14 Hepatic Arteries
K.I. Ringe
Like the lung, the liver can be subdivided into lobes and segments which are supplied by end arteries. These arteries, however, frequently have accessory branches. The branching pattern of the common hepatic artery into a left and right hepatic artery corresponds to the left and right lobe.1–4
The border between the functionally defined lobes is not the anatomical border but the line from the gallbladder to the sulcus of the inferior vena cava. Thus, the caudate and quadrate lobe are part of the left lobe and supplied with arterial blood in 90% of all cases by the left hepatic artery. The left lobe can be divided further into a medial and lateral segment, and the right lobe into an anterior and posterior segment.5–33
14.1 Arterial Blood Supply of the Liver from the Celiac Trunk Only (76%)
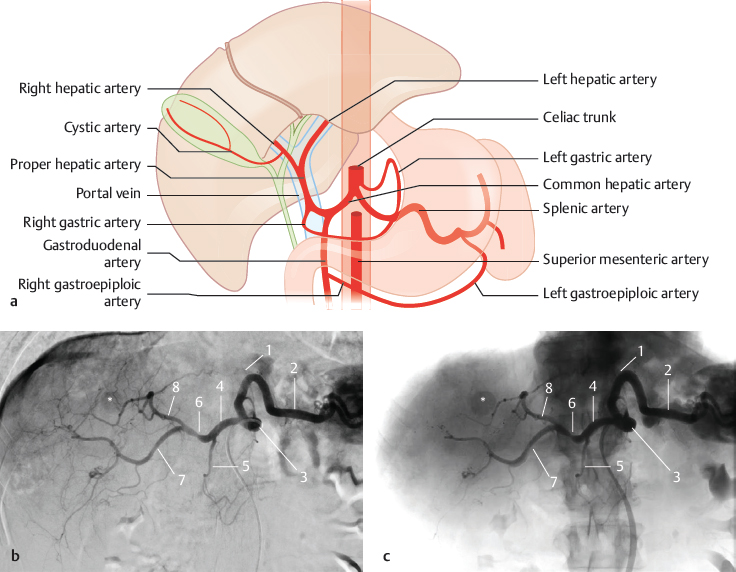
Fig. 14.1 “Normal” type shown in textbooks (50%). The common hepatic artery is a branch of the celiac trunk or originates directly from the aorta. Schematic (a) and subtracted (b) and nonsubtracted (c) DSA with a catheter placed in the celiac trunk. The patient underwent transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma (*). 1 Left gastric artery; 2 splenic artery; 3 celiac trunk; 4 common hepatic artery; 5 gastroduodenal artery; 6 proper hepatic artery; 7 right hepatic artery; 8 left hepatic artery.
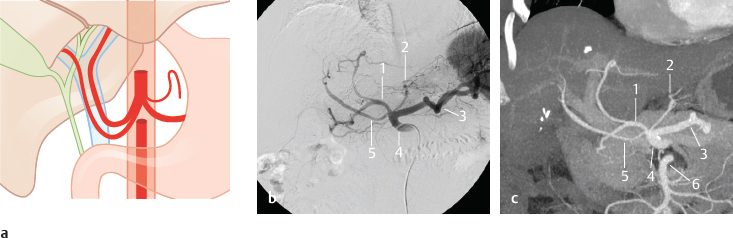
Fig. 14.2 Accessory hepatic artery from the celiac trunk or directly from the aorta, or a separate origin of the right and left hepatic arteries (2%). Schematic (a) as well as DSA (b) and coronal MIP CT (c) in a patient with an accessory hepatic artery from the celiac trunk. 1 Common hepatic artery; 2 left gastric artery; 3 splenic artery; 4 celiac trunk; 5 accessory hepatic artery; 6 superior mesenteric artery.
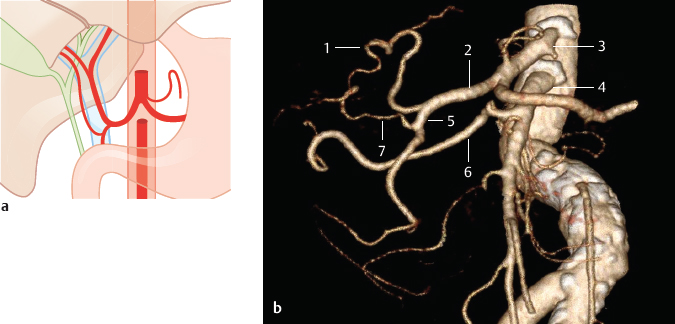
Fig. 14.3 Accessory hepatic artery from the gastroduodenal artery (2%). Schematic (a) and oblique coronal VR CT (b). The VR image shows the right hepatic artery arising from the superior mesenteric artery and an accessory hepatic artery arising from the gastroduodenal artery. In addition, kinking and profound sclerosis of the abdominal aorta are present. 1 Left hepatic artery; 2 common hepatic artery; 3 celiac trunk; 4 superior mesenteric artery; 5 gastroduodenal artery; 6 right hepatic artery; 7 accessory right hepatic artery.
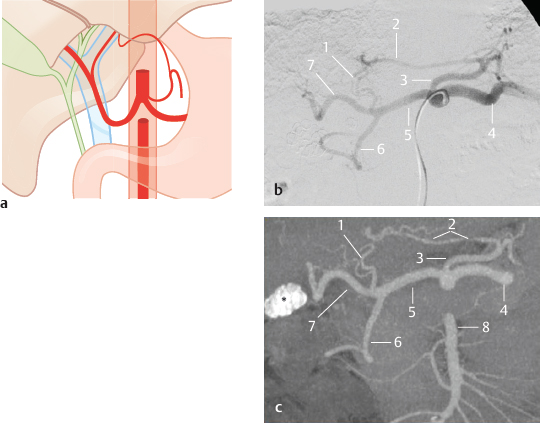
Fig. 14.4 Accessory left hepatic artery from the left gastric artery (12%). Schematic (a), as well as DSA (b) and coronal MIP CT (c) in a patient with cholecystolithiasis (*). 1 Left hepatic artery; 2 accessory left hepatic artery; 3 left gastric artery; 4 splenic artery; 5 common hepatic artery; 6 gastroduodenal artery; 7 right hepatic artery; 8 superior mesenteric artery.
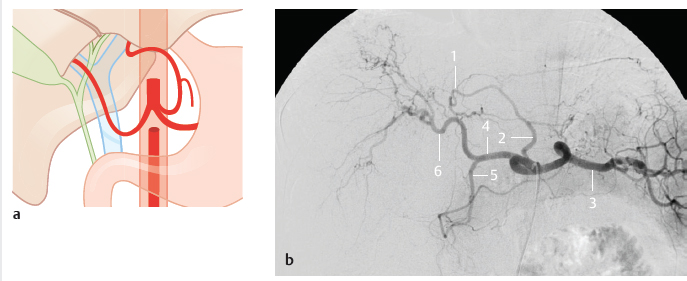
Fig. 14.5 Replaced left hepatic artery from the left gastric artery (3%). Schematic (a) and DSA (b). 1 Left hepatic artery; 2 left gastric artery; 3 splenic artery; 4 common hepatic artery; 5 gastroduodenal artery; 6 right hepatic artery.
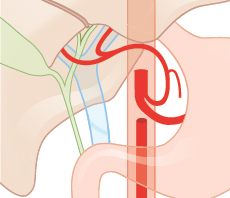
Fig. 14.6 Common hepatic artery from the left gastric artery (<1%). Schematic.
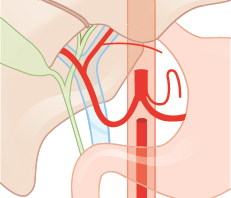
Fig. 14.7 Accessory left gastric artery from the left hepatic artery (7%). Schematic.
14.2 The Superior Mesenteric Artery Also Supplies the Liver (24%)
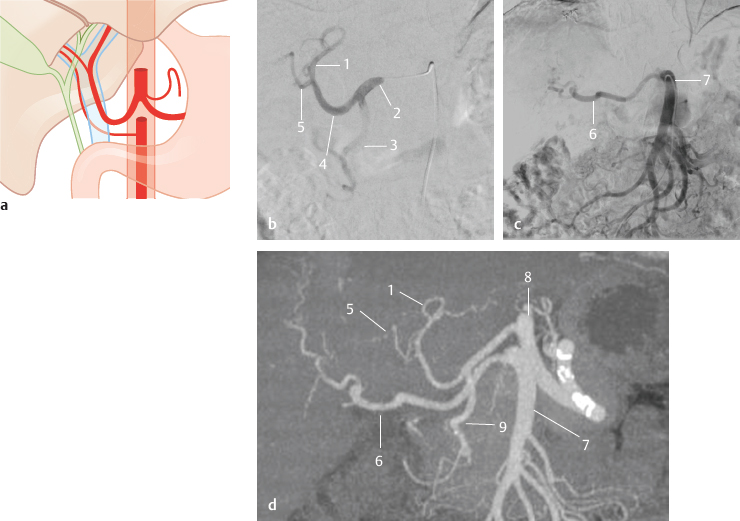
Fig. 14.8 Accessory right hepatic artery from the superior mesenteric artery (5%). Schematic (a), DSA with a diagnostic catheter placed in the common hepatic artery (b) and superior mesenteric artery (c), and coronal MIP CT (d). 1 Left hepatic artery; 2 common hepatic artery; 3 gastroduodenal artery; 4 proper hepatic artery; 5 right hepatic artery; 6 accessory right hepatic artery; 7 superior mesenteric artery; 8 celiac trunk; 9 gastroduodenal artery.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree