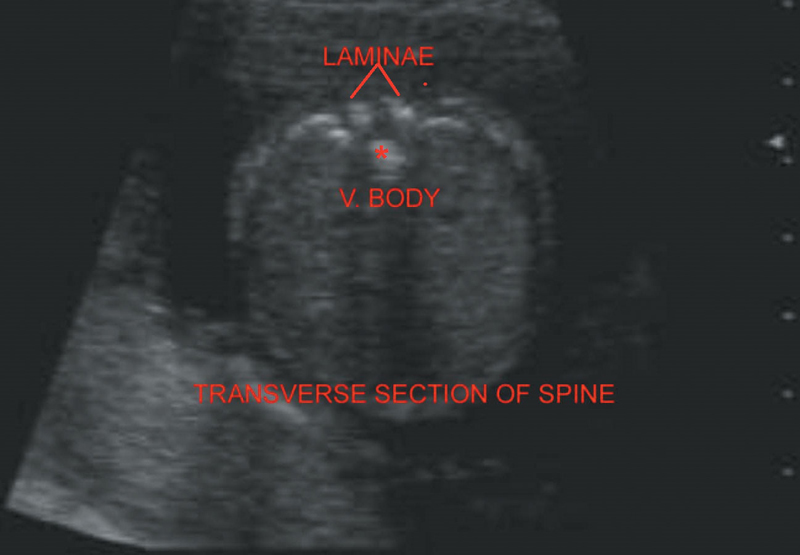
Three ossification centers, one for vertebral body anteriorly and two for laminae are visualized in the transverse section of the spine. They appear like three dots of two eyes and one nose (Figure 20.6).
Longitudinal view to demonstrate the integrity of spinal canal (Figure 20.7).
Figure 20.6 Depicts normal spine in the transverse section.
1. Spina bifida: Longitudinal scanning—Enlargement at the level of vertebral defect.
Axial—Lateral displacement of laminae.
Meningocele—Cystic structure protruding from vertebral defect (Figure 20.8).
2. Sirenomelia (Caudal regression syndrome): Variable degree of agenesis of spine and pelvis. Single/fused lower extremity. A/w single umbilical artery (SUA), renal agenesis (marked oligohydramnios), and imperforate anus.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree