Presentation and Presenting Images
( ▶ Fig. 11.1, ▶ Fig. 11.2, ▶ Fig. 11.3, ▶ Fig. 11.4, ▶ Fig. 11.5, ▶ Fig. 11.6, ▶ Fig. 11.7, ▶ Fig. 11.8)
A 67-year-old female presents for routine screening mammography.
11.2 Key Images
( ▶ Fig. 11.9, ▶ Fig. 11.10, ▶ Fig. 11.11, ▶ Fig. 11.12, ▶ Fig. 11.13, ▶ Fig. 11.14, ▶ Fig. 11.15, ▶ Fig. 11.16, ▶ Fig. 11.17, ▶ Fig. 11.18)
11.2.1 Breast Tissue Density
There are scattered areas of fibroglandular density.
11.2.2 Imaging Findings
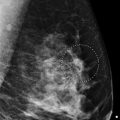
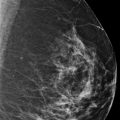
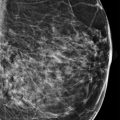
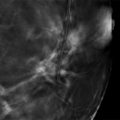
Postbiopsy clips (arrows in ▶ Fig. 11.12) are noted in the middle depth of the upper outer quadrant of each breast. The conventional mammograms and the synthetic mammograms demonstrate no suspicious calcifications, asymmetries, masses, or architectural distortions. Unread lines with the appearance of ‘hair on end’ (box) are seen on the synthetic mammograms ( ▶ Fig. 11.9, ▶ Fig. 11.10, ▶ Fig. 11.11, and ▶ Fig. 11.12) and on the first and last slices of both of the craniocaudal (CC) tomosynthesis movies ( ▶ Fig. 11.13, ▶ Fig. 11.14, ▶ Fig. 11.15, and ▶ Fig. 11.16) and on the last slices of both of the mediolateral oblique (MLO) tomosynthesis movies ( ▶ Fig. 11.17and ▶ Fig. 11.18).
11.3 BI-RADS Classification and Action
None: Technical recall
11.4 Differential Diagnosis
Technical artifact: There is detector failure occurring causing the line artifacts on the synthetic mammograms and the tomosynthesis movies. Note that these lines are in the direction of the acquisition of the tomosynthesis images.
Negative/benign study: There are no suspicious findings in either breast; however, this case is not”completely negative” due to technical factors. It should be recalled to resolve the issues.
Missed finding: Sometimes mammograms are interpreted as negative or benign when there is an abnormality. There is not a missed finding on this mammogram.
11.5 Essential Facts
As detectors become damaged the result is the failure of a line reading out during the reading of the detector. If noticed immediately by the technologist, the image can be repeated. The system may correct itself on repeat exposure.
Artifacts can obscure findings that warrant attention and can create pseudolesions.
Artifacts in digital mammography can involve the imaging detector, the equipment, the patient, and the processing and storage of the images.
Detector-based artifacts are dead pixels, dead or unread lines, non-uniformities, and ghosting.
11.6 Management and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Principles
Imaging artifacts can occur in conventional digital mammography and during tomosynthesis. It is important to recognize these promptly. Some artifacts occur due to individual patient factors (hair, clothing, motion) and others are due to technical equipment issues. It is important to recognize equipment and processing-related artifacts so they can be promptly addressed and not compromise patient care.
There is an increased radiation dose with combined conventional and tomosynthesis mammography. Having to repeat a study further increases the radiation exposure.
11.7 Further Reading
[1] Geiser W, Whitman G, Haygood T, et al. Artifacts in digital mammography. http://www.aapm.org/meetings/amos2/pdf/41–10046–70873–266.pdf
[2] Sechopoulos I. A review of breast tomosynthesis. Part II. Image reconstruction, processing and analysis, and advanced applications. Med Phys. 2013; 40(1): 014302PubMed

Fig. 11.1 Right craniocaudal (RCC) mammogram.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree