Integrated SPECT-CT Imaging in Pulmonary Thromboembolism
Christina M. Thuerl
Hans C. Steinert
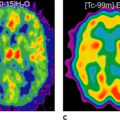
Over the last years, the use of pulmonary ventilation–perfusion scanning with nuclear methods has been superseded in part by multi-detector computed tomography (CT) pulmonary angiography, in which pulmonary emboli can be demonstrated directly. With the advent of integrated single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-CT, the complementary information obtained by CT angiography and perfusion SPECT may be relevant, because defects in the perfusion scan may readily point to anatomic emboli on CT. To what extent the combined approach will be useful has not been explored.
Clinical and Imaging Workup of Pulmonary Thromboembolism
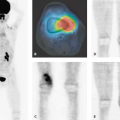
Pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) is an important cause of mortality. Therefore, early and accurate diagnosis and treatment of PE is mandatory. However, the diagnosis of PE is often delayed or the problem even remains unrecognized. Although anticoagulation is an effective therapy, risks of the treatment are well known. Because of the difficulty of diagnosing PE on the basis of clinical signs, laboratory tests and imaging studies play an important diagnostic role in the evaluation of patients with suspected PE. Traditionally, ventilation–perfusion imaging in combination with a negative chest x-ray has been used for diagnosing PE. Most PEs do not result in radiographic changes. Chest x-ray is used to exclude other thoracic abnormalities that mimic PE clinically and can produce ventilation–perfusion abnormalities. In case of an abnormal chest x-ray, nowadays multi-detector computed tomography (CT) angiography of the pulmonary vessels is performed as the first imaging technique in many institutions. It has been recognized that ventilation–perfusion scanning is not cost-effective, as it is nondiagnostic in many cases if the chest x-ray is abnormal. Therefore, multi-detector CT has become an important part of the diagnostic workup for PE (1).
In most cases, multiple pulmonary emboli occur rather than a single embolus. The emboli usually resolve after lysis, and the involved vessels return to normal. However, in some patients the emboli do not fully resolve. After repeated PE, the patient may develop secondary pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH). PAH can be caused by several different mechanisms. However, in some cases the cause remains unknown. It is important to understand the underlying cause of PAH in order to choose the appropriate treatment. The treatment of patients with primary PAH consists of supportive medical therapy and lung transplantation. In patients with secondary PAH, if the organized thrombi are present at the level of the main or lobar arteries or at the origin of the segmental vessels, pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE) is a potential curative treatment (2).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree