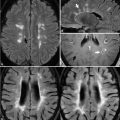
27 Neurofibromatosis and von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome NF1 or von Recklinghausen disease is an autosomal dominant disorder with diagnostic criteria including two or more of the following: a first-degree relative with NF1, axillary freckling, distinctive bone lesions, an optic glioma, a plexiform neuroma, at least six café-au-lait spots, and more than one Lisch nodule or neurofibroma. Foci of abnormal signal intensity (FASI) are the most common NF1 findings on brain MRI. The FLAIR images in Fig. 27.1A demonstrate the typical high SI appearance of FASI within their characteristic location—the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia. Pallidal lesions, in particular, may also appear as high SI on T1WI—a characteristic relating to their possible pathologic identity as hamartomas or heterotopic Schwann cells. Less commonly, FASI may involve the pons (Fig. 27.1B) or cerebellum (Fig. 27.1C
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree