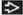Hard-Metal Disease
Tan-Lucien H. Mohammed, MD, FCCP
Key Facts
Terminology
Hard-metal disease: Pneumoconiosis due to dust inhalation of cemented tungsten carbide (WC)
Distinct histologic finding of giant cell pneumonitis
Imaging Findings
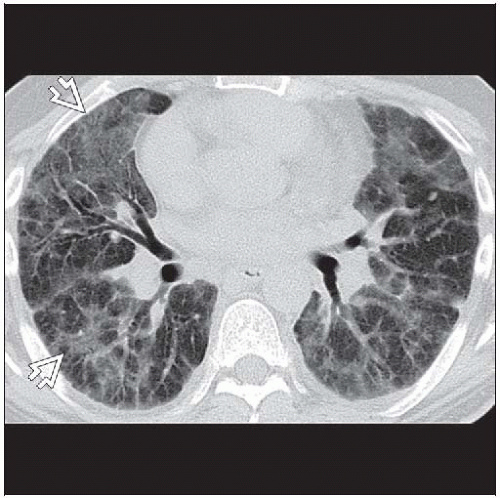
Ground-glass opacities > reticular opacities
Often panlobular
Large peripheral cystic spaces (not honeycombing): Either cysts or lobular hyperplasia
Top Differential Diagnoses
Silicosis
Coal Worker’s Pneumoconiosis
Asbestosis
Pathology
Hallmark of GIP is multinucleated giant cells, which show cannibalism
Cobalt highly soluble, rarely detected in tissue; tungsten remains and serves as marker of exposure
Disease dependent on sensitization to cobalt, not dust burden
At risk: Workers who manufacture high speed WC saws, drill bits, or sharpening discs
Clinical Issues
May recur in transplanted lung
Fibrosis may be progressive despite termination of exposure (50%)
Usually younger than those affected by other pneumoconioses
Prevention: Dust control at workplace
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Hard-metal disease (HMD), tungsten carbide pneumoconiosis, hard-metal lung, giant cell interstitial pneumonitis (GIP), cobalt lung
Definitions
Hard-metal disease: Pneumoconiosis due to dust inhalation of cemented tungsten carbide (WC)
Distinct histologic finding of giant cell pneumonitis
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Radiographic findings of interstitial lung disease in patient with history of exposure to WC
Patient position/location: Ground-glass opacities commonly panlobular or multilobular
Morphology: Nonspecific ground-glass opacities with irregular reticular opacities most common
CT Findings
Few reported cases to draw conclusions
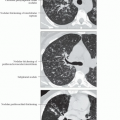
Nonspecific findings, morphology varies widely from ground-glass opacities to end-stage fibrosis
Morphology
Ground-glass opacities > reticular opacities
Often panlobular
Craniocaudad distribution
Lower lung zones or random
Fibrosis: Unclear distribution, like other dusts such as silicosis, may result in progressive massive fibrosis (PMF) in upper lung zones
Axial distribution
Random > subpleural
Centrilobular nodules, often subpleural
Large peripheral cystic spaces (not honeycombing): Either cysts or lobular hyperplasia
No reports that WC increases density of abnormal lung or lymph nodes
Other
Adenopathy (< 2 cm short axis diameter), frequency unknown
Pleural disease: Absent
Radiology-pathology correlation
Ground-glass opacities: Alveolar filing with macrophages and multinuclear giant cells (MGCs)
Centrilobular nodules: Bronchiolocentric fibrosis
Radiographic Findings
Nonspecific findings of interstitial lung disease, may be normal
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool: CT more sensitive than chest radiography
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Silicosis
Morphology
Nodules generally follow lymphatic pathways: Centrilobular, bronchovascular, subpleural
Ground-glass opacities uncommon
Distribution
Primarily upper lung zones
Chronology
Chronic silicosis usually takes decades
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree