43 Maxillary Artery
F. Goetz, A. Giesemann
The course of the maxillary artery has often been related to the lateral pterygoid muscle and the mandibular nerve branches. In addition to the variants shown here, both division of the maxillary artery and piercing of the muscle are rare findings.1–13
Pathologic conditions involving branches of the maxillary artery can be diverse. Variants and anastomoses need to be considered, especially when endovascular treatment is used.14
43.1 Course Lateral to the Lateral Pterygoid Muscle (66%)

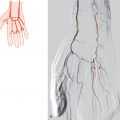
Fig. 43.1 Middle meningeal artery originates proximally to the inferior alveolar artery (60%). Schematic (a) and X-ray angiography, lateral projection, proximal external carotid artery injection (b). 1 Superficial temporal artery; 2 middle meningeal artery; 3 maxillary artery; 4 posterior auricular artery; 5 inferior alveolar artery.

Fig. 43.2 Middle meningeal artery originates opposite the inferior alveolar artery (3%). Schematic.

Fig. 43.3 Middle meningeal artery originates distally to the inferior alveolar artery (3%). Schematic.
43.2 Course Medial to the Lateral Pterygoid Muscle and Lateral to the Main Branches of the Mandibular Nerve (21%)

Fig. 43.4 Middle meningeal artery originates proximally to the inferior alveolar artery (2%). Schematic.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree