• There is usually bilateral symmetrical involvement – unilateral involvement can occur with ascending infection or renal vein thrombosis • Papillae: the papilla initially swells and may eventually slough into the pelvicalyceal system causing colic, haematuria or hydronephrosis (as it appears as a filling defect it can mimic tumour, calculus or a blood clot) • Remaining defect: calyceal clubbing resulting from a flattened or concave pyramidal tip • Medullary nephrocalcinosis: this is usually the product of a metabolic disorder resulting in a raised serum calcium or a tubular defect resulting in hypercalciuria • Cortical nephrocalcinosis: this is seen in acute cortical necrosis of any cause • Bacteriuria, pyrexia and flank pain due to an ascending infection in 85% (usually E. coli), or haematogenous seeding in 15% (S. aureus) • The kidneys are the 2nd commonest site of TB involvement after the lung (even though the CXR is normal in 35–50% of cases it usually follows haematogenous spread from the lung) Although both kidneys are seeded, clinical manifestations are usually unilateral (> 70% of cases) • Early: an enlarged kidney – ‘Tuberculous autonephrectomy’: this may progress to homogeneous calcification within a dilated pelvicalyceal system so that the kidney appears as a lobulated calcified mass – Hydrocalycosis: a local calyceal dilatation due to a partial stricture of a major infundibulum (the infundibulum appears ‘cut off’ with a complete stricture) – Ureter: a ‘corkscrew’ appearance (due to multiple stenoses) – Early: trabeculation – Late: a thick-walled small-capacity bladder demonstrating calcification • Chronic renal parenchymal inflammation with replacement of the normal renal parenchyma with lipid-laden histiocytes • This is due to a fluke infestation (Schistosoma haematobium) • This is the most common cause of a non-atheromatous RAS and is the 2nd most common cause of an RAS (15–20%) • Medial fibroplasia is the commonest form, causing multiple short stenoses (with a ‘string of beads’ appearance on angiography) • It involves the distal main renal artery (and its major branches) Formally the gold standard • An aortogram is essential to demonstrate the number and location of the renal arteries and also the presence of any aortic or proximal renal vascular abnormalities • Selective arteriography should not be performed in RAS (except as a prelude to renal angioplasty) as it may cause renal artery dissection or occlusion • The kidney must be salvageable (e.g. a renal length > 8cm and a satisfactory GFR) • Indications: resistant hypertension • Complications (with a greater potential than seen in peripheral vascular disease): renal artery rupture and perforation • Renal vein occlusion by thrombus can be caused by: membranous glomerulonephritis (the commonest adult cause) • Acute: an enlarged kidney • Chronic: a normal or atrophic kidney • Thromboembolic occlusion of a renal artery usually leads to a focal renal infarction (less commonly total infarction)
Kidneys
RENAL PARENCHYMAL DISEASE
PAPILLARY NECROSIS
CT/IVU
 the papillary and calyceal changes are rarely uniform
the papillary and calyceal changes are rarely uniform
 Acute: enlarged affected kidneys
Acute: enlarged affected kidneys
 Chronic: renal atrophy with a regular type of surface scarring (due to atrophy of the cortex overlying the damaged papillae and hypertrophy of the intervening columns of Bertin)
Chronic: renal atrophy with a regular type of surface scarring (due to atrophy of the cortex overlying the damaged papillae and hypertrophy of the intervening columns of Bertin)
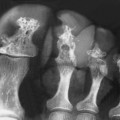
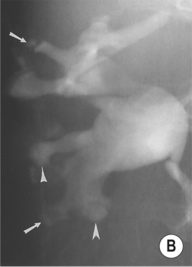
 ‘Lobster claw deformity’: initially the necrotic areas erode the papilla tip and excavate from the fornices into the pyramids
‘Lobster claw deformity’: initially the necrotic areas erode the papilla tip and excavate from the fornices into the pyramids
 ‘Egg in cup’ appearance: with progression contrast curves around the papilla from both fornices
‘Egg in cup’ appearance: with progression contrast curves around the papilla from both fornices
 if the papillae fail to separate (necrosis in situ) the calyces may appear normal
if the papillae fail to separate (necrosis in situ) the calyces may appear normal  the papillae may calcify (with spotty calcification in a ring or triangle around a translucent centre)
the papillae may calcify (with spotty calcification in a ring or triangle around a translucent centre)
NEPHROCALCINOSIS
CT/IVU
 calcification is usually bilateral and diffuse
calcification is usually bilateral and diffuse
 calcification is usually punctate and patchy (classically with a ‘tramline’ appearance)
calcification is usually punctate and patchy (classically with a ‘tramline’ appearance)
Glomerulonephritis  acute tubular necrosis
acute tubular necrosis  acute cortical necrosis
acute cortical necrosis
No papillary or calyceal abnormality  no focal cortical loss
no focal cortical loss
Papillary necrosis  medullary sponge kidney
medullary sponge kidney  megacalycosis/polycalycosis
megacalycosis/polycalycosis
Papillary or calyceal abnormality  no focal cortical loss
no focal cortical loss
Obstructive nephropathy  focal reflux nephropathy
focal reflux nephropathy
Papillary or calyceal abnormality  focal cortical loss
focal cortical loss
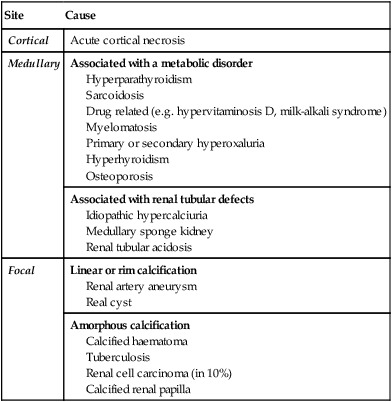
Site
Cause
Cortical
Acute cortical necrosis
Medullary
Associated with a metabolic disorder
Hyperparathyroidism
Sarcoidosis
Drug related (e.g. hypervitaminosis D, milk-alkali syndrome)
Myelomatosis
Primary or secondary hyperoxaluria
Hyperhyroidism
Osteoporosis
Associated with renal tubular defects
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
Medullary sponge kidney
Renal tubular acidosis
Focal
Linear or rim calcification
Renal artery aneurysm
Real cyst
Amorphous calcification
Calcified haematoma
Tuberculosis
Renal cell carcinoma (in 10%)
Calcified renal papilla
RENAL TRACT INFECTION/INFLAMMATION
ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS
DEFINITION
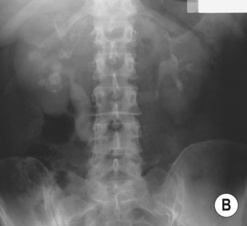
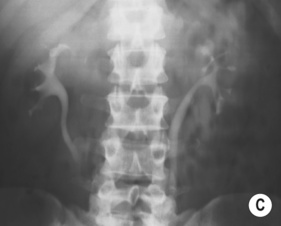
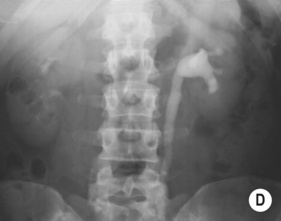
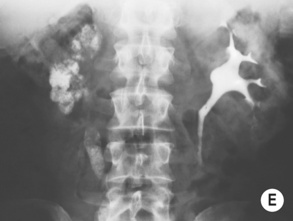
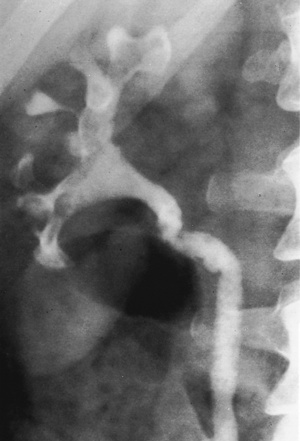
RENAL TUBERCULOSIS (TB)
DEFINITION
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
IVU/CT
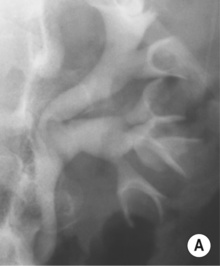
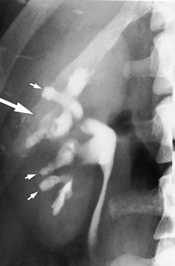
 irregularity and destruction of ≥ 1 papillae (resembling papillary necrosis)
irregularity and destruction of ≥ 1 papillae (resembling papillary necrosis)
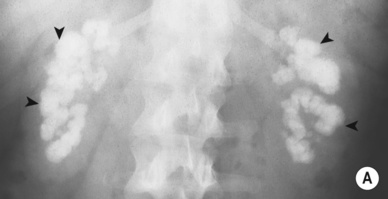
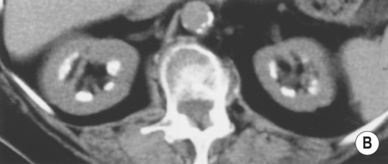
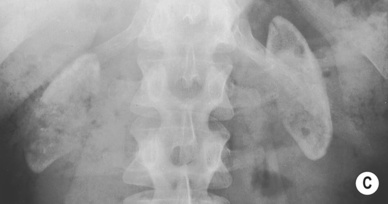
 Renal calcification (30%): this appears as punctate or curvilinear renal parenchymal calcification or as calcification within a caseous pyonephrosis (with a characteristic cloudy appearance in the distribution of the dilated calyces)
Renal calcification (30%): this appears as punctate or curvilinear renal parenchymal calcification or as calcification within a caseous pyonephrosis (with a characteristic cloudy appearance in the distribution of the dilated calyces)
 Ureteric calcification: this is the 2nd commonest site of calcification with a typical beaded appearance
Ureteric calcification: this is the 2nd commonest site of calcification with a typical beaded appearance  calcification of the bladder, vas deferens and seminal vesicles is rarely seen
calcification of the bladder, vas deferens and seminal vesicles is rarely seen
 Cavitations: these are usually irregular and communicate with the collecting system
Cavitations: these are usually irregular and communicate with the collecting system  widespread cavitations may mimic hydronephrosis (but the pelvis and infundibula of the calyces are not dilated unless there is an associated obstruction)
widespread cavitations may mimic hydronephrosis (but the pelvis and infundibula of the calyces are not dilated unless there is an associated obstruction)
 Fibrotic strictures: these can occur anywhere within the renal tract
Fibrotic strictures: these can occur anywhere within the renal tract
 a ‘pipestem’ appearance (due to a rigid and aperistaltic ureter)
a ‘pipestem’ appearance (due to a rigid and aperistaltic ureter)
 bladder wall irregularity
bladder wall irregularity  a slight decrease in capacity
a slight decrease in capacity
 bladder TB is almost always associated with renal TB
bladder TB is almost always associated with renal TB  often there is VUR into a widely dilated upper tract
often there is VUR into a widely dilated upper tract
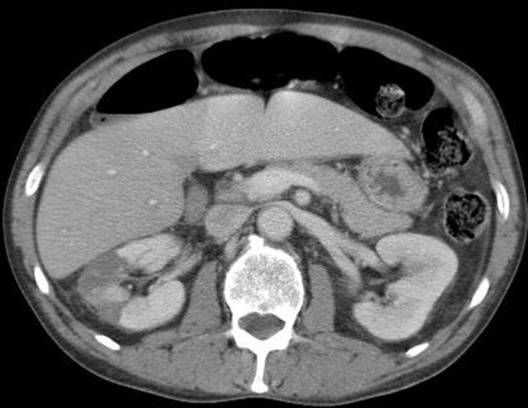
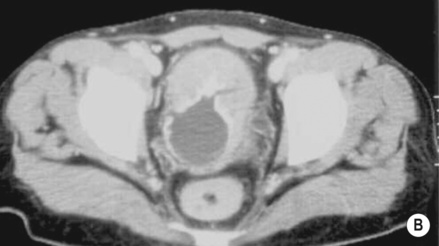
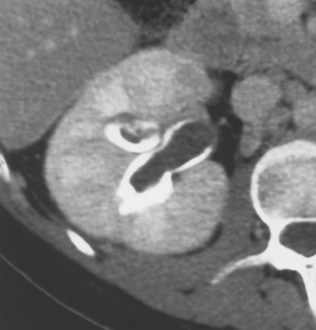
XANTHOGRANULOMATOUS PYELONEPHRITIS (XGP)
DEFINITION
 it is secondary to chronic urinary infection (e.g. E coli or Proteus mirabilis) and obstructing calculus disease
it is secondary to chronic urinary infection (e.g. E coli or Proteus mirabilis) and obstructing calculus disease  it is associated with diabetes
it is associated with diabetes
SQUAMOUS METAPLASIA, LEUKOPLAKIA, MALACOPLAKIA, AND CHOLESTEATOMA
DEFINITION
BILHARZIA (URINARY SCHISTOSOMIASIS)
DEFINITION
 the worm enters the skin and matures within the liver (via the portal vein)
the worm enters the skin and matures within the liver (via the portal vein)  ova are then deposited within the bladder or ureteric submucosa (via the perivesical plexus)
ova are then deposited within the bladder or ureteric submucosa (via the perivesical plexus)  the ova produce an inflammatory reaction, leading to granuloma and stricture formation
the ova produce an inflammatory reaction, leading to granuloma and stricture formation
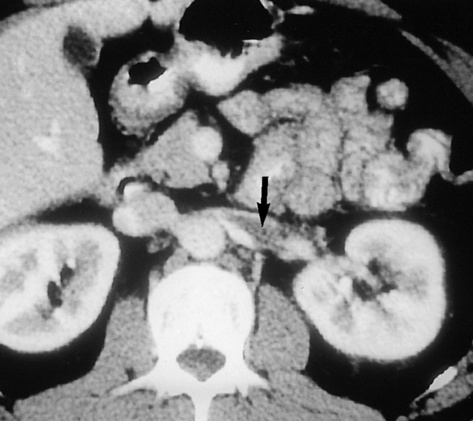
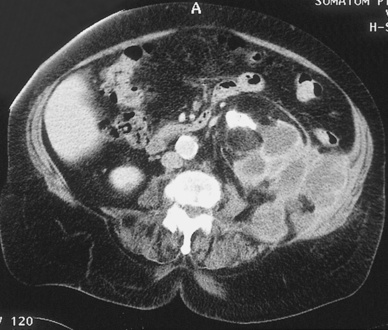
RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS (RAS)
RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS (RAS)
DEFINITION
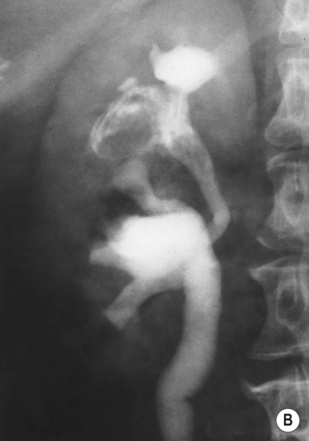
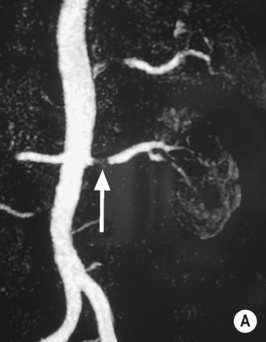
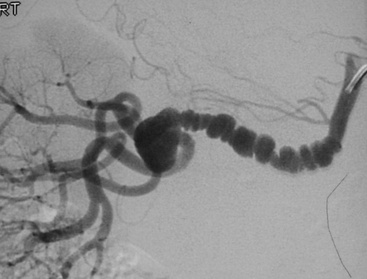
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)
 it typically occurs in young women
it typically occurs in young women
 it can also affect the external iliac and carotid arteries
it can also affect the external iliac and carotid arteries
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
DSA
 it is increasingly being replaced by non-invasive methods
it is increasingly being replaced by non-invasive methods
PEARLS
Renal angioplasty and stenting
 the best results are obtained with FMD
the best results are obtained with FMD
 renal failure
renal failure  flash pulmonary oedema
flash pulmonary oedema
 branch occlusion
branch occlusion  occlusion of the main renal artery
occlusion of the main renal artery  cholesterol emboli
cholesterol emboli  a short-term deterioration in renal function (due to the contrast medium given)
a short-term deterioration in renal function (due to the contrast medium given)
RENAL VASCULAR ABNORMALITIES
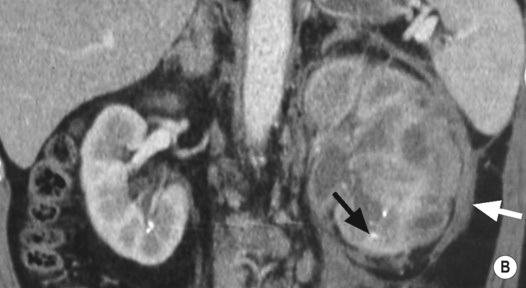
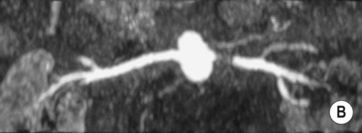
RENAL ARTERY ANEURYSMS
DEFINITION
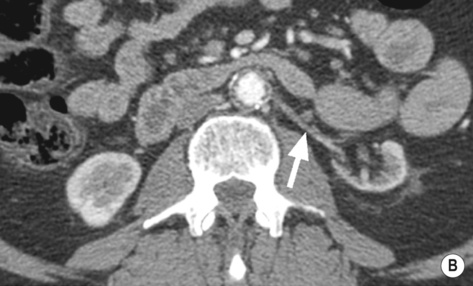
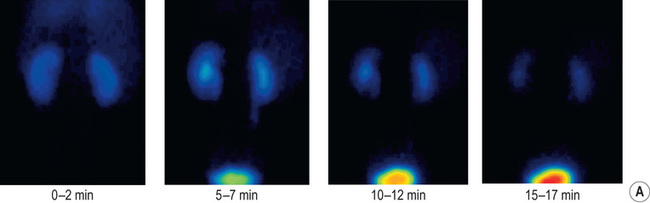
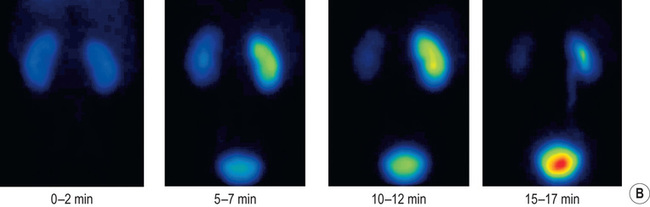
RENAL VEIN THROMBOSIS
DEFINITION
 nephrotic syndrome
nephrotic syndrome  dehydration
dehydration  hypercoagulable states
hypercoagulable states  renal or left adrenal tumours
renal or left adrenal tumours
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
IVU
 a faint or absent nephrogram
a faint or absent nephrogram  absent pelvicalyceal filling (which may also be stretched and compressed by an oedematous renal parenchyma)
absent pelvicalyceal filling (which may also be stretched and compressed by an oedematous renal parenchyma)  rarely there may be an increasingly dense nephrogram (± striations)
rarely there may be an increasingly dense nephrogram (± striations)
 retroperitoneal venous collaterals can indent the PC system
retroperitoneal venous collaterals can indent the PC system
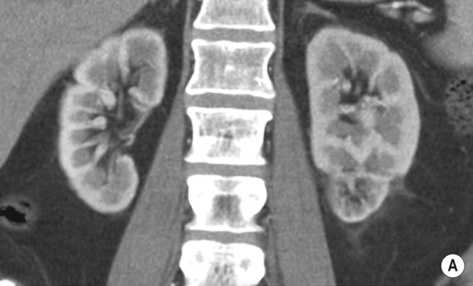
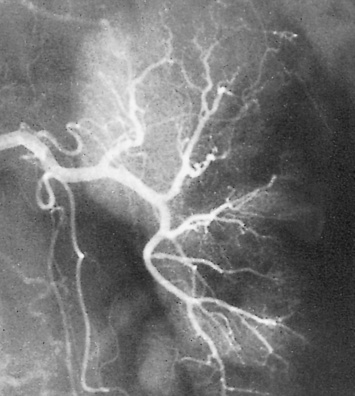
RENAL INFARCTION
DEFINITION
 over time the infarcted area decreases in size with scar formation and tissue retraction
over time the infarcted area decreases in size with scar formation and tissue retraction

 it is usually primarily renal but may be part of a systemic vasculitis (e.g. SLE, PAN, Goodpasture’s or Wegener’s)
it is usually primarily renal but may be part of a systemic vasculitis (e.g. SLE, PAN, Goodpasture’s or Wegener’s) no papillary or calyceal abnormality
no papillary or calyceal abnormality smooth, normal pelvicalyceal systems
smooth, normal pelvicalyceal systems  prominent renal sinus fat
prominent renal sinus fat it usually follows an episode of severe ischaemia associated with hypotension, dehydration, or nephrotoxin exposure
it usually follows an episode of severe ischaemia associated with hypotension, dehydration, or nephrotoxin exposure increased echogenicity within the cortex and pyramids
increased echogenicity within the cortex and pyramids little or no filling of the pelvicalyceal system
little or no filling of the pelvicalyceal system the insult is more severe than that seen with ATN and is usually due to obstetric shock
the insult is more severe than that seen with ATN and is usually due to obstetric shock chronic: cortical calcification
chronic: cortical calcification diabetes
diabetes  sickle-cell disease or trait
sickle-cell disease or trait  obstruction complicated by infection
obstruction complicated by infection  acute infection
acute infection  haemophilia
haemophilia  renal vein thrombosis
renal vein thrombosis  acute renal failure in infancy
acute renal failure in infancy it is usually bilateral (but can be unilateral or segmental)
it is usually bilateral (but can be unilateral or segmental) phaeochromocytoma
phaeochromocytoma  horseshoe kidney
horseshoe kidney  Caroli’s disease
Caroli’s disease  hemihypertrophy
hemihypertrophy cortical scarring (representing parenchymal loss) with underlying clubbed calyces
cortical scarring (representing parenchymal loss) with underlying clubbed calyces  localized scars are more common within the upper pole (R>L)
localized scars are more common within the upper pole (R>L)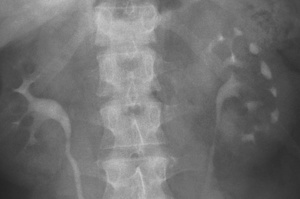

 vesicoureteric reflux (VUR)
vesicoureteric reflux (VUR)  urinary obstruction
urinary obstruction  pregnancy
pregnancy  instrumentation
instrumentation  immune deficiency
immune deficiency it can however be useful if the diagnosis is in doubt or to exclude obstruction or abscess development
it can however be useful if the diagnosis is in doubt or to exclude obstruction or abscess development delayed and poor pelvicalyceal system filling
delayed and poor pelvicalyceal system filling  a dense, persistent or striated nephrogram (with severe disease)
a dense, persistent or striated nephrogram (with severe disease) the affected segments are hypoechoic (they can be hyperechoic with haemorrhage)
the affected segments are hypoechoic (they can be hyperechoic with haemorrhage)  reduced corticomedullary differentiation (due to oedema)
reduced corticomedullary differentiation (due to oedema)  focal or diffuse reduced perfusion
focal or diffuse reduced perfusion renal swelling with acute disease
renal swelling with acute disease any abnormal parenchymal enhancement may persist for > 2 months and may develop into a scar
any abnormal parenchymal enhancement may persist for > 2 months and may develop into a scar emphysematous pyelonephritis
emphysematous pyelonephritis  xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis  cortical atrophy and renal failure
cortical atrophy and renal failure fungal infections
fungal infections  glomerulonephritis
glomerulonephritis  interstitial nephritis
interstitial nephritis
 papillary ulceration occurs early, with later spread to the collecting system leading to fibrosis and stricture formation
papillary ulceration occurs early, with later spread to the collecting system leading to fibrosis and stricture formation haematuria
haematuria  sterile pyuria
sterile pyuria
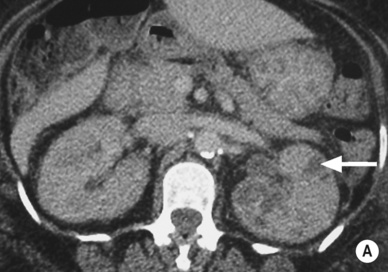
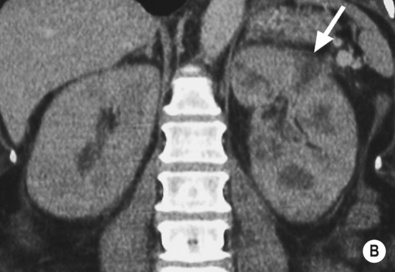
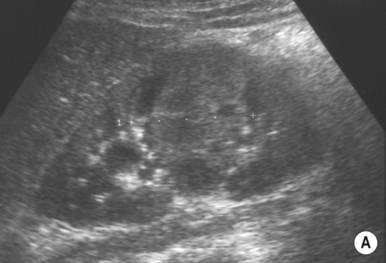
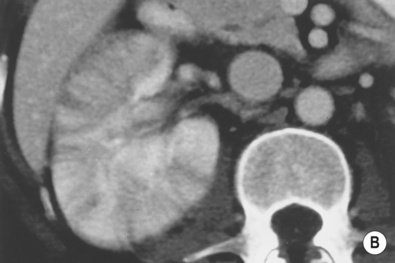
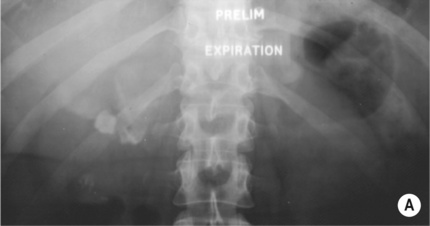
 it is associated with diabetes and obstruction
it is associated with diabetes and obstruction there is a high mortality rate (> 60%) and it may require nephrectomy
there is a high mortality rate (> 60%) and it may require nephrectomy it has a lower mortality rate, and percutaneous drainage and antibiotics may be sufficient
it has a lower mortality rate, and percutaneous drainage and antibiotics may be sufficient the patient is usually diabetic
the patient is usually diabetic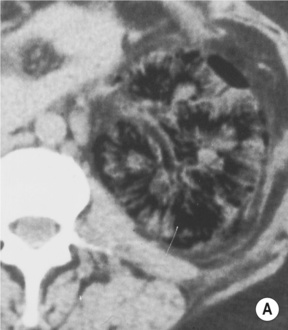

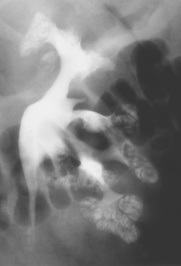
 the focal form can mimic a tumour
the focal form can mimic a tumour an enlarged (global or focal) non-excreting kidney
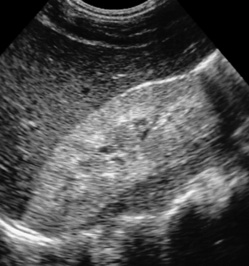
an enlarged (global or focal) non-excreting kidney  dilated affected calyces with internal echoes or debris
dilated affected calyces with internal echoes or debris  a heterogeneous kidney with multiple non- or rim-enhancing low attenuation areas (−15 to −20 HU) representing dilated calyces and xanthomas
a heterogeneous kidney with multiple non- or rim-enhancing low attenuation areas (−15 to −20 HU) representing dilated calyces and xanthomas  perinephric extension (± a thickened Gerota’s fascia)
perinephric extension (± a thickened Gerota’s fascia)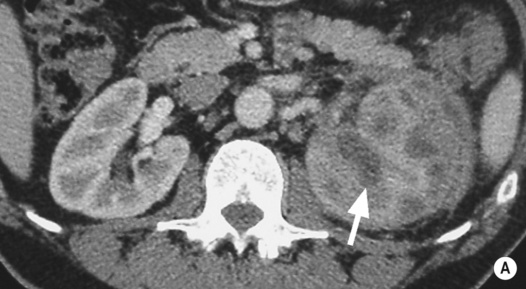
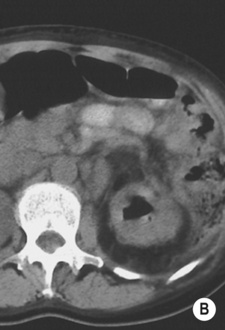
 there are enhancing thick irregular walls (± perinephric inflammatory change)
there are enhancing thick irregular walls (± perinephric inflammatory change)  gas within the lesion is diagnostic
gas within the lesion is diagnostic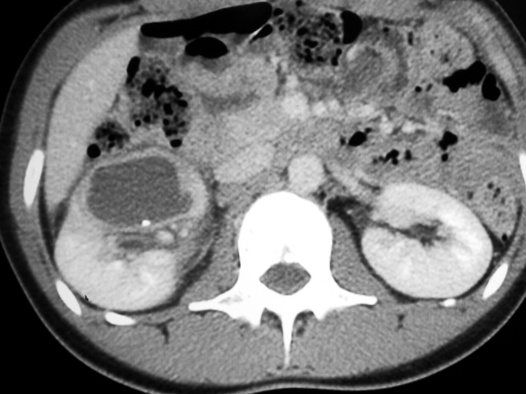
 absent renal function
absent renal function this may extend in any direction
this may extend in any direction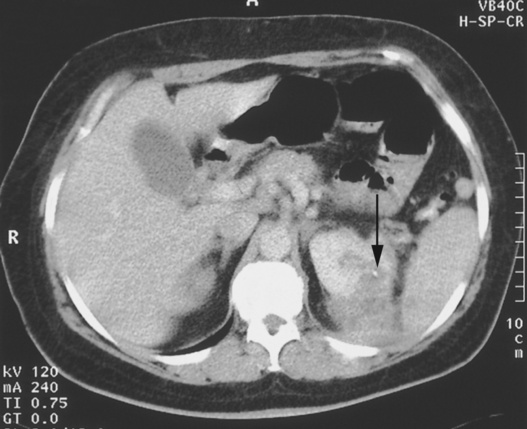
 it is associated with recurrent urinary tract infections and calculi
it is associated with recurrent urinary tract infections and calculi it appears as thickened folds and irregularity of the renal pelvis
it appears as thickened folds and irregularity of the renal pelvis small plaques are visible on the mucosal surfaces (bladder > upper urinary tract)
small plaques are visible on the mucosal surfaces (bladder > upper urinary tract) there may be impaired renal function if the parenchyma is involved
there may be impaired renal function if the parenchyma is involved it is associated with urinary tract infection and chronic obstruction
it is associated with urinary tract infection and chronic obstruction there can be multiple filling defects (representing granulomas or ureteritis cystica)
there can be multiple filling defects (representing granulomas or ureteritis cystica)  parallel lines of ureteric calcification can be seen
parallel lines of ureteric calcification can be seen diabetics are at increased risk
diabetics are at increased risk it is highly echogenic on US, and it may demonstrate air within the collecting system and bladder
it is highly echogenic on US, and it may demonstrate air within the collecting system and bladder there is a risk of septicaemia and endotoxic shock (especially with attempted drainage)
there is a risk of septicaemia and endotoxic shock (especially with attempted drainage) debris or gas (dense shadowing) within the renal pelvis
debris or gas (dense shadowing) within the renal pelvis  cortical loss or a perinephric abscess if long-standing
cortical loss or a perinephric abscess if long-standing there may be a renal or perinephric abscess
there may be a renal or perinephric abscess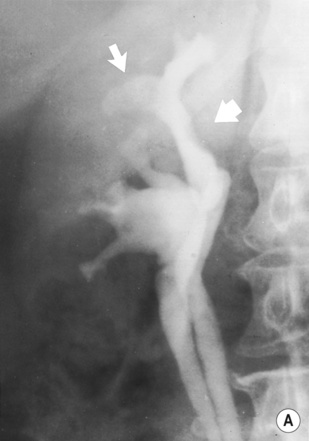

 the resultant increased renin (and angiotensin II) levels leads to vasoconstriction
the resultant increased renin (and angiotensin II) levels leads to vasoconstriction atheroma involves the origin (ostial) or proximal ⅓ of the renal artery
atheroma involves the origin (ostial) or proximal ⅓ of the renal artery  there can be post-stenotic dilatation
there can be post-stenotic dilatation
 renal arterial lesions are caused by eccentric atheromatous plaques of the proximal renal artery
renal arterial lesions are caused by eccentric atheromatous plaques of the proximal renal artery aortic disease may consist of diffuse or focal stenoses, occlusion, or a fusiform AAA
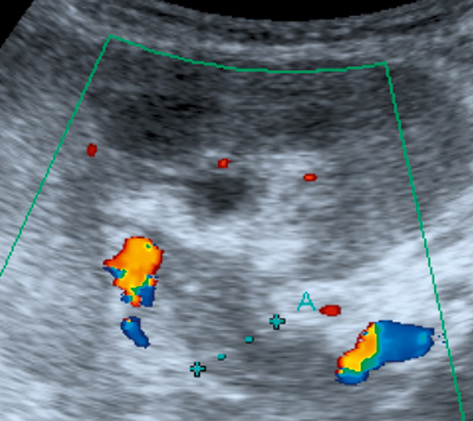
aortic disease may consist of diffuse or focal stenoses, occlusion, or a fusiform AAA a renal artery to aortic velocity ratio (RAR) > 3.5
a renal artery to aortic velocity ratio (RAR) > 3.5  a ‘parvus and tardus’ effect within the intrarenal vessels (due to velocity reduction and slowing of the acceleration of the systolic upstroke)
a ‘parvus and tardus’ effect within the intrarenal vessels (due to velocity reduction and slowing of the acceleration of the systolic upstroke)
 it has a sensitivity (97%) and specificity (92%) comparable with intra-arterial angiography for detecting stenoses within the main and segmental arteries
it has a sensitivity (97%) and specificity (92%) comparable with intra-arterial angiography for detecting stenoses within the main and segmental arteries



 it may be associated with Williams’ syndrome or neurofibromatosis
it may be associated with Williams’ syndrome or neurofibromatosis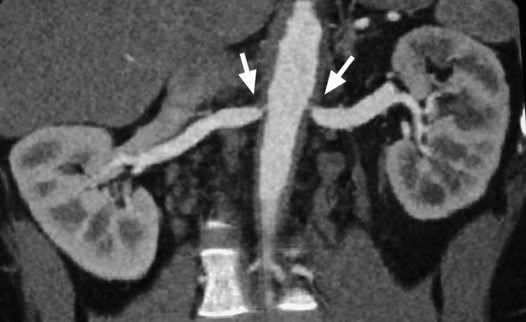
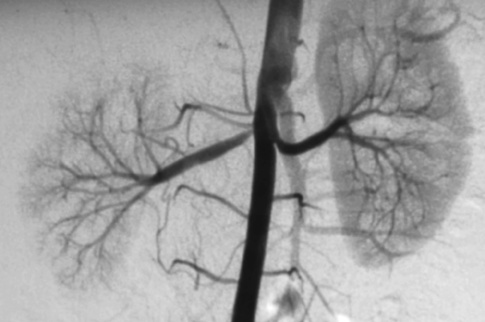
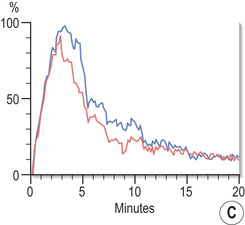
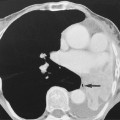
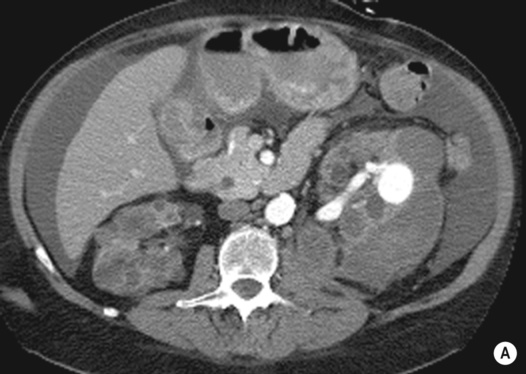
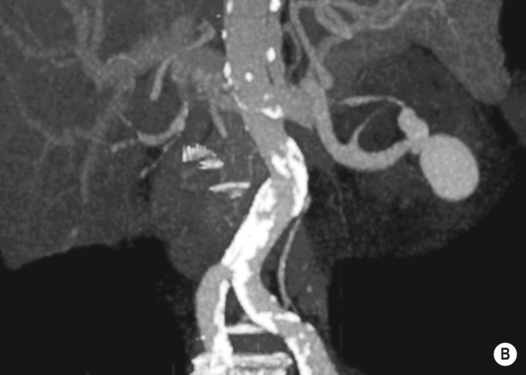
 blue line, left kidney).*
blue line, left kidney).*
 mycotic
mycotic  post-traumatic
post-traumatic  atherosclerotic
atherosclerotic  vasculitic
vasculitic  fibromuscular hyperplasia
fibromuscular hyperplasia both will demonstrate aneurysmal dilatation
both will demonstrate aneurysmal dilatation absent wall calcification
absent wall calcification  occurring during pregnancy
occurring during pregnancy aneurysms tend to be more peripheral than with FMD
aneurysms tend to be more peripheral than with FMD it may lead to impaired renal function due to a ‘steal’ effect
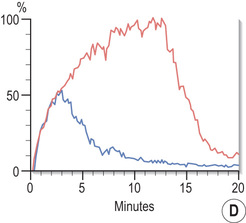
it may lead to impaired renal function due to a ‘steal’ effect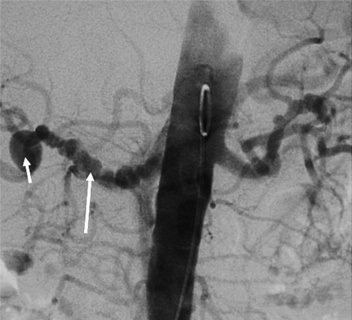
 with chronicity venous collaterals can open with only slightly impaired renal function
with chronicity venous collaterals can open with only slightly impaired renal function renal vein thrombus and a lack of flow within the main veins (± reversed end diastolic flow within the parenchymal veins)
renal vein thrombus and a lack of flow within the main veins (± reversed end diastolic flow within the parenchymal veins) prolonged irregular parenchymal enhancement
prolonged irregular parenchymal enhancement  prolonged corticomedullary differentiation
prolonged corticomedullary differentiation  the ‘cortical rim’ sign
the ‘cortical rim’ sign  delayed or absent contrast medium excretion
delayed or absent contrast medium excretion 3D gadolinium-enhanced MRA may differentiate benign from tumour thrombus
3D gadolinium-enhanced MRA may differentiate benign from tumour thrombus selective renal venography may identify any filling defects
selective renal venography may identify any filling defects
 aortic aneurysm
aortic aneurysm  trauma
trauma  thrombosis (due to atheroma or vasculitis)
thrombosis (due to atheroma or vasculitis) this can progress to a shrunken end-stage kidney
this can progress to a shrunken end-stage kidney there is failure of tracer uptake on later images
there is failure of tracer uptake on later images T1WI + Gad: no enhancement
T1WI + Gad: no enhancement