A. T2c
B. T3a
C. T3b
D. T4a
2 A 57-year-old asymptomatic male with no past medical history presents with an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 7.2 ng/mL). What is the reported sensitivity of transrectal grayscale ultrasound for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer?
A. <1%
B. 10%
C. 50%
D. 90%
3 A 33-year-old male with acute scrotal pain undergoes Doppler ultrasound of his testicles with a linear 12-MHz transducer. How do high-frequency ultrasound transducers compare to low-frequency ultrasound transducers with respect to imaging depth and spatial resolution?
A. High-frequency transducers have less penetration and greater spatial resolution.
B. High-frequency transducers have more penetration and greater spatial resolution.
C. High-frequency transducers have less penetration and less spatial resolution.
D. High-frequency transducers have more penetration and less spatial resolution.
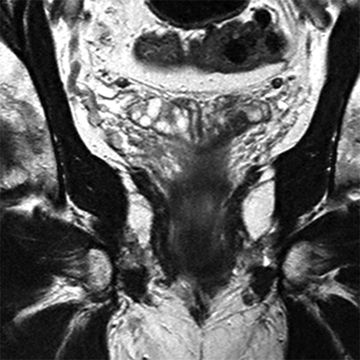
4 A 30-year-old male with scrotal swelling and scrotal pain undergoes Doppler ultrasound. What is the clinical significance of the findings in the left scrotal sac?
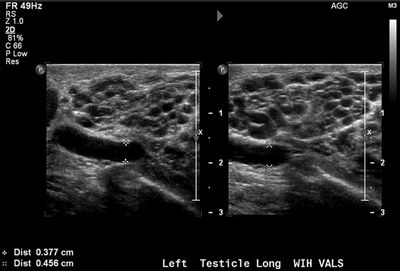
A. Benign finding of no clinical significance
B. Risk factor for infertility
C. Risk factor for testicular cancer
D. Risk factor for sexually transmitted infection
5 Modern multiparametric prostate MRI incorporates multiple advanced anatomic and functional pulse sequences. Which of the following pulse sequences utilize strong bipolar gradients to differentiate moving from stationary spins?
A. Fast spin echo and spin echo
B. Spin echo and balanced gradient echo
C. Balanced gradient echo and echo planar imaging
D. Echo planar imaging and phase contrast
6 A 60-year-old male with an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 10.5 ng/mL) and two negative prostate biopsies undergoes prostate MRI. The following images were obtained. What type of pulse sequence was most likely used for these single-shot acquisitions?
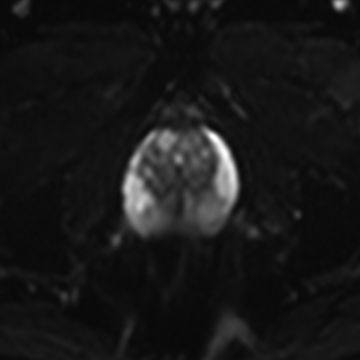
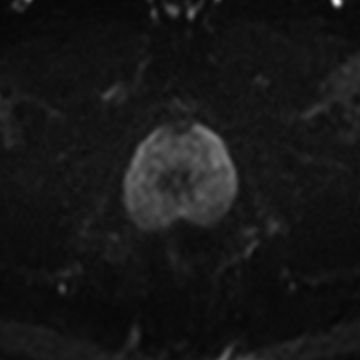
A. T2-weighted fast spin echo
B. T2*-weighted gradient-recalled echo
C. Balanced gradient-recalled echo
D. Echo planar imaging
7 A 50-year-old trauma victim presents with groin pain. A Doppler ultrasound is performed, and an abnormality is identified in his right testicle. What is the most likely diagnosis?
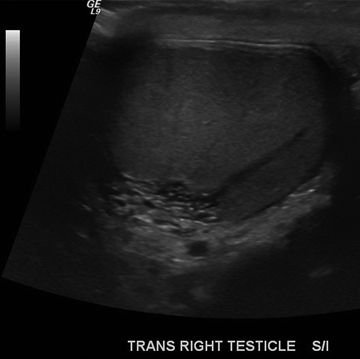
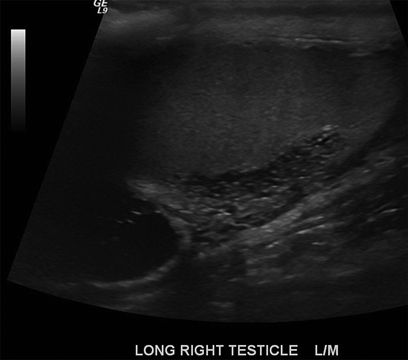
A. Benign finding (ignore)
B. Contained rupture
C. Germ cell tumor
D. Vascular malformation
8 A 32-year-old male presents with scrotal pain, and a Doppler ultrasound is performed. Which of the following risk factors is most likely related to the imaging findings?
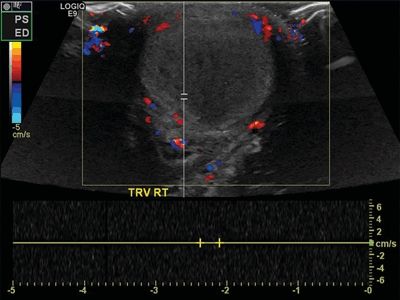
A. Testicular microlithiasis
B. “Bell clapper” deformity
C. Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection
D. Human immunodeficiency virus infection
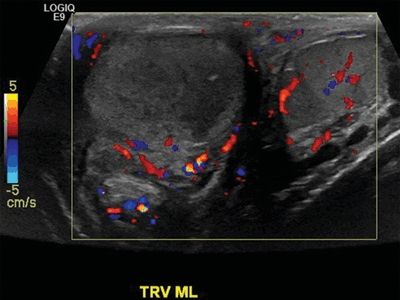
9 A 32-year-old male presents with scrotal swelling. A Doppler ultrasound is performed. Which of the following is a strong risk factor for this disease?
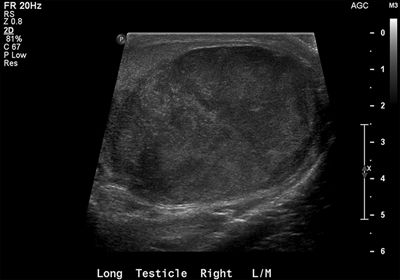
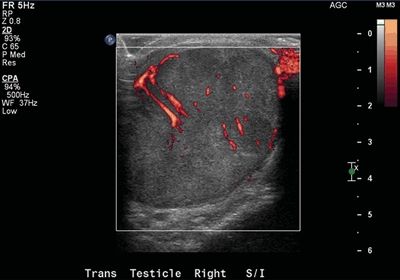
A. Cryptorchidism
B. Prior vasectomy
C. Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection
D. Renal agenesis
10 A 42-year-old male presents with a palpable finding in his left scrotum. An ultrasound is performed demonstrating a solid mass. What imaging finding is most helpful for determining whether this mass is benign or malignant?
A. Presence of calcifications
B. Degree of vascularity
C. Echogenicity
D. Location in or outside the testicle
11 A 60-year-old male with a palpable prostate nodule undergoes transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided sextant biopsy. The pathology returns consistent with multifocal bilateral Gleason 4 + 4 = 8 prostate cancer. A bone scan is performed. How should the images be interpreted?
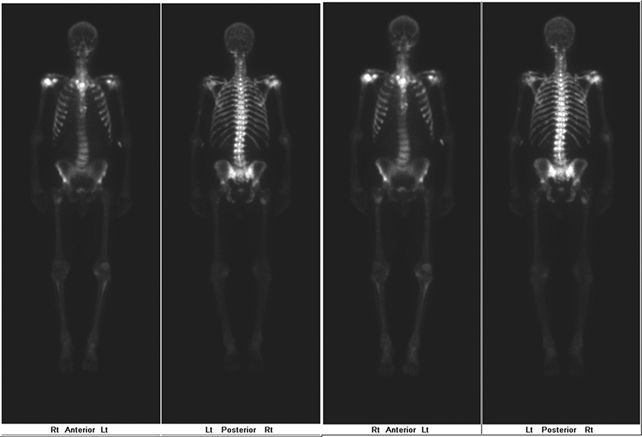
A. Normal study
B. Degenerative change
C. Hyperparathyroidism
D. Widespread metastases
12 A 25-year-old male notices a palpable lump in his scrotum. An ultrasound is performed. What is the most likely diagnosis?
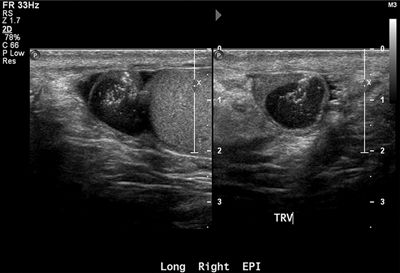
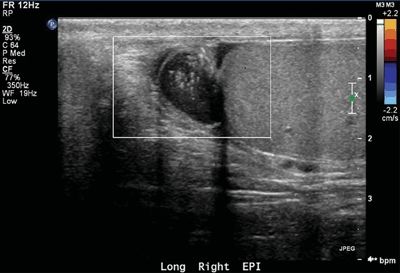
A. Spermatocele
B. Adenomatoid tumor
C. Varicocele
D. Seminoma
13 A 30-year-old male with abdominal pain and weight loss undergoes an abdominopelvic CT examination. Multiple enlarged lymph nodes are identified suggestive of metastatic disease. What is the typical nodal drainage of the male gonads?
A. Inguinal and external iliac lymph nodes
B. Obturator and internal iliac lymph nodes
C. Paracaval and para-aortic lymph nodes
D. Paraceliac and gastrohepatic lymph nodes
14 A 50-year-old female with multiple cardiovascular risk factors and congestive heart failure presents with left perineal swelling, warmth, and erythema. What is the definitive management for this condition?
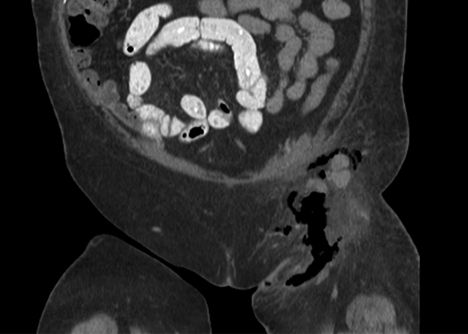
A. Observation
B. Diuretic therapy
C. Needle aspiration
D. Operative debridement
15 A 19-year-old male with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome presents with bilateral scrotal masses. Which tumors of the scrotal sac are associated with this disease?
A. Seminoma
B. Embryonal cell carcinoma
C. Epididymal cystadenoma
D. Spermatic cord liposarcoma
16 A 60-year-old asymptomatic male with an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 9.7 ng/mL) is diagnosed with Gleason 3 + 4 = 7 prostate cancer in 3 of 12 sextant core biopsies. What is the likelihood that this patient will have osseous metastatic disease detectable on imaging?
A. <1%
B. 5%
C. 20%
D. 50%
17 A 5-year-old male with scrotal swelling undergoes a scrotal ultrasound demonstrating bowel in the left scrotal sac. The bowel is followed cephalad along a superolateral course to the level of the inferior epigastric artery, where it is seen to wrap lateral to the artery and enter the peritoneal cavity. What type of hernia does this most likely represent?
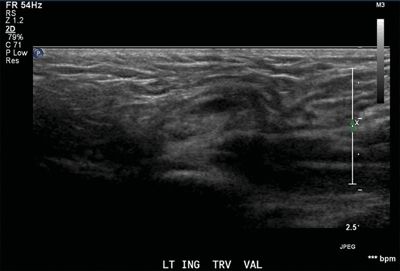
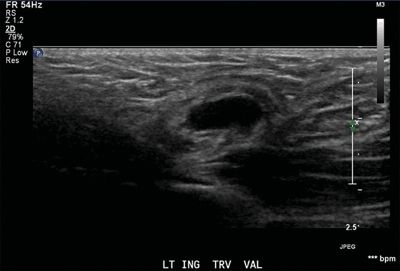
A. Direct inguinal hernia
B. Indirect inguinal hernia
C. Femoral hernia
D. Obturator hernia
18 A 43-year-old male with HIV presents with a large verrucous growth on his scrotum and perineum as shown on the coronal contrast-enhanced CT image below. He is diagnosed with Buschke-Löwenstein disease. This is strongly associated with what entity?
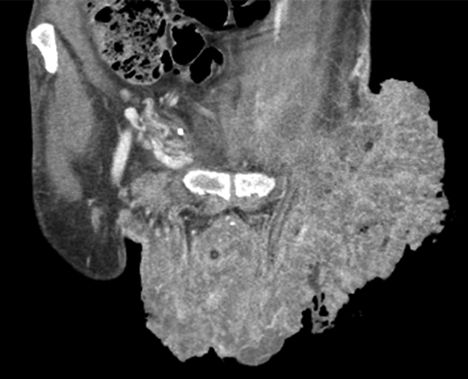
A. Adenocarcinoma
B. Squamous cell carcinoma
C. Melanoma
D. Basal cell carcinoma
19 A 55-year-old male with an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 8.9 ng/mL) and a prior negative prostate biopsy undergoes prostate MRI. A nodule is identified in the anterior transition zone with an apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value of 700 × 10−6 mm2/s. What does the ADC map represent?
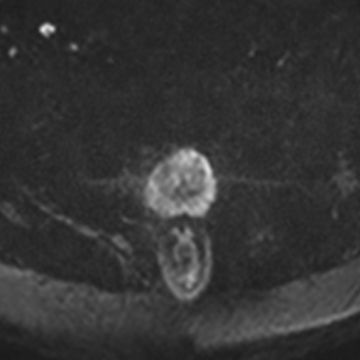
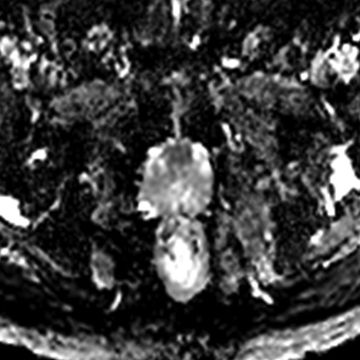
DWI (b = 800 s/mm2)ADC map
A. An inverted pixel-by-pixel map of signal intensity (SI) at the highest acquired b value
B. An inverted pixel-by-pixel map of SI at the lowest acquired b value
C. A pixel-by-pixel map of the slope of SI measured across different acquired b values
D. A pixel-by-pixel map of the slope of ln(SI) measured across different acquired b values
20 A 19-year-old male presents with scrotal swelling after a straddle injury. A Doppler ultrasound is performed. What is the best next step?
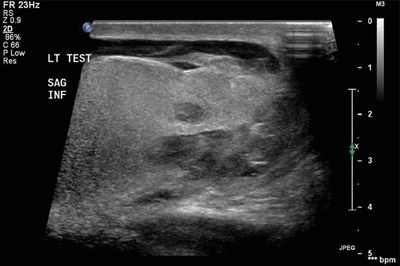
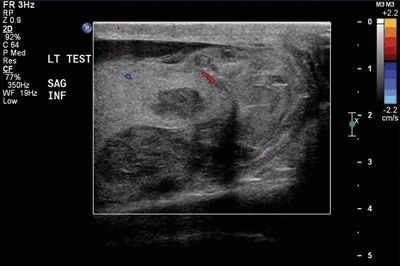
A. Imaging follow-up
B. Intravenous antibiotics
C. Percutaneous biopsy
D. Operative management
21 A 75-year-old male with a palpable prostate nodule undergoes a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided prostate biopsy demonstrating multifocal Gleason 4 + 5 = 9 prostate cancer throughout the right gland. A multiparametric prostate MRI is performed that demonstrates a large mass in the right anterior transition zone. Which of the following is an accepted specific sign of extracapsular disease?
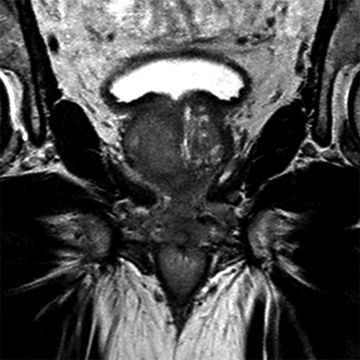
Coronal 2D T2-Weighted Fast Spin Echo
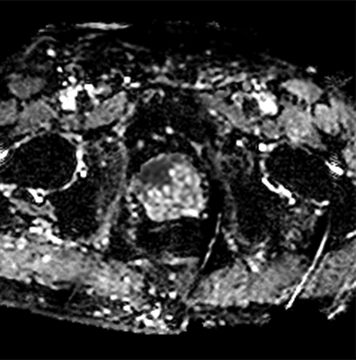
Axial ADC map
A. Focal capsular bulge
B. ADC <800 × 10−6 mm2/s
C. ≥5 mm of capsular abutment
D. Nonvisible T2-hypointense capsule
22 MR spectroscopy has been explored as a method of improving detection of prostate cancer. What is the characteristic spectroscopic pattern of prostate cancer?
A. Elevated citrate:choline ratio
B. Elevated citrate:creatine ratio
C. Elevated choline:citrate ratio
D. Elevated creatine:citrate ratio
23 A 33-year-old male with priapism undergoes Doppler imaging of his penis. Which of the following correctly describes the flow detection characteristics of color and power Doppler imaging?
A. Power Doppler imaging is velocity dependent and color Doppler imaging is not.
B. Power Doppler imaging is less sensitive to slow flow than is color Doppler imaging.
C. Power Doppler imaging is direction independent and color Doppler imaging is not.
D. Power Doppler imaging is more affected by aliasing than is color Doppler imaging.
24 A 60-year-old male with elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 7.1 ng/mL) undergoes a transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy. Four days later, he presents with scrotal pain and swelling. A Doppler ultrasound is performed. What is the best next step?
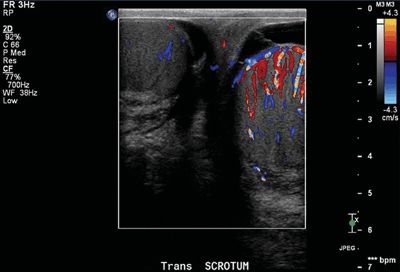
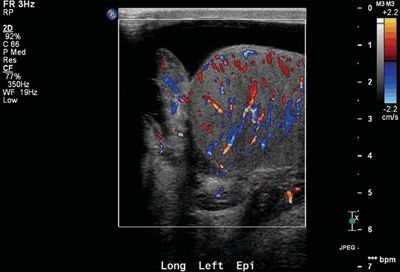
A. Observation
B. Antibiotic therapy
C. Surgical detorsion
D. Prostatectomy
25 A 50-year-old male with T3aNxMx Gleason 4 + 4 = 8 prostate cancer undergoes an In-111 capromab pendetide (ProstaScint) scan. What is the most appropriate interpretation of the imaging findings?
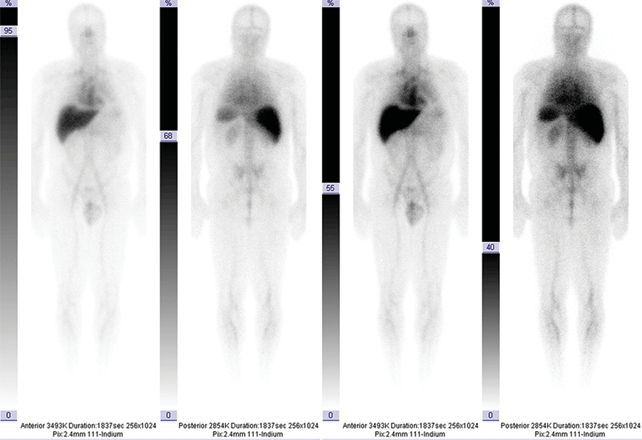
A. Normal study
B. Hepatic metastatic disease
C. Osseous metastatic disease
D. Pulmonary metastatic disease
26 A 16-year-old male with groin pain undergoes a scrotal ultrasound. Multiple masses are identified in both testicles. Which of the following diseases is associated with this imaging finding?
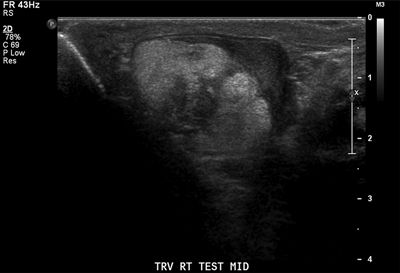
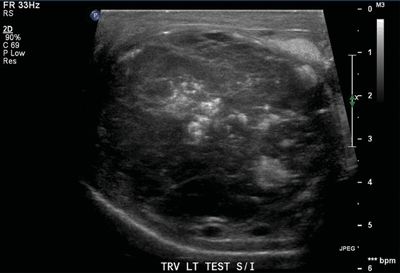
A. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2
B. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
C. von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
D. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
27 A 20-year-old male with a suspected hernia and no relevant history undergoes a scrotal ultrasound. What is the most appropriate management for this imaging finding?
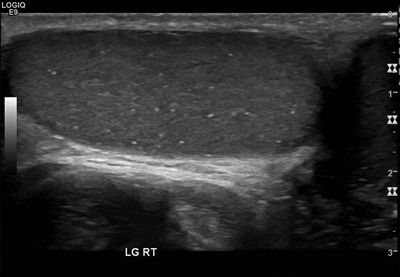
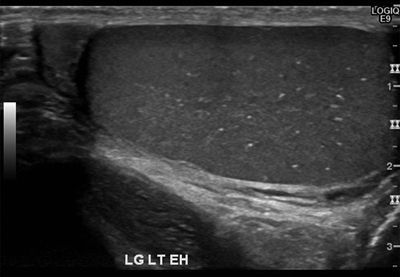
A. Ignore (benign incidental finding)
B. Regular scrotal self-examination
C. Follow-up ultrasound every 6 months
D. Prophylactic bilateral orchiectomy
28 A 60-year-old male with T2bN0Mx Gleason 3 + 4 = 7 prostate cancer undergoes prostatectomy. Two years later, his prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 1.2 ng/mL) becomes detectable. Dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted gradient echo imaging is performed (on left), and subtractions are generated (on right). What is the best next step?
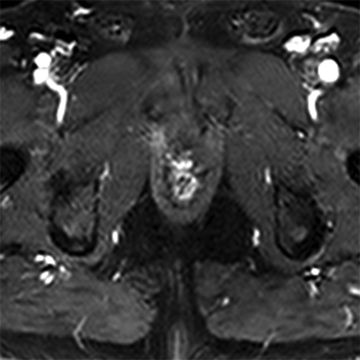
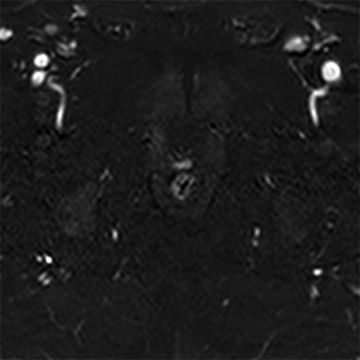
A. Observation with PSA monitoring
B. Observation with serial prostate MRI
C. Antibiotic therapy and drain placement
D. Salvage radiotherapy
29 A 69-year-old male with an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA, 18.4 ng/mL) and a prior negative prostate biopsy undergoes prostate MRI. Diffusion-weighted imaging is performed. Which of the following has been shown to correlate with high Gleason score prostate cancer?
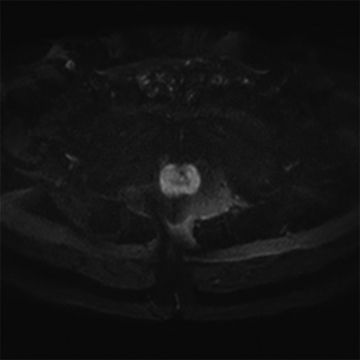
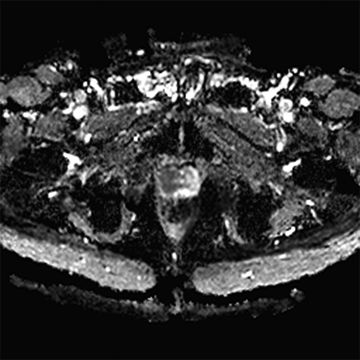
A. Signal intensity on trace b = 800 s/mm2 diffusion images >800
B. Signal intensity on trace b = 800 s/mm2 diffusion images <800
C. Signal intensity on ADC map >850 × 10−6 mm2/s
D. Signal intensity on ADC map <850 × 10−6 mm2/s
30 A 55-year-old male with right lower quadrant pain undergoes a CT of the abdomen and pelvis. Plaque-like calcifications are identified within the penis. What is most likely calcified?
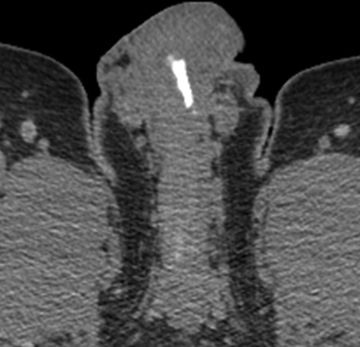
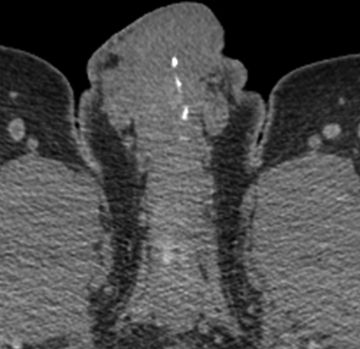
A. Arteries of the corpora cavernosa
B. Veins of the corpora cavernosa
C. Tunica albuginea
D. Tunica vaginalis
Answers and Explanations
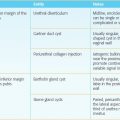
1 Answer C. Seminal vesicle invasion signifies T3b disease according to the AJCC 2010 TNM classification system. The various T stages of prostate cancer are shown below. Of these, the most important to memorize for the radiologist is T2 versus T3.
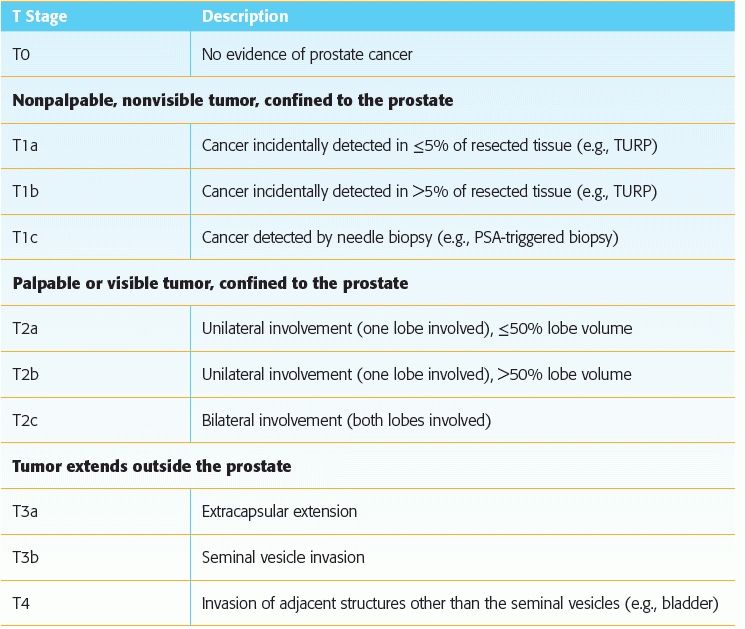
Reference: Prostate. In: Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al. (eds). AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2010: 457–468.
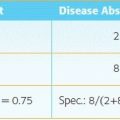
2 Answer C. The sensitivity of grayscale transrectal ultrasound for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer is reported to be approximately 50%, though even this is probably an overestimation. Grayscale ultrasound is not a reliable method of detecting primary prostate cancer. Ultrasound is primarily used to guide transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided biopsies. TRUS-guided biopsies are usually nontargeted and randomly directed (i.e., sextant biopsy). Sampling during a random TRUS-guided biopsy usually consists of 12 or more core biopsy specimens obtained using a template approach, with intentional oversampling of the peripheral zone. The anterior gland and transition zone are often undersampled or not sampled at all.
References: Carter HB, Hamper UM, Sheth S, et al. Evaluation of transrectal ultrasound in the early detection of prostate cancer. J Urol 1989;142:1008–1010.
Terris MK, Freiha FS, McNeal JE, et al. Efficacy of transrectal ultrasound for identification of clinically undetected prostate cancer. J Urol 1991;146:78–83.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree