KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Cystic dilatation of obstructed periductal glands of bile ducts
- •
Retention cyst of peribiliary gland
Imaging
- •
Well-defined, cystic structures adjacent to portal triads
- •
Usually multiple; discrete, round/oval/tubular, or confluent configuration
- •
Variable size, from 2 mm to 2 cm
- •
Smooth and thin walls without internal echoes
- •
No enhancement of contents on CECT or MR
- •
Nonopacification with direct cholangiography or hepatobiliary-phase MR using hepatocyte-specific contrast agent
- ○
Do not communicate with biliary tree
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Biliary ductal dilatation
- •
Caroli disease
- •
Hepatic autosomal dominant polycystic disease
- •
Periportal edema/inflammation
Pathology
- •
Disturbed portal venous flow, periductal fibrosis, and inflammation → obliteration of neck of peribiliary glands → formation of retention cyst
- •
Associated with chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, liver transplantation
Clinical Issues
- •
Peribiliary cysts are typically asymptomatic; symptoms often related to underlying liver disease
- •
Obstructive jaundice may occur in end-stage liver cirrhosis or as complication of postliver transplantation
- •
May increase in size and number of cysts as cirrhosis progresses
Scanning Tips
- •
Do not confuse peribiliary cysts for biliary ductal dilatation
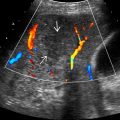
 clustered in a linear configuration located along the portal vein
clustered in a linear configuration located along the portal vein  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree