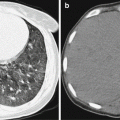
Fig. 16.1
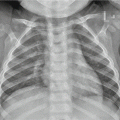
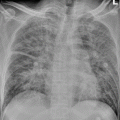
Neonatal tetanus complicated by pulmonary atelectasis (a) Chest X-ray demonstrates no obvious abnormality when hospitalized. (b) By reexamination after 8 days, chest X-ray demonstrates atelectasis of the upper lobe in the right lung (Reprint with permission from Chang SC, et al. Pediatr Neonatol, 2010, 51(3): 182)
16.7.1.2 CT Scanning
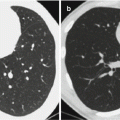
CT scanning demonstrates thickened and blurry bronchovascular bundle in the middle and lower fields of both lungs. The lesions are mostly small patches of cloudy shadows, with some fusing into large flakes or triangular parenchymal shadows. In the cases with pulmonary atelectasis, the demonstrations also include lobular, segmental, or lobar atelectasis.
16.7.2 Central Nervous System
16.7.2.1 CT Scanning
Encephaledema has CT demonstrations of low-density shadows in cerebral parenchyma with unclearly defined boundaries, unclearly defined borderline between the gray and white matters, and absence of some sulci. In the case of cerebral parenchymal hemorrhage, CT scanning demonstrates spots, patches, round or roundlike-shaped shadows in high density, with surrounding flakes of low-density shadows due to encephaledema. In the cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage, CT scanning demonstrates absent sulci and cisterns and increased destiny. And the CT demonstrations of subdural hematoma include crescent-shaped high-density shadows under bone lamella and migration of brain parenchyma inwards due to compression.
16.7.2.2 MR Imaging
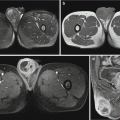
MR imaging of cases with acute encephaledema demonstrates flakes of high T1 and high T2 signals. The cases of cerebral hemorrhage show spots or flakes of equal/high signal by T1WI and high or mixed signal by T2WI.
16.8 Basis for Diagnosis
16.8.1 Neonatal Tetanus
Based on the history of delivery mode, the diagnosis can be made for the cases choosing traditional mode of delivery or possible incomplete sterilization when the umbilical cord was severed. The disease has typical symptoms and etiological examinations by bacteria culture are not necessary for the diagnosis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree