Foot Procedures
Julia Crim, MD
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Tarsometatarsal (TMT)
Metatarsophalangeal (MTP)
PRE-PROCEDURE
Indications
Most foot injections are therapeutic
Useful to treat pain, identify source of pain
Can be used to evaluate cartilage, ligament injury
Usually in subtalar and metatarsophalangeal joints
Getting Started
Medications
Povidone-iodine (Betadine) or chlorhexidine gluconate (Betasept) antiseptic
1% lidocaine, 5 cc
0.5% bupivacaine, 5 cc
Nonionic iodinated contrast
For therapeutic arthrogram: Corticosteroid
For MR: Gadolinium mixed to dilution of 1:200 with iodinated contrast, bupivacaine
Equipment list: Standard arthrogram tray
PROCEDURE
Equipment Preparation
Use same 25-gauge needle for superficial anesthesia and joint injection
Procedure Steps
Posterior subtalar joint
Patient in lateral decubitus position
Affected side up, foot supported on towels, pillow under knee as needed
Adjust rotation of foot until lateral process talus and angle of Gissane clearly seen
Localize for injection between tip of lateral process and angle of Gissane
Can confirm location on AP or mortise view
Talocalcaneonavicular joint
Middle and anterior subtalar facets communicate with each other and talonavicular joint
Easiest way to inject middle, anterior subtalar facets is by injecting talonavicular joint
Patient supine, knee bent, foot flat on fluoroscopy table
Localize for injection between talus and navicular on AP view
Contrast flow into subtalar joint often seen best on lateral view
Calcaneocuboid joint
Position as for posterior subtalar joint
Rotate foot until joint in profile
Usually achieved with slight internal rotation
Naviculocuneiform joint
Patient supine, knee bent, foot flat on fluoroscopy table
Localize for injection between navicular and 1st or 2nd cuneiform on AP view
Tarsometatarsal joint
Patient supine, knee bent, foot flat on fluoroscopy table
If using C-arm, angle beam slightly to catch joint in optimal profile
3 separate joint capsules
1st TMT: Inject at center of joint
2nd-3rd TMT: May inject either ray, choose site where less severe osteoarthritis allows easier joint entry
4th-5th TMT: Turn foot to internal oblique position, inject either ray
Metatarsophalangeal joints
Patient supine, knee bent, foot flat on fluoroscopy table
Inject centered on joint
Findings and Reporting
Pain relief
Variant communications between joints
Contrast extravasation from joints
PROBLEMS & COMPLICATIONS
Problems
Posterior subtalar injections often misplaced
Be certain to visualize lateral portion of joint when injecting from lateral approach
Lateral process of talus and angle of Gissane are key landmarks
Osteophytes may block injection, especially in midfoot
Osteophytes may not be seen well on fluoroscopy if en face
Turn foot or fluoroscope to see and avoid osteophytes
“Walk” needle along bone surface until able to advance
Anesthetize periosteum well if using this technique
SELECTED REFERENCES
1. Lucas PE et al: Fluoroscopically guided injections into the foot and ankle: localization of the source of pain as a guide to treatment—prospective study. Radiology. 204(2):411-5, 1997
2. Mitchell MJ et al: Localization of specific joint causing hindfoot pain: value of injecting local anesthetics into individual joints during arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 164(6):1473-6, 1995
Image Gallery
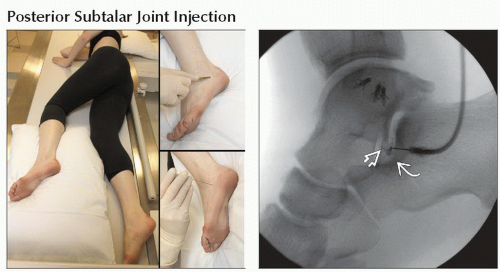 (Left) Clinical photograph shows patient positioned for posterior subtalar joint injection. (Right) Lateral arthrogram shows needle between tip of lateral process talus
 and calcaneal angle of Gissane and calcaneal angle of Gissane  . Contrast is flowing away from needle tip into joint. . Contrast is flowing away from needle tip into joint.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|


