CHAPTER 6 ![]()
Practice Test 1
Questions
1. Radiation therapy is a treatment that utilizes
(A) drugs to treat cancer that may have spread
(B) high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells
(C) radioactive tracers to track the path of cancer to the lymph nodes
(D) potent pain medication to treat the severe pain from cancer
2. Between ages 20 and 30 an asymptomatic woman should be having a mammogram every
(A) year
(B) 2 years
(C) 3 years
(D) none of the above
3. Medical history may include questions on hormone use because
(A) synthetic hormones such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) will always cause breast cancer
(B) the use of reproductive hormones can increase risk factors for breast cancer
(C) family history of hormone use predisposes a woman to cancer
(D) personal history of hormone use decreases a woman’s risk for breast cancer
4. In imaging implants some of the projections taken will include an image of the implant. In these projections the compression is used
(A) to allow a uniform density
(B) for immobilization only
(C) to separate the breast tissue
(D) to separate and spread out the implant
5. The glandular dose is a measure of
(A) the radiation dose to the skin of the breast
(B) the dose to the radiosensitive cells of the breast
(C) the significant background dose recorded in United States
(D) the radiation dose to the gonads
6. Which of the following is true of screen-film systems?
(A) Screen-film systems have a higher spatial resolution than digital systems.
(B) Screen-film systems have a wide latitude and dynamic range than digital systems.
(C) When compared to a digital system screen-film systems help to increase workflow.
(D) Screen-film systems typically result in less repeats due to exposure errors when compared to digital systems.
7. In digital imaging, a graph of the density range to the log of relative exposure is a
(A) shallow sloping curve
(B) steep sloping curve
(C) linear response
(D) curvilinear response
8. In the American College of Radiology (ACR)-approved accreditation phantom, the total number of fibers, speck groups, and masses are
(A) 5 fibers, 5 speck groups, and 5 masses
(B) 5 fibers, 6 speck groups, and 5 masses
(C) 6 fibers, 5 speck groups, and 5 masses
(D) 5 fibers, 5 speck groups, and 6 masses
9. The circular pigmented area around the nipple is called the
(A) skin
(B) areola
(C) Montgomery gland
(D) ampulla
10. A keratosis is demonstrated mammographically as a
(A) sharply outlined multilobulated lesion
(B) sharply outlined lesion with a halo
(C) mixed-density circular lesion with a radiolucent center
(D) mixed-density oval lesion
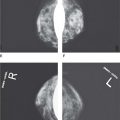
11. Figure 6-1 indicates
(A) mammographically benign calcifications
(B) malignant calcifications
(C) keratosis
(D) fibroadenomas
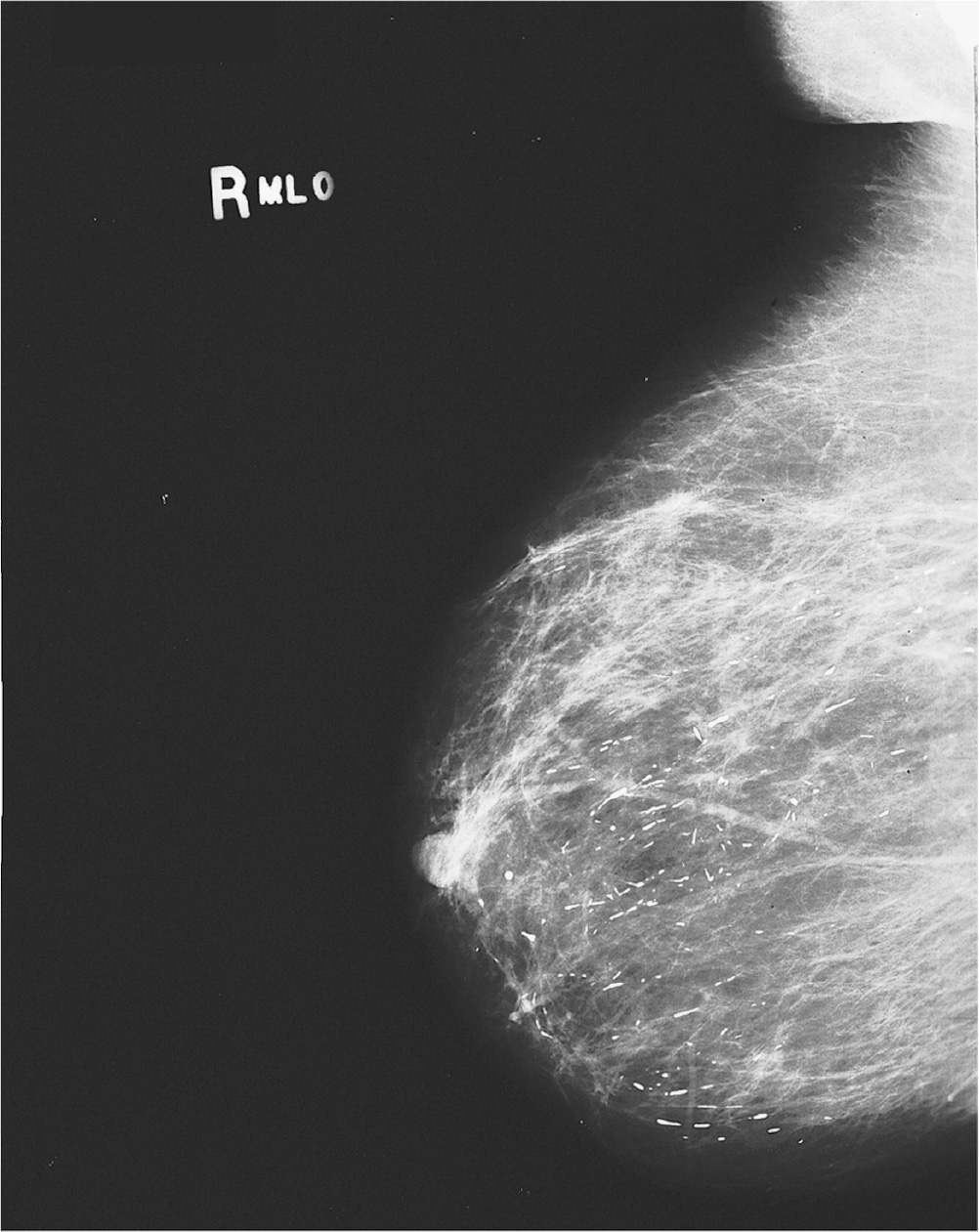
Figure 6-1.
12. The advantages of a quality assurance program such as the MQSA includes all of the following except
(A) increased efficiency
(B) cost-effectiveness
(C) allows manipulation of the final image
(D) improved patient satisfaction
13. In magnification, what immediate role does the large object-to-image receptor distance (OID) play in reducing scattered radiation?
(A) It allows the use of lower peak kilovoltage (kVp) values.
(B) There is increased SOD which allows for absorption of the scattered radiation.
(C) Most of the scattered radiation misses the detector.
(D) The larger OID utilizes a smaller SID.
14. Using a small focal-spot size is recommended for magnification
(A) to reduce the resultant loss of image detail
(B) because of increased patient dose
(C) to compensate for the small OID
(D) to compensate long exposure times
15. What is the best placement for the needle wire during needle localization?
(A) The needle wire should pass immediately below the lesion.
(B) The needle wire should pass immediately above the lesion.
(C) The needle wire should pass through the lesion.
(D) The needle wire should pass immediately beside the lesion.
16. Although it may mean losing some of the lateral breast tissue, in imaging for the craniocaudal (CC) projection, most experts agree that all efforts should be made to maximize imaging of the medial breast tissue. Why?
(A) Medial breast is imaged best on the CC.
(B) Medial breast is imaged only on the CC.
(C) Most cancers are found in the medial breast.
(D) The lateral breast is generally distorted on the CC.
17. Which is true when positioning for all tangential (TAN) projections?
(A) The patient is always in the CC position.
(B) The central ray is always directed vertically.
(C) The central ray is always parallel to the plane of the breast.
(D) The central ray is always parallel to the skin surface.
18. In the rolled medial (RM) position, the inferior (lower) surface of the breast is rolled in which direction?
(A) laterally
(B) medially
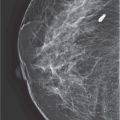
(C) inferiorly
(D) superiorly
19. A radiopaque implant that is used in breast reconstruction and can be adjusted for cup size after surgical placement in the breast is the
(A) silicone gel implant
(B) flap implant
(C) silicone liquid implant
(D) saline implant
20. In addition to the routine CC and mediolateral oblique (MLO), a routine series for a postmastectomy patient could also include the
(A) axillary tail (AT)
(B) ML
(C) TAN
(D) lateromedial oblique (LMO)
21. Men with a family history of breast cancer will
(A) have a greater risk for breast cancer
(B) have a minor risk for breast cancer
(C) have no significantly increased risk for breast cancer
(D) always get breast cancer
22. The clinical breast examination (CBE) should be performed
(A) at or near the time of the annual mammogram
(B) only by the radiologist
(C) monthly, preferably at the same time of the month
(D) at least twice a year
23. The absorbed dose in mammography is generally _______ the entrance skin exposure (ESE).
(A) significantly higher than
(B) significantly lower than
(C) about the same as
(D) slighter higher than
24. In the compression test required by The Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA), the maximum compression for the initial power drive should not exceed
(A) 100 N
(B) 200 N
(C) 400 N
(D) 500 N
25. Collimation should not extend beyond any edge of the detector by more than
(A) 1% of the SID
(B) 2% of the SID
(C) 3% of the SID
(D) 4% of the SID
26. Inherent filtration will include filtration by all of the following except
(A) exit port of the tube
(B) compression paddle
(C) molybdenum filters
(D) mirror assembly
27. The MQSA standards were enacted
(A) because mammography was overregulated
(B) to address the inconsistent quality mammograms that were available
(C) to enforce continuing education for radiologic technologist
(D) to enforce continuing education for radiologist
28. Grids in mammography are utilized
(A) during normal imaging
(B) during magnification imaging only
(C) only if requested by the radiologist
(D) to reduce radiation dose to the patient
29. Breast tissue can extend medially to the
(A) latissimus dorsi muscle
(B) midsternum
(C) retromammary space
(D) inframammary crease
30. Which of the following hormones has the most influence on the normal physiological changes of the breast?
(A) estrogen and prolactin
(B) estrogen and progesterone
(C) prolactin and estrogen
(D) progesterone and prolactin
31. Which of the following is (are) considered a first-degree relative?
(A) mother and aunt
(B) first cousin and mother
(C) aunt and sister
(D) sister and mother
32. A woman should perform breast self-examination (BSE) monthly to
(A) become familiar with both of her breasts
(B) excise cancerous lumps
(C) determine skin versus breast tissue calcifications
(D) monitor nipple discharge
33. The breast of a woman below age 35 is
(A) not related to radiation sensitivity
(B) less sensitive to radiation
(C) less sensitive to low-dose radiation
(D) more sensitive to radiation
34. In the low kVp range using a molybdenum target tube, what type of photon interaction predominates?
(A) photoelectric
(B) Compton
(C) Bremsstrahlung
(D) coherent
35. In digital imaging a repeat analysis test is
(A) unnecessary—digital imaging automatically corrects exposure mistakes
(B) necessary—digital imaging cannot correct for overexposure
(C) unnecessary—digital imaging corrects unsharpness by altering the spatial display
(D) necessary—digital imaging cannot correct factors such as motion unsharpness
36. The same mammographer should view the phantom images because
(A) subjective judgment about images is always difficult
(B) it is not wise to have different individuals handling the phantom
(C) not all mammographers know the MQSA regulations
(D) given set values, different mammographers will calculate the densities differently
37. The from below (FB) projection utilizes a beam directed
(A) perpendicular to the detector
(B) horizontally
(C) tangentially
(D) parallel to the detector
38. Changes in the breast due to radiation therapy include
(A) erythema
(B) edema
(C) hardening
(D) all of the above
39. Scanning the breast to locate a cancer based on the vast amount of glucose/sugar utilized by cancer cells is the technique used in
(A) scintigraphy
(B) PEM imaging
(C) MRI
(D) lymphoscintigraphy
40. Which of the following projections could be used to replace the MLO in patients where the MLO is not possible?
(A) ML
(B) LM
(C) RL
(D) AT
41. Which of the following does not describe mammography filtration?
(A) It shapes the emerging beam by absorbing low-energy x-rays that would only be absorbed by the superficial tissue and contribute to patient dose.
(B) It will affect the HVL of the emerging x-ray beam.
(C) Filtration makes the emerging beam compatible with the breast characteristics.
(D) The filtration used in mammography imaging is never aluminum.
42. The best time for a woman to perform a BSE is
(A) before the start of menstruation
(B) immediately, at the start of menstruation
(C) within 5-10 days after the start of menstruation
(D) anytime
43. Evaluations such as the mammography equipment evaluation (MEE) is performed by the
(A) radiologic assistant
(B) mammographer
(C) medical physicist
(D) radiologist
44. The test pattern used to measure the resolution of a digital system
(A) SNR
(B) SMPTE
(C) CNR
(D) MTF
45. Which of the following tests are performed monthly?
(A) phantom images
(B) repeat/reject analysis
(C) compression check
(D) visual checklist
46. On a reject/repeat analysis, the rate was lower than 5% but one category of the reject/repeat analysis is significantly higher than others. What should be done?
(A) Although the rate is below 5%, that one area should be targeted for improvement.
(B) If the other categories are within normal limits, that area can be disregarded.
(C) Because the rate was more than 2%, the entire department needs to be reassessed.
(D) With an overall rate lower than 5%, one high rate is statistically meaningless.
47. Typically, grid ratios in mammography range from
(A) 7:1 to 8:1
(B) 6:1 to 7:1
(C) 4:1 to 6:1
(D) 3:1 to 5:1
48. Positron emission tomography/mammography (PET or PEM) imaging is useful in staging tumors because
(A) the positron emitting isotopes are radioactive
(B) PET or PEM imaging can display the extent and location of the tumor
(C) the positron emitting isotopes will destroy the tumor bed
(D) PET or PEM imaging tracks the increased blood flow from the cancerous tumor
49. Medical history is important in
(A) assessing risk factors for breast cancer
(B) preventing breast cancer
(C) evaluating treatment options
(D) more than 1 of the above
50. Unlike general radiography x-ray tubes, some mammography tubes are tilted 6-24 degrees from the horizontal. The effect of this is to
(A) allow the use of smaller focal-spot size
(B) minimize the heel effect
(C) increase resolution
(D) all of the above
51. The retromammary space describes the area
(A) between the breast and pectoral muscle
(B) separating the skin of the breast from the deep fascia
(C) separating the skin from the superficial fascia
(D) between the glandular tissue and the inframammary fold
52. In which of the following are breast cysts least common?
(A) young women in their early 20s
(B) premenopausal woman
(C) postmenopausal woman on estrogen therapy
(D) women aged 70
53. The CC shows a circumscribed oval radiolucent lesion. There was a definite halo surrounding the lesion. It is most likely to be a
(A) fibroadenoma
(B) galactocele
(C) cyst
(D) hematoma
54. The indirect effect of breast compression on Compton interaction is
(A) The absolute number of Compton interactions increases.
(B) The absolute number of Compton interactions decreases.
(C) Compression has no affect on Compton interactions.
(D) Compression affects Compton interaction only above 70 kVp.
55. Visual inspection done during CBE involves
(A) feeling for changes in the breast
(B) looking for changes in the breast
(C) palpating the breast
(D) examining areas under the armpit
56. Grids with strips that are linear, but slanted to match the divergence of the x-ray beam are _____ grids.
(A) parallel
(B) crossed
(C) focused
(D) moving
57. Fatty tissue is generally radiolucent and will show on the mammogram as
(A) glandular areas
(B) high-optical density areas
(C) low-optical density areas
(D) white or gray areas
58. The mammogram of a woman age 50 who has recently started estrogen replacement therapy is likely to show a breast that is
(A) more fibroglandular than her past mammographic study
(B) more fatty than her previous mammogram
(C) less fibrous and less glandular than her previous studies
(D) unchanged from her previous mammograms
59. The mammogram shows an oval-shaped lesion with mixed density. The lesion has a central radiolucent area and is freely movable. This lesion is most likely to be a
(A) fibroadenoma
(B) hematoma
(C) lymph node
(D) galactocele
60. The method of locating the lymph node/s through which cancer is leaving the breast is called
(A) scintigraphy
(B) PEM imaging
(C) MRI
(D) lymphoscintigraphy
61. The change in OID could cause loss of image detail in magnification mammography. What factor/s helps to compensate for this loss of image detail?
(A) decreased OID and breast compression
(B) increased focal-spot size and breast compression
(C) decreased focal-spot size and compression of the part
(D) increased OID and compression of the part
62. What does the actual focal-spot size measure?
(A) the area on the anode exposed to electrons
(B) the area projected on the patient
(C) the area projected on the detector
(D) the nominal focal-spot size
63. The mammography report has an assessment finding of breast imaging reporting and data system (BIRAD) 0. This means that
(A) the mammogram is negative
(B) there is a high probability of a benign finding
(C) additional imaging is needed
(D) the findings are suspicious
64. Differentiate between repeat and reject images.
(A) Repeat is the percentage of repeats from a specific cause. Reject is the percentage of repeats from multiple causes.
(B) Rejects are all images that are discarded. Repeat are images that resulted in extra radiation dose to the patient.
(C) Repeats are all images that are discarded. Rejects are images that resulted in extra radiation dose to the patient.
(D) Rejects are images discarded after any QC testing. Repeats are any images thrown out.
65. What is epithelial hyperplasia?
(A) a calcified hematoma resulting from trauma
(B) an oil cyst within the breast
(C) an overgrowth of cells in the ducts or lobules
(D) an epidermoid cyst on the skin of the breast
66. Figure 6-2 shows a (an)
(A) ruptured implant
(B) encapsulated implant
(C) herniated implant
(D) implant removal
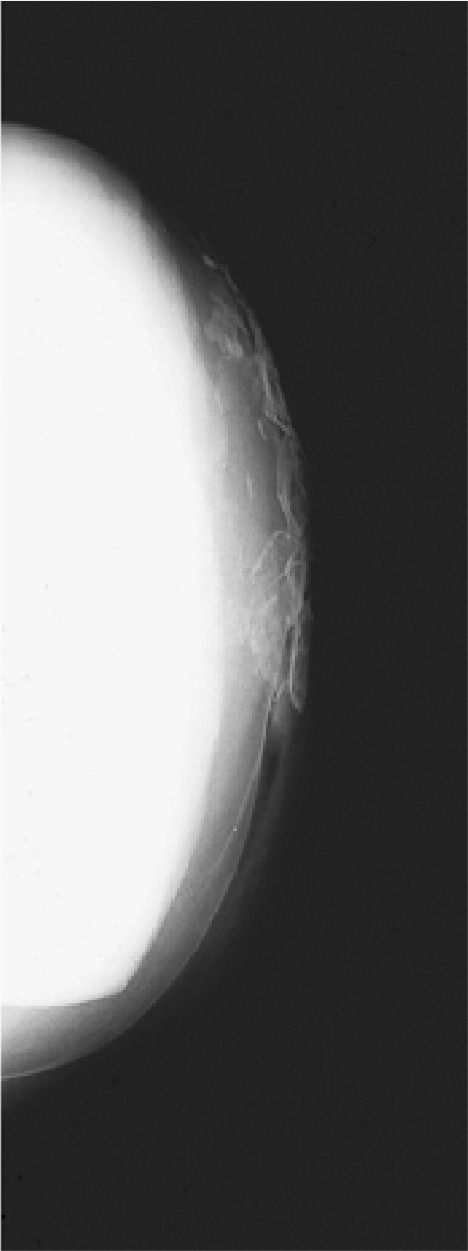
Figure 6-2. (Reproduced with permission from Peart O: Lange Q&A: Mammography Examination, 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2008.)
67. After a 4-projection mammogram, calcifications are visualized superior to the nipple but only on the MLO projection. What additional projection would best be used to locate the position of the lesion?
(A) exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL)
(B) cleavage (CV)
(C) ML
(D) AT
68. Approximately how much contrast agent is injected into the breast during ductography?
(A) approximately 1 cc
(B) 15-25 cc
(C) 30-40 cc
(D) approximately 50 cc
69. What does the glandular dose measure?
(A) the average dose to the patient’s skin
(B) the absorbed dose to the skin
(C) the absorbed dose at the tissue level
(D) the same as the entrance skin dose
70. Which of the following relationships does not change when moving from routine to magnification mammography?
(A) OID
(B) focal spot size
(C) SID
(D) SOD
71. Who performs the compression device check for mammography QC?
(A) physicist
(B) any staff technologist
(C) radiologist
(D) mammographer
72. A galactocele is
(A) a lesion associated with trauma to the breast
(B) a benign milk-filled cyst
(C) associated with eggshell-like calcification
(D) associated with a central radiolucent hilus
73. Instead of using a grid, what does magnification mammography use to reduce scatter during normal imaging?
(A) lead shielding
(B) increased OID
(C) a low milliamperes (mAs) technique
(D) increased SID
74. Most of the glandular tissue is arranged in the breast around the
(A) medial and upper-inner quadrants
(B) lateral and lower inner quadrants
(C) central and upper-outer quadrants
(D) medial and upper-outer quadrants
75. A beryllium (Be) window on the x-ray tube enhances contrast by
(A) increasing the output of the x-ray tube
(B) reducing production of scattered radiation
(C) transmitting more low-energy photons
(D) transmitting more high-energy photons
76. Proper compression of the breast is indicated when the
(A) patient is in pain
(B) compression paddle stops
(C) breast is taut
(D) breast feels soft
77. Which factors cause increased skin dose in magnification?
(A) larger OID and smaller focal spot size
(B) increased mA and larger SOD
(C) increased OID and decreased SOD
(D) smaller OID and larger SID
78. In radiology, according to the line-focus principle, the effective focal spot is
(A) larger than the actual focal spot
(B) smaller than the actual focal spot
(C) the same as the actual focal spot
(D) decreased as the target angle increases
79. Figures 6-3A and 6-3B are mammograms of the same patient. Figure 6-3B was taken 6 months after Figure 6-3A. These mammograms have the characteristic appearance of a
(A) resolving oil cyst
(B) galactocele
(C) resolving postsurgical scar
(D) hematoma
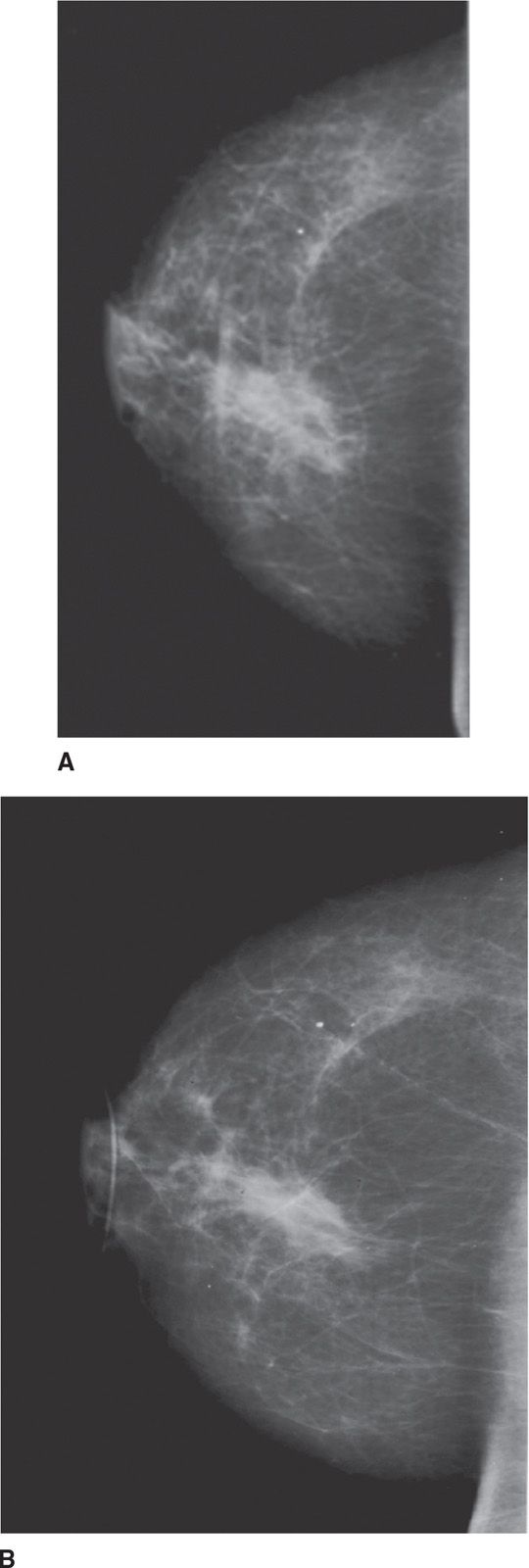
Figure 6-3. (Reproduced with permission from Peart O: Lange Q&A: Mammography Examination, 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2008.)
80. When using the air-gap technique in magnification mammography what additional step is necessary?
(A) grid use
(B) decrease SID
(C) increase OID
(D) increase SID
81. Which of the following projections would best separate superimposed 12-o’clock and 6-o’clock masses?
(A) MLO
(B) XCCL
(C) CC
(D) AT
82. In positioning terminology, CV means
(A) compressed position
(B) cranial view
(C) cleavage view
(D) compression view
83. Malignant casting-type calcifications can appear on the mammogram as
(A) granulated sugar or crushed stone calcifications
(B) eggshell-like calcifications
(C) elongated, branching, and needle-like calcifications
(D) fragmented, linear branching calcifications
84. The functional milk-producing units of the breast are contained within the
(A) lactiferous sinuses
(B) lobules
(C) ampulla
(D) areola
85. What is the grid ratio?
(A) the height of the lead strips divided by the distance between each strip
(B) the height of the lead strips multiplied by the distance between each strip
(C) twice the height of each lead strip
(D) the distance between each strip divided by the height
86. The AT projection best demonstrates the
(A) subareolar area
(B) medial aspect of the breast
(C) axillary aspect of the breast
(D) lower-inner quadrant of the breast
87. The lesion seen on Figure 6-4 has the characteristic appearance of a/an
(A) oil cyst
(B) stellate lesion
(C) galactocele, calcified
(D) fibroadenoma
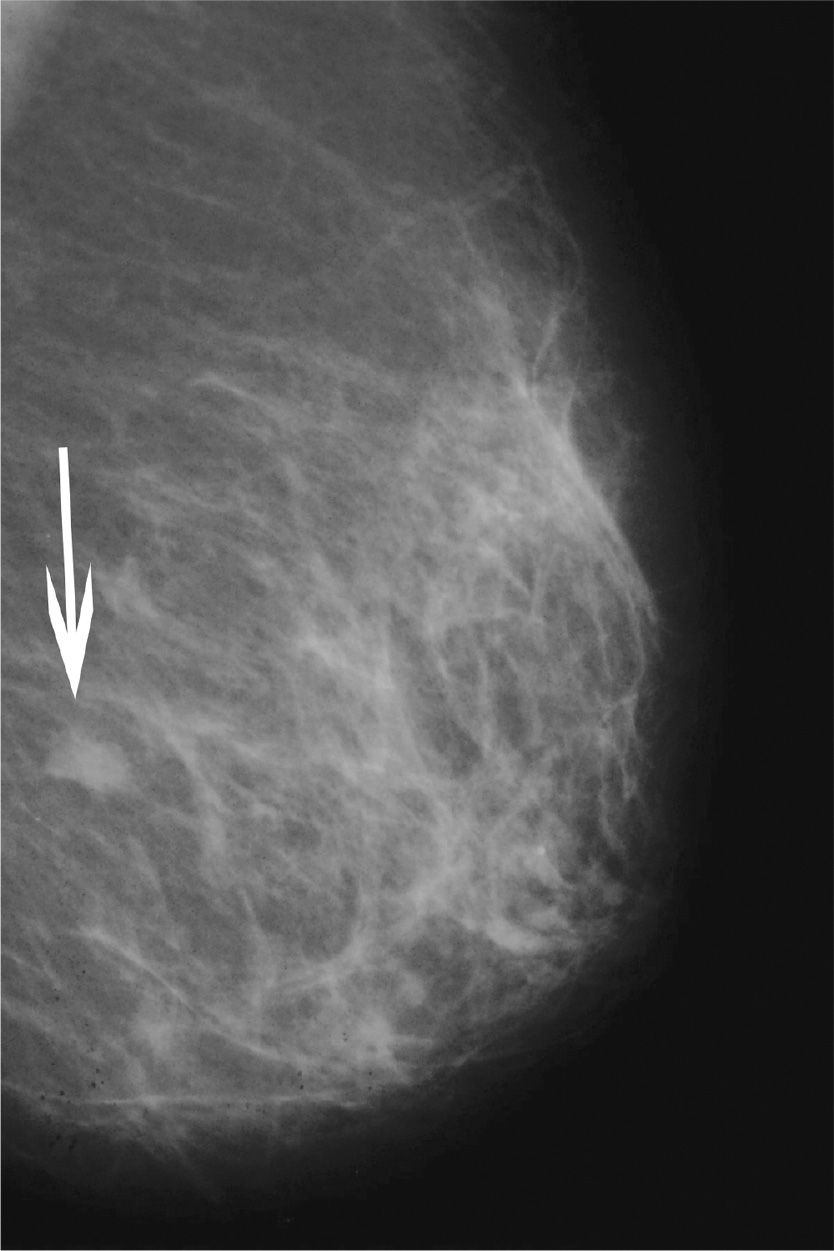
Figure 6-4.
88. The patient had trauma to the breast 1 month ago and has developed a lump. Such an injury may show mammographically as a
(A) galactocele
(B) hematoma
(C) lymph node
(D) fibroadenoma
89. A device used to convert light to a digital signal is a/an
(A) film digitizer
(B) DICOM
(C) ADC
(D) DAC
90. If too much upper axilla and shoulder are under the compression paddle when imaging for the MLO, the effect is to
(A) inhibit proper compression of the upper breast
(B) inhibit proper compression of the lower breast
(C) ensure equal compression of the upper and lower breast
(D) ensure proper compression of the lower breast
91. Which of the following types of breast imaging methods will fall under the category of nuclear imaging?
(A) PEM
(B) MRI
(C) ultrasound
(D) digital tomosynthesis
92. The area of low optical density in the upper part of Figure 6-5 best represents
(A) a pacemaker
(B) the patient’s chin
(C) a hematoma
(D) port-a-cath
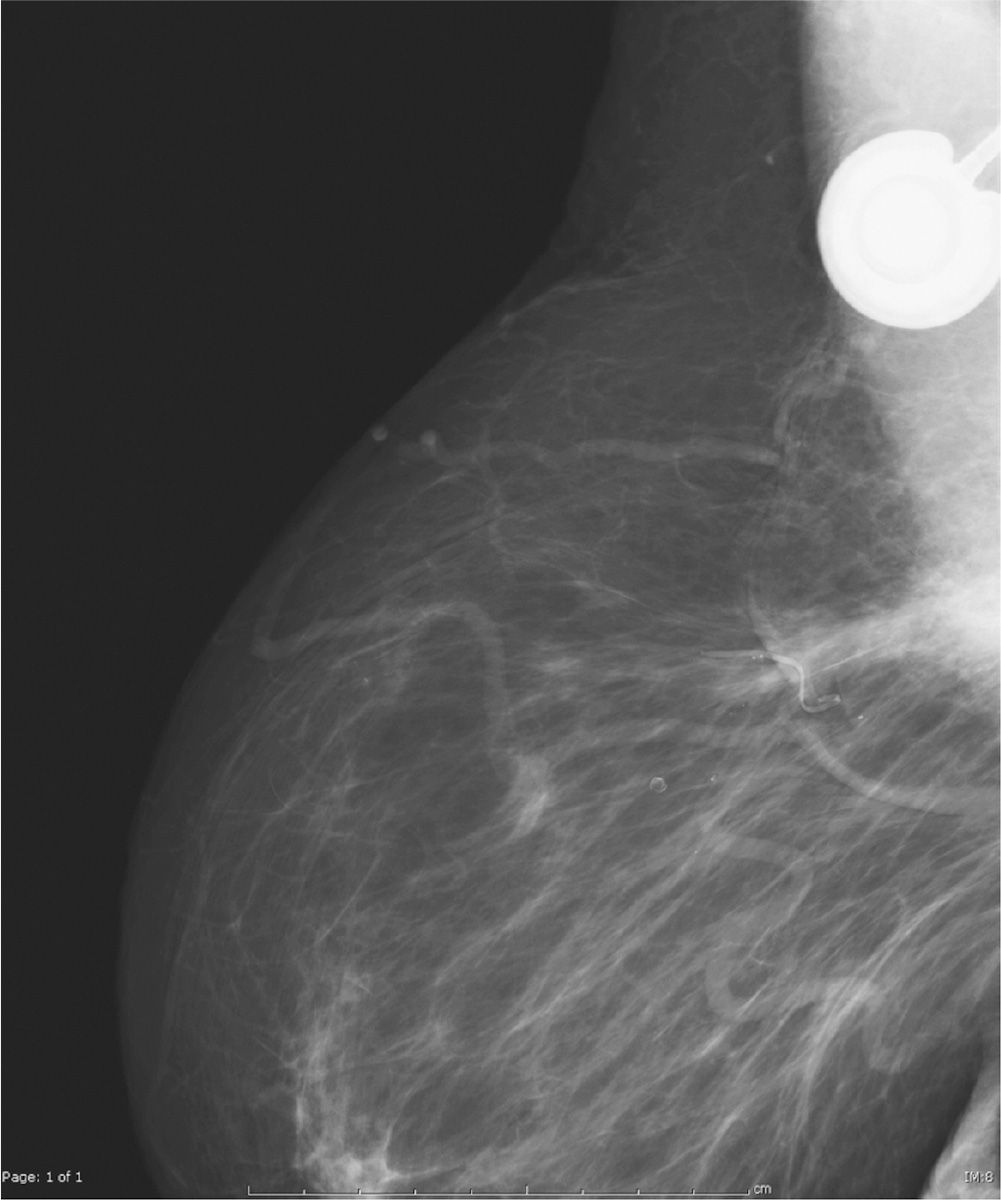
Figure 6-5. (Reproduced with permission from Peart O: Lange Q&A: Mammography Examination, 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2008.)
93. A rolled projection can be performed to
(A) separate superimposed tissues
(B) identify microcalcifications
(C) localize a skin lesion
(D) determine the location of a finding seen only on 1 of the standard projection
94. Ideally, in an open surgical biopsy, when should a breast tissue specimen be imaged?
(A) immediately after surgery
(B) within 24 hours of the surgery
(C) just prior to the surgery
(D) after the lesion is removed but before the surgical site is closed
95. Which projection gives a mirror image of the MLO?
(A) ML
(B) LM
(C) LMO
(D) AT
96. The nominal focal spot size of the mammography unit is 0.3. This means that the
(A) actual focal spot size is 0.3
(B) effective focal spot size is 0.3
(C) both effective and actual focal spot size is 0.3
(D) actual focal spot is smaller than 0.3
97. Women with postlumpectomy could have magnified images taken of the tumor bed to
(A) confirm the removal of the cancer
(B) check calcium deposits that may result from radiation and surgical changes
(C) all of the above
(D) none of the above
98. Figure 6-6 shows a routine screening mammogram, CC projection. What projection could best image the missed area?
(A) XCCL
(B) CV
(C) ML
(D) AT
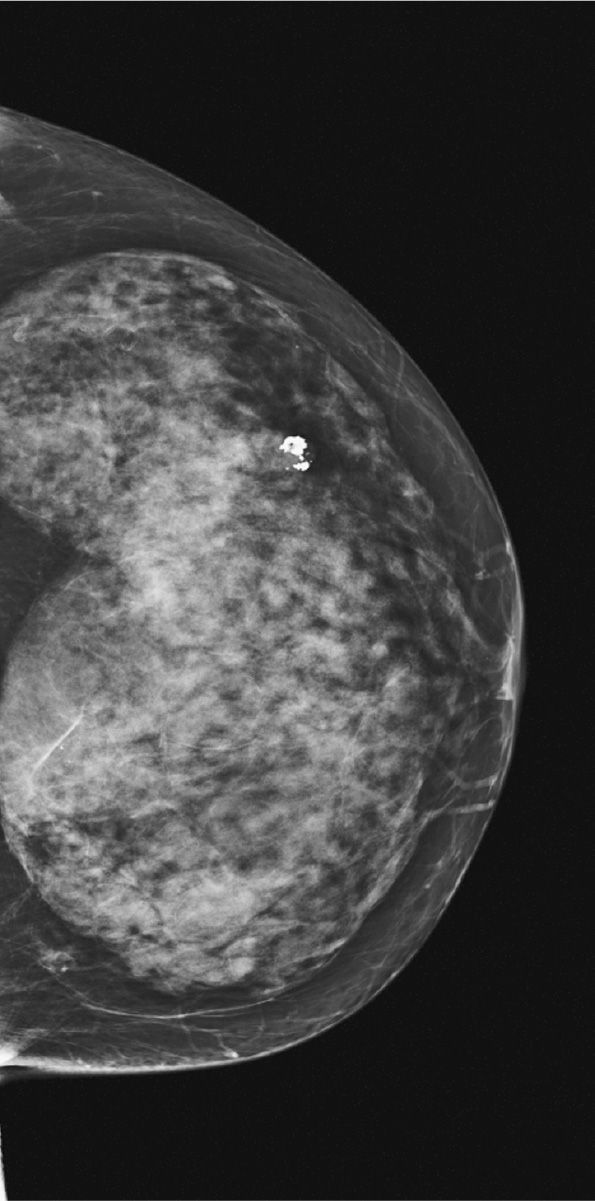
Figure 6-6.
99. Where is the grid placed?
(A) above the breast
(B) between the breast and the image plate or detector
(C) below the image plate
(D) between the breast and the x-ray tube
100. All of the following statements are unique to the PSP, CM systems and are not present in flat panel detector FFDM systems except
(A) IP can be damaged or dropped during transport
(B) the system has a wide latitude and dynamic range
(C) low exposure can create a noisy image
(D) the imaging system is susceptible to scratches
101. The purpose of the mammography certification and accreditation process is to
(A) provide legal mammography services
(B) enforce minimum national quality standards for mammography
(C) ensure that all women have access to a certified mammography facility
(D) authorize certain states to certify mammography facilities and conduct inspections
102. A facility has a sign posted advising patients to contact a designated person within the organization with comments. This facility is meeting the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)’s
(A) medical outcome audit program
(B) record-keeping program
(C) patient communication of results program
(D) customer complaint program
103. A hamartoma is
(A) a malignant tumor of the breast
(B) a benign tumor of the breast
(C) associated with trauma of the breast
(D) associated with nursing
104. During lactation the contraction of which cells help to eject milk from the alveoli?
(A) epithelial cells
(B) myoepithelial cells
(C) basement cells
(D) superficial cells
105. A finding of BIRAD 2 on the mammogram means that the mammogram
(A) cannot accurately evaluate the breast
(B) showed benign findings
(C) showed suspicious findings
(D) is suggestive for malignancy
106. Erythema of the breast is an indication
(A) of inflammatory breast cancer
(B) of a breast abscess
(C) of a breast infection
(D) that further testing of the breast is necessary
107. Which of the following is used as a treatment for estrogen-dependent tumors in postmenopausal and premenopausal women?
(A) radiation therapy
(B) chemotherapy
(C) Tamoxifen
(D) antibody therapy
108. In flat-panel detector systems, the spatial resolution of the system is controlled by the
(A) pixel number
(B) DEL size
(C) matrix size
(D) TFT number
109. A thin supportive layer located between the basal surface of the epithelium and the connective tissue layer of the lobule is called
(A) chief cells
(B) myoepithelial
(C) basement membrane
(D) superficial A cells
110. A “camel’s nose” breast contour can be prevented in the MLO projection by
(A) including all of the breast under the compression paddle
(B) angling the detector parallel to the pectoralis muscle
(C) properly supporting the anterior breast during compression
(D) ensuring that the nipple remains in profile during compression
111. The superoinferior oblique (SIO) will best demonstrate the
(A) OUQ and the LOQ of the breast
(B) LIQ and the UIQ of the breast
(C) UIQ and LOQ of the breast
(D) LIQ and the OUQ of the breast
112. The basic premise of a medical audit is that
1. all positive mammograms should be followed
2. the pathology results of all biopsies performed should be collected
3. all pathology results should be correlated with the radiologist’s findings
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
113. Under the MQSA, how long are facilities required to maintain the records of a patient who died shortly after her first mammogram?
(A) 5 years
(B) 10 years
(C) 20 years
(D) permanently
114. Under which of the following circumstances would the triangulation technique be necessary?
(A) to locate an abnormality visualized on 1 projection only
(B) during routine mammography screening
(C) when performing spot magnification
(D) to locate a palpable lesion
115. A dimpled skin condition seen in cases of lymphatic edema of the breast is called
(A) inflammatory carcinoma
(B) ductal ectasia
(C) plasma cell mastitis
(D) peau d’orange
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree