In the paediatric skeleton the soft bone tends to bend and partially break • Greenstick fracture: the bone cortex and periosteum break on the convex side of a long bone only • Torus fracture: the bone cortex buckles on the concave side • Plastic bowing: a long bone bends, rather than breaks (multiple oblique microfractures are present) • Children’s physes are more likely to fail than the ankle ligaments • Triplane and Tillaux fractures tend to occur in adolescence around the time of distal tibial epiphyseal fusion • Non-accidental injury (NAI): a spectrum of injuries due to child abuse • Clinical presentation: this ranges from vague minor symptoms to life-threatening shock
Paediatric fractures
SPECIFIC PAEDIATRIC FRACTURES
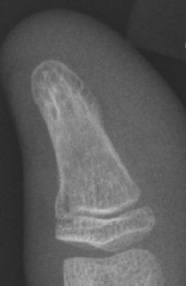
GREENSTICK/TORUS FRACTURE/PLASTIC BOWING
Definition
 in the forearm, a non-bowed bone may fracture or dislocate
in the forearm, a non-bowed bone may fracture or dislocate
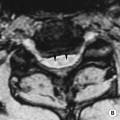
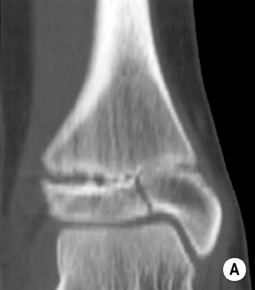
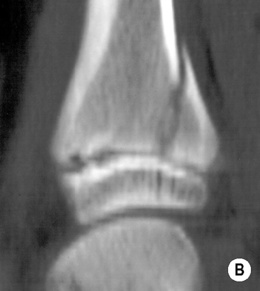
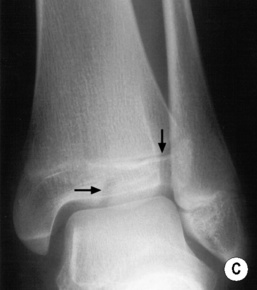
ANKLE FRACTURES
Definition
 those of the distal tibia and fibula fuse at the same time (if only one is fused suspect an epiphyseal injury)
those of the distal tibia and fibula fuse at the same time (if only one is fused suspect an epiphyseal injury)
 CT is used for assessment prior to reduction
CT is used for assessment prior to reduction
RADIOLOGY OF NON-ACCIDENTAL INJURY
RADIOLOGY OF NON-ACCIDENTAL INJURY
DEFINITION
 this includes physical, sexual and emotional abuse
this includes physical, sexual and emotional abuse

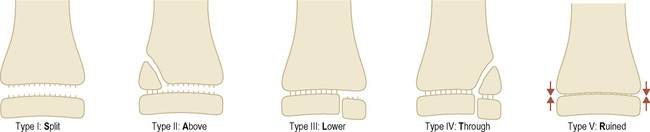
 injuries become more serious as the numeral rises, with an associated risk of growth disturbance
injuries become more serious as the numeral rises, with an associated risk of growth disturbance  there is a worse prognosis within the lower limb than the upper limb
there is a worse prognosis within the lower limb than the upper limb good prognosis
good prognosis poorer prognosis
poorer prognosis it is usually associated with types 1–IV injuries
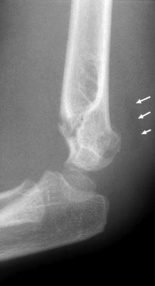
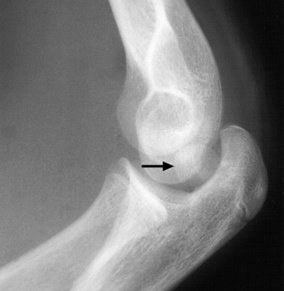
it is usually associated with types 1–IV injuries it is a transverse fracture of the distal humerus (proximal to the humeral condyles)
it is a transverse fracture of the distal humerus (proximal to the humeral condyles) the mid-third of the capitellum is displaced posterior to the anterior humeral line
the mid-third of the capitellum is displaced posterior to the anterior humeral line it may be associated with ulnar nerve injury
it may be associated with ulnar nerve injury it may not be seen on an initial XR (perform delayed XR or scintigraphy)
it may not be seen on an initial XR (perform delayed XR or scintigraphy)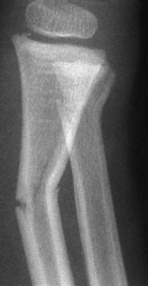
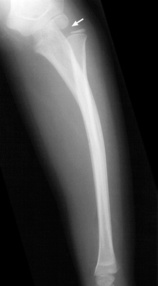
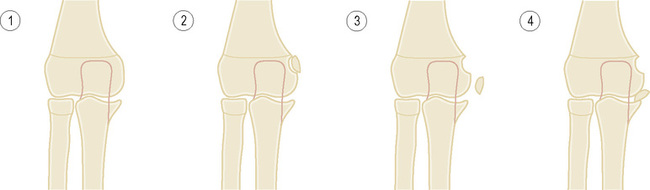
 2, slight alvusion
2, slight alvusion  3, major avulsion
3, major avulsion  4, major avulsion and the epicondyle lies within the joint.
4, major avulsion and the epicondyle lies within the joint.  a foreign body may be evident
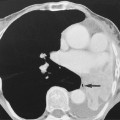
a foreign body may be evident CT is the investigation of choice
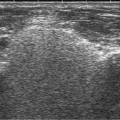
CT is the investigation of choice  US is portable and readily available
US is portable and readily available