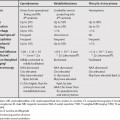
62 The most common cause of transudative effusion is congestive heart failure. The most common cause of exudative effusion is infection or pneumonia. In older patients, exudative effusions secondary to malignancy should be considered (Table 62.1). Thick enhancing pleural rind suggests exudative effusion. Pleural-based soft tissue nodules may be seen in malignant effusions on computed tomography (CT). Lung cancer and breast lymphomas are the cause of 75% of malignant effusions. A hematocrit effect (layering of blood products) should be looked for on the narrow mediastinal window to assess for hemothorax.
Pleural Effusions
Exudative versus Transudative Effusion on Computed Tomography
Mechanisms by which Malignancy Leads to Pleural Effusion