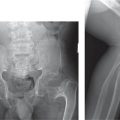
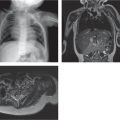
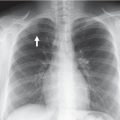
Campomelic dysplasia
Fig. 5.14, p. 501 |
Hypoplastic tibia, scapula, and vertebral bodies. Pear-shaped iliac bones, long femora that are anteriorly bowed, and deficient ossification of the pubis. Radial head dislocation. |
Pulmonary hypoplasia and laryngeal and tracheal stenosis. Ureteral stenosis. Thoracic platyspondyly and kyphosis. Multiple cutaneous dimples in the arms and legs. |
Thanatophoric dysplasia |
Kleeblattschädel (cloverleaf skull), very short ribs, small scapulae, severe platyspondyly, U- or H-shaped vertebral bodies, small iliac bones, horizontal acetabular roofs, small sacroiliac notches, bowing of long bones (French telephone receiver femurs). |
Most common form of skeletal dysplasia that is lethal in the neonatal period. |
Achondrogenesis |
Poor mineralization of skull, absent or minimal ossification of vertebral bodies, short thin ribs, multiple fractures, deformed and short iliac wings and long bones, absent ossification of pubis. |
Micromelic dwarfism. Fetal hydrops and polyhydramnios. |
Achondroplasia, homozygous form |
Short long bones, flat vertebral bodies, large skull. |
Radiographic manifestations lie between thanatophoric dysplasia (see subsequent discussion) and heterozygous achondroplasia (see Table 5.3 ). May be diagnosed in second trimester.65 |
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune syndrome)
Fig. 5.2, p. 493 |
Small thorax with short bulbous ribs, small pelvis with short flared iliac bones, trident acetabula, infero-lateral spur adjacent to sciatic notch, cone-shaped epiphyses of hands. |
Spectrum from lethal to latent forms. Renal, hepatic, and pancreatic dysplasia. Medullary cystic change of the kidneys. Retinal dystrophy. |
Osteogenesis imperfecta type II |
Very little ossification of skull, wormian bones, beaded ribs, short distorted long bones, multiple fractures, flattened acetabula and iliac wings. |
Blue sclera. Types I, III, IV have better prognosis. |
Chondrodysplasia punctata (rhizomelic type)
Fig. 5.58, p. 534 |
Symmetric rhizomelic shortening of long bones, punctate calcific deposits in cartilaginous skeleton. |
Approximately fifty percent may survive to 6 y. Other types have better prognosis.12 |
Hypophosphatasia, lethal form |
Partially ossified skull, no ossification of vertebral pedicles, short abnormal ribs, bent and unusually shaped long bones, spurs in the middle portions of long bones (Bowdler spur). |
Blue sclera. Infantile (lethal), childhood, and adult types. Fetal type on prenatal US: failure to observe a fetal head by 16 wk gestation. |
Schneckenbecken dysplasia |
Snail-shaped ilia, flat acetabular roofs, handlebar clavicles, hypoplastic scapula, dumbbell-shaped very short long bones, wide fibula, and round vertebral bodies.12 |
Hypoplastic vertebral bodies with relatively well-preserved posterior arches.13 |
Short rib-polydactyly syndromes (types I–III) |
Dolichocephaly, hypoplastic mandible, short horizontally oriented ribs. Short long bones. Small iliac bones and flattened acetabular roofs. |
Types range from lethal to more mild forms. Types II and IV have near normal pelvis. Polydactaly is sometimes absent in types III and IV.12 |