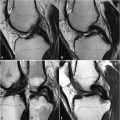
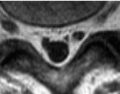
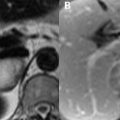
78 Meniscal Tears II Vertical meniscal tears are oriented perpendicular to the meniscus on coronal images. An example of such a tear within the lateral meniscus is seen in the coronal FS T2WI of Fig. 78.1A. This hyperintense tear (white arrow) extends to both superior and inferior articular surfaces, establishing it as a grade 3B lesion. In this image, there is also hyperintensity within the lateral femoral condyle and to a lesser extent within the lateral tibial plateau, reflecting edema from bone contusion. Due to the possibility of homogeneous fat suppression, T1WI are superior to FS T2WI for the detection of marrow pathology. Note the relative graininess of the FS T2WI in Fig. 78.1A compared with the FS PDWI in Fig. 78.1B, owing to the FS T2WI being obtained at a lower field strength (1.5 T vs 3 T) and the intrinsically lower SNR of this sequence compared with PDWI. Tears may also be grouped based on surface pattern into radial, longitudinal, and flap types. These tears all extend to the superior or inferior articular surface, in contrast to a pure horizontally oriented (cleave) tear (see Fig. 77.1C,D). Nonpure horizontal (see Fig. 77.1A,B
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree