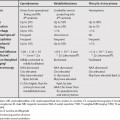
102 It is sometimes difficult to differentiate perforated from nonperforated appendicitis. Abscess and extraluminal air are the most specific findings for perforated appendicitis, but have low sensitivity. Periappendiceal inflammatory stranding and focal defect in the enhancing appendiceal wall are more sensitive, but less specific. Partial volume averaging is often misinterpreted as a focal defect in the appendiceal wall. The visualization of appendicoliths increases the probability of perforation. The presence of one or more appendicoliths in association with periappendiceal inflammation is highly suspicious for perforation.1,2
Perforated Appendicitis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree