Fig. 25.1
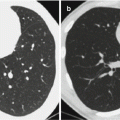
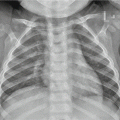
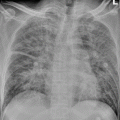
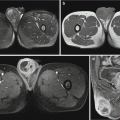
Acute disseminated encephalomeningitis. (a) MRI T2WI demonstrates multiple round-like high-signal lesions in bilateral semioval centrum with different sizes and clearly defined boundaries. (b) Contrast imaging demonstrates slight enhancement of the lesions and some lesions in a ring-shaped enhancement. (c) DWI demonstrates restricted diffusion of the lesions. (d, e) T2WI demonstrates high signal in the subcutaneous swelling of the left upper extremity, which is demonstrated in a ring-shaped enhancement by contrast imaging. (f ) Fine needle aspirate of arm swelling shows numerous microfilariae (arrows) of Wuchereria bancroftialong with adult female worm (arrow head) (Reproduced with permission from Paliwal VK, et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2012, 83 (3): 347)
25.7.2 Lymphatic System
Ultrasonography demonstrates obvious enlargement of lymph nodes with cystic changes. In the cases of filarial lymphangitis, peristalsis of filariae can be observed in the dilated lymph vessels. By following up some patients receiving medication therapy, the peristalsis of filariae in the dilated lymph vessels was found to be decreased or even disappeared. In the cases of filarial lymph edema, the skin layers and structures are unclearly defined, with thickened subcutaneous tissues and deep fascia as well as blurry subfascial muscular tissues and fibers. The echoes from subcutaneous tissue are subject to changes, with cracks and effusion of different severity. No blood flow signal is demonstrated in the thickened subcutaneous tissues. MRI T2WI favorably demonstrates extensive subcutaneous lymphatic dilation in the lower limbs of elephantiasis cases, with crude reticular high signal. Lymphangiography can demonstrate inflammations of the dilated afferent lymph vessel and the narrow efferent lymph vessel, as well as defective parenchyma of lymph nodes.
Case Study 2
A girl aged 12 years, with painless enlarged lymph nodes in the right groin for 4 months. She had no history of extremity abnormality or bacterial infection. By physical examination, three painless and movable lymph nodes can be palpated, which feel like elephant skin. The size of the largest lymph node is approximately 3.5 × 3.0 cm. There were no skin abnormalities and no extremity and vulva edema.
For case detail and figures, please refer to Dreyer G, et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2001, 65 (3): 204.
25.7.3 Respiratory System
The lesions of the respiratory system are usually divided into two types. One type of the lesions is resulted from direct invasion of the pathogens into the lungs. These lesions are pulmonary infarction caused by stagnation of filariae in the pulmonary vein, with the most common manifestation of singular pulmonary nodule in a size of below 3 cm. The other types of lesions are pulmonary lesions caused by allergic reactions, with common clinical manifestations of tropical pulmonary eosinophilia (TPE) syndrome. Chest X-ray demonstrates thickened lung markings and extensive miliary spots of shadows. The typical manifestation of TPE is characterized by infiltration of the upper and middle fields of both lungs that is more obvious in the peripheral areas. The atypical manifestations include pulmonary cavity, small patches of inflammatory exudation, and pleural effusion, with occasional occurrence of large flakes of pneumonia lesions. Sandhu et al. reported a group of ten patients with filarial pulmonary lesions. In their report, X-rays and CT scanning demonstrated diffusive lesions in both lungs, with inferior lobes not involved in some cases. CT scanning more favorably demonstrated reticular nodular shadow, bronchiectasia, air-trapping sign, calcification, and mediastinal lymphadenectasis.
25.7.4 Scrotum
Ultrasonography is commonly applied for the examination of the scrotum, with clear demonstrations of the occurrence and severity of hydrocele as well as the cystoid structure in the testes and epididymis. The solid lesions are demonstrated as curve-shaped high echo. Real-time ultrasonography demonstrates irregular twist or snaking motion, which is known as the filaria dance sign. The sign indicates the activity of the pathogen. A dynamic monitoring of its activities can provide evidence for assessing the therapeutic effectiveness.
Case Study 3
A male patient aged 17 years, with swelling and dull pain of the scrotum for 3 months.
For case detail and figures, please refer to Shetty GS, et al. Padiatr Radiol, 2012, 42 (4): 486.
Breast filariasis has a characteristic manifestation of calcification of the mammary glands. The calcifications are in hollow-tube pattern and have a cluster-like distribution. The calcifications are mainly located around the mammary areola or at the posterior region of mammary glands, with a different running course from the mammary ducts. The real-time ultrasonography can also demonstrate filaria dance signs in the breast lumps. The lesions may also be in changes of mammary lobular hyperplasia, with ultrasound demonstrations of weak-echogenic masses with no capsule and clearly defined boundaries.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree