Principles of fluoroscopy
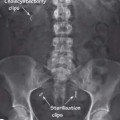
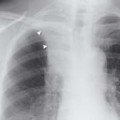
Fluoroscopy allows dynamic real-time imaging of the patient, which can provide information regarding the movement of anatomical structures or devices within the patient. Fluoroscopy is based on X-ray imaging and the physical principles are similar to the plain X-ray imaging chain from X-ray beam generation to image display (see Chapter 1). However, the procedure is performed using a specifically designed X-ray machine and uses real-time acquisition techniques and hardware.
The fluoroscopy machine
There are two main types of fluoroscopy machines:
- Continuous low energy X-ray production systems.
- Pulsed X-ray production systems – these are used more commonly in practice due to the lower radiation dose given to the patient (and to radiological staff).
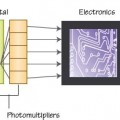
Fluoroscopy machines are designed to specifically manage the heat generated from the repeated exposure in fluoroscopic imaging. They also use lower beam energies and exposures compared with plain X-ray imaging techniques and thus image intensifiers
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree