KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Malignant spread of neoplasm to hepatic parenchyma
Imaging
- •
Grayscale ultrasound
- ○
Hypoechoic metastasis: Usually from hypovascular tumors
- ○
Hyperechoic metastasis: Hypervascular metastasis
- ○
“Bull’s-eye” or “target” metastatic lesions: Solid mass with hypoechoic rim or halo
- ○
Cystic/necrotic metastases: Mural nodules, thick walls, fluid-fluid levels, internal septa/debris
- ○
Calcified metastases: Mucinous or ossific primaries
- ○
Infiltrative/diffuse metastases: Lung or breast primary; may mimic cirrhosis, especially treated breast cancer, which can have pseudocirrhosis appearance
- ○
- •
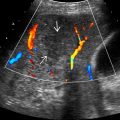
Color Doppler ultrasound
- ○
Metastatic lesions follow vascularity of primary tumor
- ○
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound increases detectability of hepatic metastases
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Cysts (vs. hypoechoic or cystic metastases)
- •
Abscesses (vs. hypoechoic metastases)
- •
Hemangiomas (vs. hyperechoic metastases)
- •
Multifocal hepatocellular carcinomas or cholangiocarcinomas (vs. “target” lesion)
- •
Steatosis (vs. hypo-/hyperechoic metastasis)
- •
Hepatic adenomatosis
Clinical Issues
- •
Most common malignant tumor of liver
Scanning Tips
- •
Rule out other other causes of multiple liver lesions, e.g., hepatic cysts, abscesses, or hemangiomas
- •
Always correlate with clinical history and look for evidence of primary tumor
 in which rounded lesions are surrounded by a hypoechoic rim.
in which rounded lesions are surrounded by a hypoechoic rim.