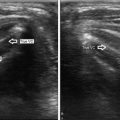
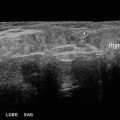
Fig. 18.1
(a) Grayscale US . Diffusely enlarged right lobe of the thyroid with a heterogeneous echotexture characteristic of thyroiditis. (b) Power Doppler US. Diffusely enlarged right lobe of the thyroid with a heterogeneous echotexture and increased vascular flow characteristic of thyroiditis
Power Doppler demonstrated increased vascular flow in the thyroid gland (Fig. 18.1b).
Diagnosis of US-Guided FNA /Cytology: (Right lobe) Hashimoto’s thyroiditis/lymphocytic thyroiditis
18.3.2 Case 2: Diffuse Thyroid Disease (Nodular Thyroiditis)
Clinical Scenario: A 56-year-old man with multiple thyroid nodules. US was performed to assess the palpable thyroid nodules.
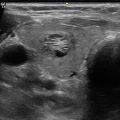
Imaging Features: Ultrasound. Enlargement of the thyroid gland with what appears to be multiple well-circumscribed nodules in the transverse plane (Fig. 18.2a, b). Increased vascular flow demonstrated on power Doppler within suspected multiple thyroid nodules (Fig. 18.2c, d)
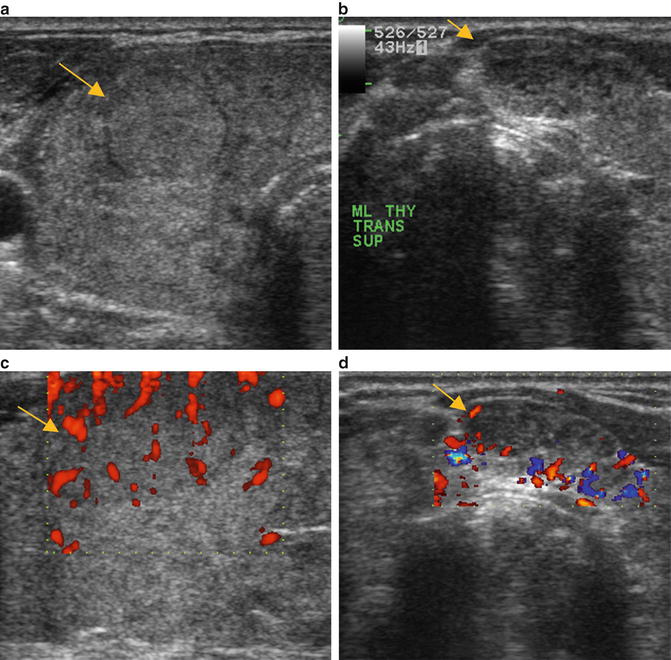

Fig. 18.2
(a) Grayscale US . Enlarged thyroid gland with what appears to be multiple well-circumscribed nodules in the transverse plane that ultimately proved by US-guided FNA to be pseudo-nodules of thyroiditis (arrow). (b) Grayscale US. Enlarged thyroid gland with what appears to be multiple well-circumscribed nodules in the transverse plane that ultimately proved by US-guided FNA to be pseudo-nodules of thyroiditis (arrow). (c) Power Doppler US. Increased vascular flow demonstrated on power Doppler within suspected multiple thyroid nodules. (d) Power Doppler US. Increased vascular flow demonstrated on power Doppler within suspected multiple thyroid nodules that were ultimately found on FNA or cytology to be composed of a polymorphous lymphoid population and Hürthle-like cells consistent with chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis
Diagnosis of US-Guided FNA /Cytology: Polymorphous lymphoid population and Hürthle-like cells consistent with chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis documenting that the thyroid contained pseudo-nodules caused by thyroiditis
18.3.3 Case 3: Diffuse Thyroid Disease (Thyroiditis)
Clinical Scenario: A 28-year-old female with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Screening ultrasound examination was performed to exclude an associated thyroid cancer.
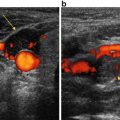
Imaging Features: Ultrasound. Non-homogenous thyroid gland in the longitudinal plane with no discrete suspicious nodules present to suggest a thyroid carcinoma (Fig. 18.3a): Power Doppler demonstrates increased vascular flow throughout the thyroid gland (Fig. 18.3b). Benign-appearing lymph nodes are present inferior to the left thyroid lobe which is a characteristic finding of thyroiditis (Fig. 18.3c).
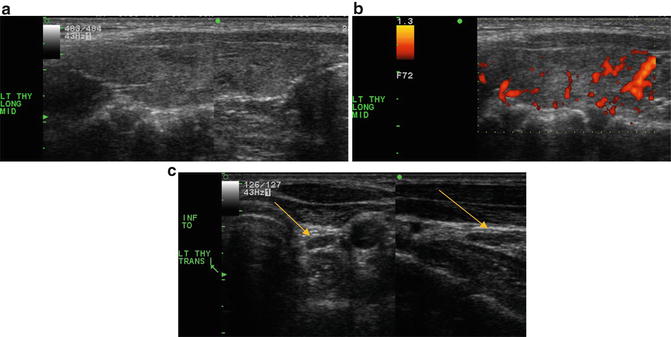

Fig. 18.3
(a) Grayscale US . Non-homogenous thyroid gland in the longitudinal plane. The appearance is characteristic of thyroiditis with no discrete suspicious nodules to suggest a thyroid carcinoma. (b) Power Doppler US. Mild increased vascularity of the thyroid gland which combined with the non-homogenous echogenicity is suggestive of thyroiditis. (c) Grayscale US. Benign-appearing lymph nodes that are present inferior to the left thyroid lobe which combined with the non-homogenous echogenicity are characteristic findings of thyroiditis (arrow)
Diagnosis of US-Guided FNA /Cytology: Biopsy not indicated in this case of well–established thyroiditis based on the US images, even in a patient whose underlying genetic condition (FAP) may predispose to thyroid cancer
18.3.4 Case 4: Diffuse Thyroid Disease (Thyroiditis vs. Leukemia )
Clinical Scenario: A 31-year-old female who presents with an enlarged, painful thyroid. US was performed to assess the palpable thyromegaly.
Imaging Features: Ultrasound. There is a heterogeneous echotexture of the thyroid gland with a lobulated contour imaged in the longitudinal plane (Fig. 18.4a). Power Doppler . Increased vascular flow throughout the gland (Fig. 18.4b). Computed tomography. Contrast-enhanced CT demonstrates diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland (Fig. 18.4c).
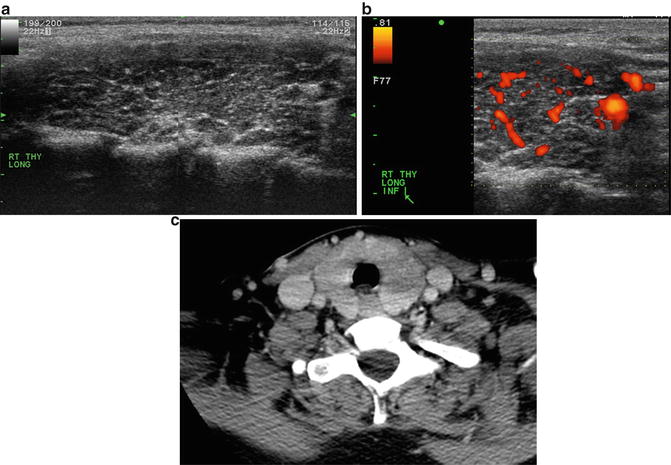

Fig. 18.4
(a) Grayscale US . There is a heterogeneous echotexture of the thyroid gland with a lobulated contour imaged in the longitudinal plane. (b) Power Doppler US. Increased vascular flow throughout the thyroid gland. (c) CT. Contrast-enhanced CT demonstrates diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland
No suspicious nodes were present in the central compartment or lateral neck.
Diagnosis of US–Guided FNA /Cytology: (Right thyroid lobe) Polymorphous lymphoid infiltrate and rare thyroid follicular epithelium with reactive features, consistent with lymphocytic thyroiditis; immunophenotypic characterization of this aspirate by flow cytometry shows polytypic B cells and unremarkable T and NK cells. There is no immunophenotypic support for a B– or T–cell neoplasm.
18.3.5 Case 5: Lymphoma
Clinical Scenario: A 63-year-old female with a palpable right neck mass. Ultrasound was performed to assess the mass for thyroid cancer.
Imaging Features: Ultrasound. Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland with a heterogeneous echotexture containing multiple nodular components and a lobulated contour seen in the longitudinal plane (Fig. 18.5a). Power Doppler . Increased flow throughout the gland including within one of the nodules (Fig. 18.5b). Contrast-enhanced CT. Diffuse enlargement of the right lobe and a right lateral jugular territory neck node of concern imaged in the transverse plane (Fig. 18.5c)
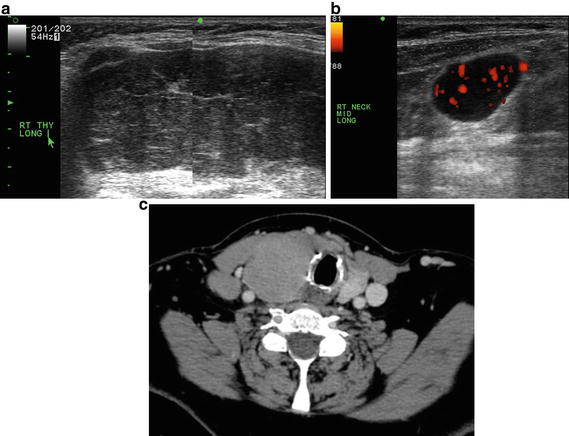

Fig. 18.5
(a) Grayscale US . Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland with a heterogeneous echotexture containing multiple nodules and a lobulated contour seen in the longitudinal plane. (b) Power Doppler US. Increased flow throughout the thyroid gland including within one of the thyroid nodules. (c) Contrast–enhanced CT. Diffuse enlargement of the right lobe and a right lateral jugular territory cervical lymph node of concern for malignancy
Diagnosis of US-Guided FNAs/Cytology: ((A) Right thyroid) Large cell lymphoma, ((B) Right neck node) large cell lymphoma
18.3.6 Case 6: Prostate Cancer
Clinical Scenario: A 67-year-old male who presents with enlarged palpable thyroid. US was performed to assess thyroid and difficulty swallowing.
Imaging Features: Ultrasound. Diffuse enlargement of the left thyroid in the longitudinal plane with multiple punctate hyperechoic foci and no discrete mass (Fig. 18.6a). Power Doppler . Increased vascular flow in the enlarged thyroid gland (Fig. 18.6b). Power Doppler. Increased vascular flow in a suspicious right inferior jugular territory lymph node detected on ultrasound (Fig. 18.6c). Contrast-enhanced CT. Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland with a suspicious right inferior neck node (Fig. 18.6d)
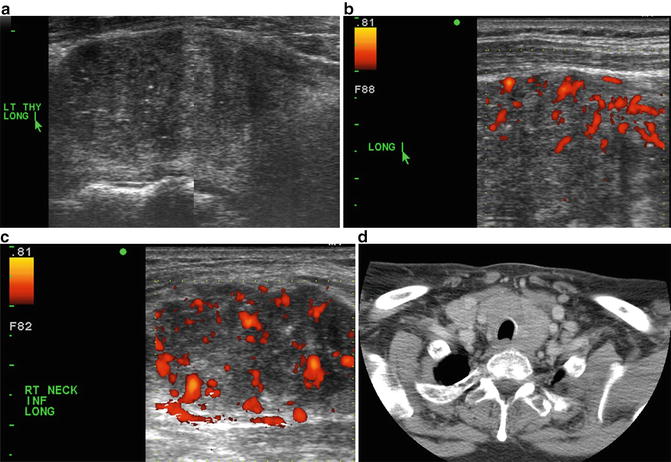

Fig. 18.6
(a) Grayscale US . Diffuse enlargement of the left thyroid in the longitudinal plane with multiple punctate hyperechoic foci and no discrete mass. (b) Power Doppler US. Increased vascular flow in the enlarged thyroid gland. (c) Power Doppler US. Increased disorganized vascular flow in a suspicious right inferior jugular territory lymph node detected on ultrasound. (d) Contrast–enhanced CT. Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland with a suspicious right inferior cervical lymph node
Diagnosis of US-Guided FNA /Cytology: (Right thyroid lobe) Adenocarcinoma compatible with prostatic primary
18.3.7 Case 7: Diffuse Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Clinical Scenario: A 25-year-old female with the sensation of left neck fullness. Ultrasound was requested to assess for soft tissue mass.
Imaging Features: Ultrasound. Diffuse enlargement of the left thyroid (Fig. 18.7a) with mildly increased vascular flow in the enlarged gland (Fig. 18.7b).
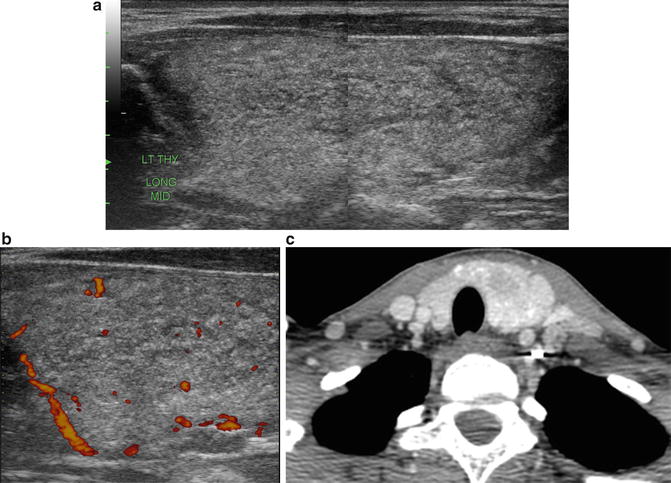

Fig. 18.7
(a) Grayscale US. Diffuse enlargement of the left thyroid gland. (b) Power Doppler US. Mildly increased vascular flow in the enlarged thyroid gland. (c) Contrast-enhanced CT. Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland
Contrast-enhanced CT. Diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland (Fig. 18.7c)
Diagnosis of US-Guided FNA /Cytology: ((A) Left thyroid) Papillary thyroid carcinoma
18.4 Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules : Benign
Sonographic features that suggest a benign thyroid nodule include a simple thyroid cyst, or complex cyst, with no intranodular calcification or intranodular vascular flow on power Doppler imaging.
18.4.1 Case 8: Thyroid Cyst
Clinical Scenario: A 43-year-old male with multiple palpable thyroid nodules. Ultrasound was requested to assess the palpable thyroid nodules.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree