KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Benign tumor composed of dilated vascular channels lined by single layer of endothelial cells and supported by thin, fibrous stroma
Imaging
- •
Typical hemangioma: Well-defined, uniformly hyperechoic mass
- •
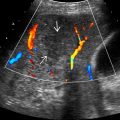
Internal vascularity often undetectable with color Doppler
- •
May see posterior acoustic enhancement
- •
“Typical atypical” hemangioma: Hyperechoic rim with hypoechoic center
- •
Contrast-enhanced imaging
- ○
Arterial hyperenhancement: “Flash fill” homogeneous hypervascularity or nodular discontinuous hyperenhancement
- ○
Centripetal fill-in on later images
- ○
Enhancement follows blood pool
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Focal steatosis
- •
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- •
Hypervascular metastases
- •
Focal nodular hyperplasia
- •
Hepatic adenoma
Pathology
- •
Large vascular channels lined by single layer of endothelial cells supported by thin, fibrous septa
- •
Most common benign tumor of liver
Scanning Tips
- •
Hemangiomas may change in echogenicity at different times of scanning due to rate of blood flow within lesion
- •
To help improve visualization, try B-color ultrasound or 9-MHz linear transducer for more superficially located lesions
 and multiple internal fibrous septa
and multiple internal fibrous septa  , which are separating vascular channels
, which are separating vascular channels  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree