CHAPTER 7 ![]()
Practice Test 2
Questions
1. A clinical breast examination (CBE) and breast self-examination (BSE) are similar in that both
(A) involve looking and feeling for changes in the breast
(B) are done by a trained medical professional
(C) are done monthly
(D) are done yearly
2. The most common cause of undercompression is
(A) a faulty compression paddle
(B) inadequate compression by the mammographer
(C) patient pain tolerance level
(D) broken automatic compression device
3. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 affects radiology and other hospital departments by its focus on
(A) patient record confidentiality
(B) facility reimbursement
(C) quality management
(D) risk management
4. Ductal papilloma is
(A) a benign proliferation of tissue in the male breast
(B) a malignant tumor involving the ducts
(C) a collection of blood in the breast, which can occur after surgery
(D) benign growths involving the milk ducts
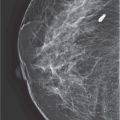
5. The right craniocaudal (RCC) of the routine imaging series showed a small, irregular-shaped lesion at posterior margin of the image plus scattered calcifications including calcification clusters (Figure 7-1). Typically, the radiologist will recommend _______ as the next immediate step.
(A) ultrasound to assess the content of the lesion and provide an analysis of the calcifications
(B) spot compression including magnification to assess calcifications and the margins of the lesion
(C) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess for malignancy and to assess any calcifications
(D) a breast biopsy to check for malignancy
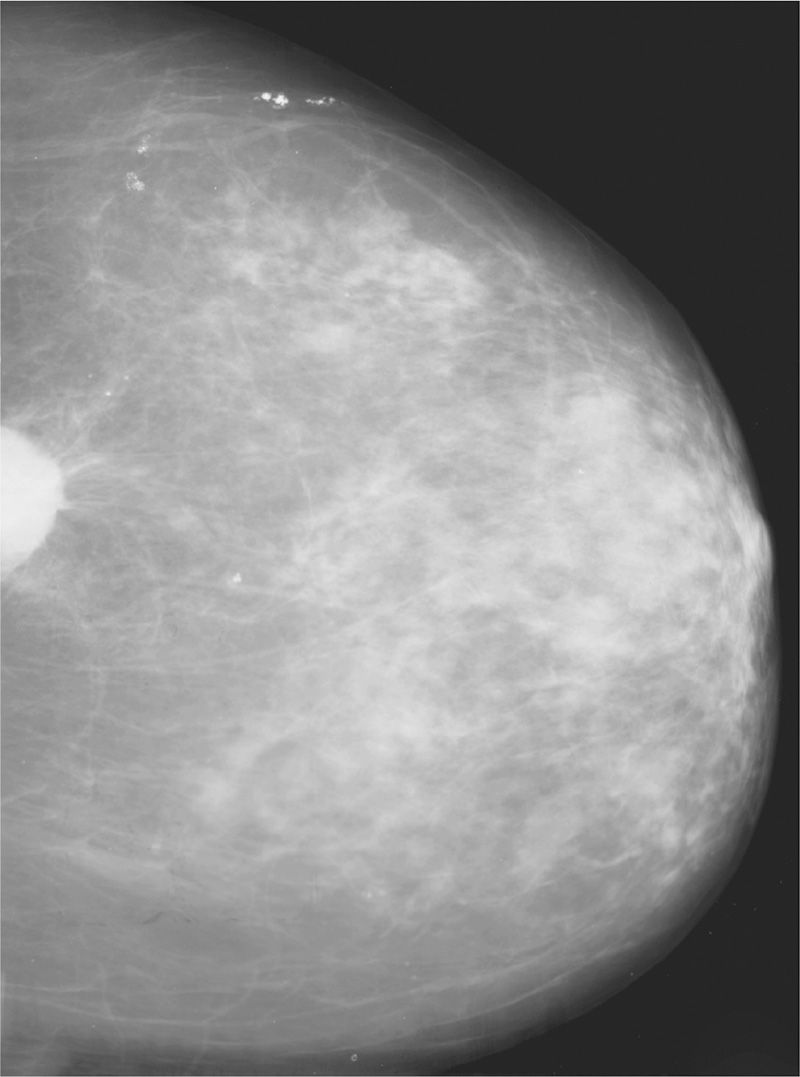
Figure 7-1.
6. A bunch of 8 bits equals 1
(A) pixel
(B) byte
(C) matrix
(D) bit depth
7. Which of the following could be used when imaging extremely small breasts in the craniocaudal (CC) position?
(A) spatula
(B) mediolateral (ML)
(C) cleavage view (CV)
(D) exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL)
8. In the tangential (TAN) projection, any tube angulation will depend on
(A) the size of the patient’s breast
(B) the location of the abnormality
(C) the position of the midaxillary line in relation to the detector
(D) whether the abnormality is palpable or nonpalpable
9. A small but growing cancer may not be obvious to the individual because it often presents as
(A) skin irritation
(B) inverted nipples
(C) a painless mass
(D) a painful mass
10. Mammography is more accurate in
(A) premenopausal women
(B) postmenopausal women
(C) women with fibrocystic breast
(D) women with dense breast tissue
11. In taking medical history, hormone use (both natural and artificial) are taken into account because
(A) hormones cause breast cancer
(B) early menarche can increase breast cancer risks
(C) late menarche can increase breast cancer risks
(D) contraceptive use lower the risks for breast cancer
12. One major difference between collimation in mammography and collimation in general radiography is that
(A) in mammography the entire detector area is exposed
(B) decreasing collimation increases exposure in mammography
(C) mammography uses a variety of beam-limiting devices
(D) in radiography the entire detector area is always exposed
13. Line pair per millimeter is the unit of
(A) matrix size
(B) spatial resolution
(C) field-of-view (FOV)
(D) bit depth
14. Image brightness is adjusted changing by changing the
(A) milliamperes (mAs)
(B) peak kilovoltage (kVp)
(C) window level
(D) window width
15. The retromammary space is filled with
(A) supportive and connecting tissue
(B) adipose tissue
(C) fibroglandular tissue
(D) blood vessels
16. The fatty versus fibroglandular nature of breast tissue is affected by which of the following?
(A) age
(B) hormone use
(C) number of pregnancies
(D) all of the above
17. In positioning for the exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL) projection, if the shoulder of the affected side is in the way of the compression device
(A) push the shoulder down
(B) a 5-degree lateral tube angulation can be utilized
(C) use 5-degree medial tube angulation to avoid superposing the shoulder on breast tissue
(D) reduce the patient’s lateral rotation
18. In the craniocaudal (CC) position the pectoral muscle is seen
(A) all the time
(B) rarely if ever
(C) about 30%-40% of the time
(D) about 50% of the time
19. Between ages 20 and 39, a woman should have a clinical breast examination (CBE) every
(A) year
(B) 2 years
(C) 3 years
(D) 4 years
20. The lesion seen in Figure 7-2 is not palpable and is not associated with nipple or skin changes. It has the characteristics of a/an
(A) invasive ductal breast carcinoma
(B) mammographically malignant tumor
(C) mammographically benign tumor
(D) nonspecific lesion; further testing is indicated
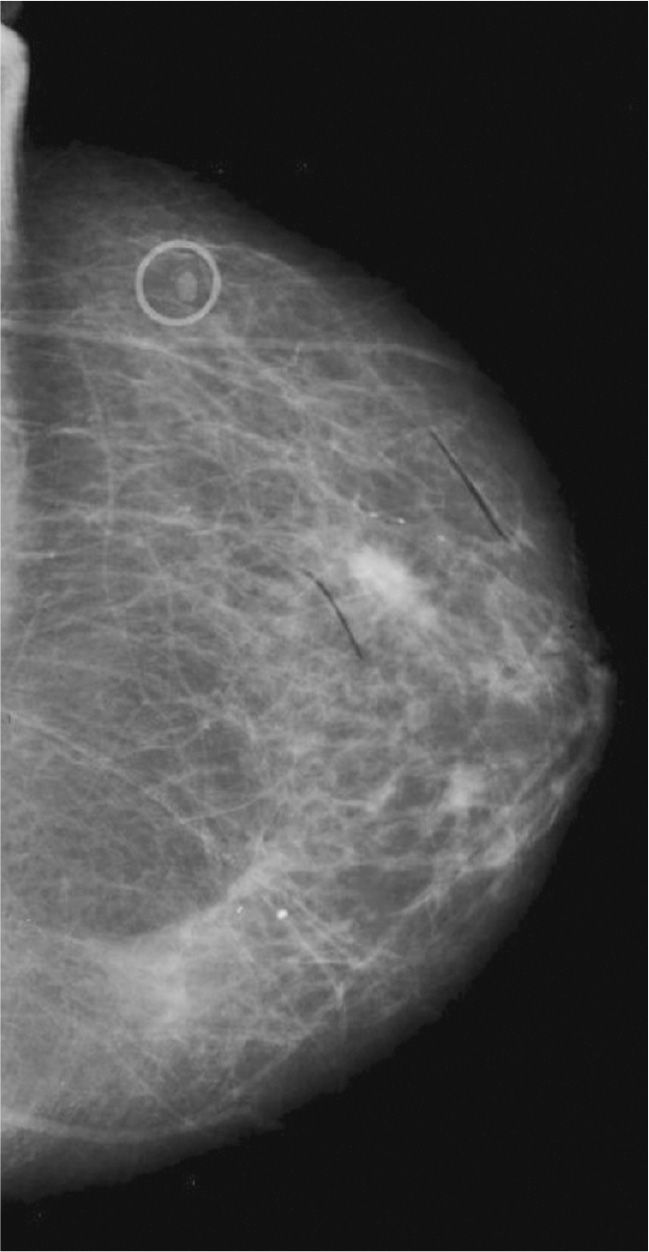
Figure 7-2.
21. Regardless of the reason, if the proper amount of compression cannot be applied which of the following must apply?
(A) The patient must be told.
(B) The patient’s doctor must be told.
(C) The radiologist must be told.
(D) It must be noted on the patient’s history form.
22. On the craniocaudal (CC) image the posterior nipple line (PNL) line should extend to the
(A) level of the nipple
(B) posterior breast or edge of the image
(C) level of the inframammary crease
(D) most anterior breast
23. The interspace material of the mammography linear grid is generally made of
(A) carbon or wood
(B) aluminum
(C) any high radiopaque material
(D) lead
24. Which section of the breast is poorly visualized on the craniocaudal (CC) projection?
(A) medial
(B) axial
(C) lateral
(D) superior
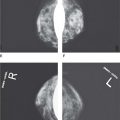
25. Figure 7-3 shows a radiograph of the left mediolateral oblique (LMLO). Why should this radiograph be repeated? The patient and mammographer’s identification plus the projection has been removed to avoid Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) violations.
(A) The pectoral muscle should be concave anteriorly.
(B) The pectoral muscle should be convex anteriorly.
(C) The inframammary fold is closed.
(D) The posterior breast tissue is missing.
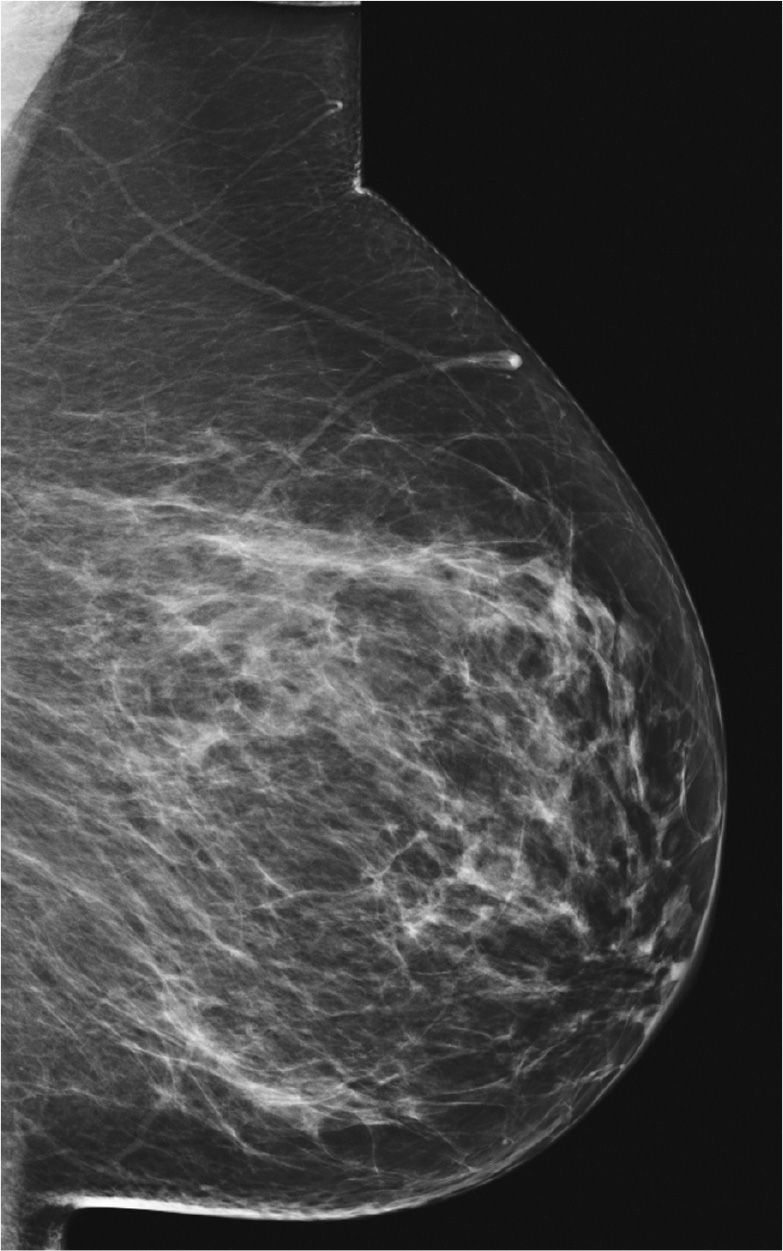
Figure 7-3.
26. Increasing the image contrast is achieved by
(A) increasing window level
(B) decreasing window level
(C) increasing window width
(D) decreasing window width
27. Which projection could be used to demonstrate a deep medial lesion not seen on the craniocaudal (CC)?
(A) axillary tail (AT)
(B) exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL)
(C) cleavage view (CV)
(D) mediolateral oblique (MLO)
28. After a routine 4-projection mammographic series, the nipple is not seen in profile on any of the images. Additional projections are done if
1. the nipple is indistinguishable from a mass
2. a subareolar abnormality is suspected
3. the nipple is not marked with a BB (lead shot)
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
29. On the radiograph, Figure 7-4, the arrow indicates
(A) a malignant lesion
(B) glandular tissue
(C) muscle
(D) fatty tissue
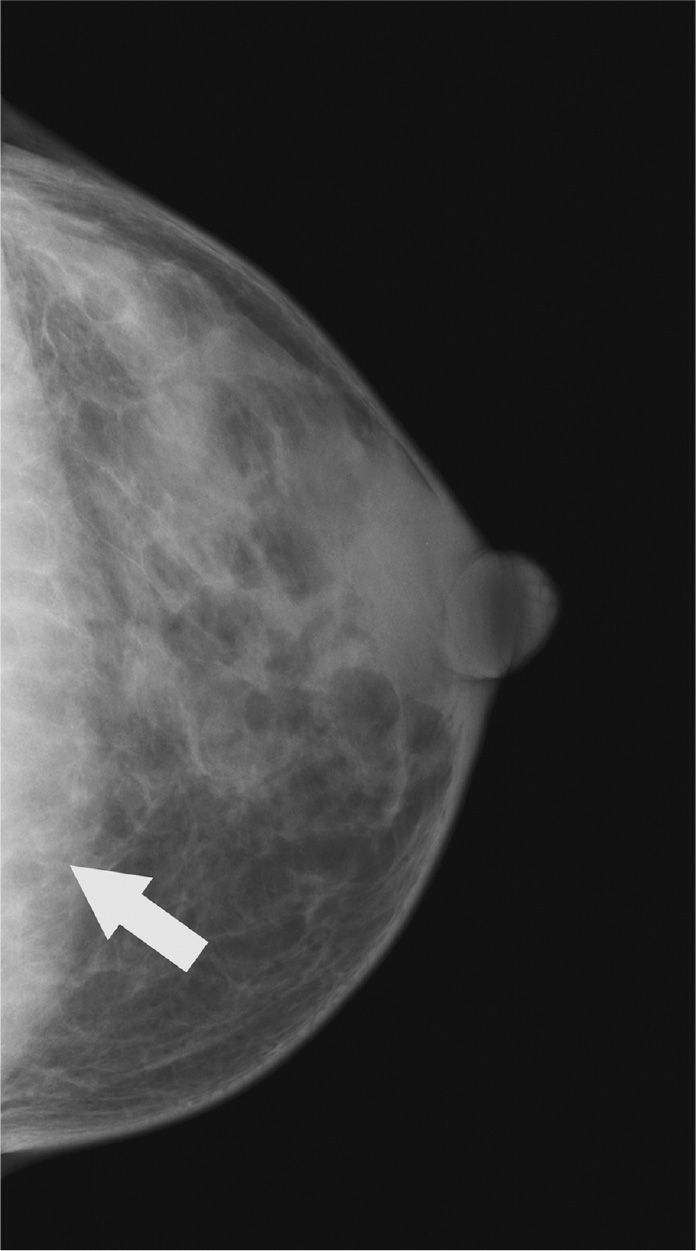
Figure 7-4.
30. Your patient’s sister was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 35. Your patient is considered to have
(A) a greater risk for breast cancer
(B) a lower risk for breast cancer
(C) no significantly increased risk for breast cancer
(D) a personal history of breast cancer
31. The Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) mandates that the average glandular dose received per projection/position during routine mammography screening should not exceed
(A) 1 mGy (100 mrad)
(B) 2 mGy (200 mrad)
(C) 3 mGy (300 mrad)
(D) 4 mGy (400 mrad)
32. The device used to convert films in an analog imaging system to a digital version is called
(A) film digitizer
(B) Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM)
(C) analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
(D) digital-to-analog converter (DAC)
33. The computer network that allows images to be viewed at various monitors or transmitted or stored is termed
(A) local area network (LAN)
(B) picture archiving and communications system (PACS)
(C) Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM)
(D) wide area network (WAN)
34. Which of the following statement on heath-care records is false?
(A) Health records must include all signed informed consent forms.
(B) Patients have a right to amend their health-care records.
(C) Patients can access their health records.
(D) Health-care records cannot be used in a court of law.
35. Montgomery glands are specialized
(A) sweat glands
(B) sebaceous gland
(C) Cooper ligaments
(D) hair follicles
36. A woman taking estrogen replacement therapy may notice changes in the breast such as
(A) breast enlargement
(B) increase in fibroadenomas
(C) increase in breast cysts
(D) all of the above
37. Paget disease of the breast is a (an)
(A) infiltrating carcinoma generally limited to the breast
(B) form of carcinoma associated with changes of the nipple
(C) benign breast condition that is relatively common
(D) malignant form of breast carcinoma involving the lobules
38. In a digital image what determines the matrix size?
(A) the number of bit in each pixel
(B) the number of pixels in the rows and columns
(C) the picture element in the matrix
(D) the number of gray shades that a pixel can produce
39. A set of computer software standards that permits a wide range of digital imaging programs to understand each other
(A) DIGCOM
(B) PACS
(C) DICOM
(D) PCAS
40. Picture archiving and communications system (PACS) network typically would include
(A) digital images from multiple modalities
(B) images from a single modality only
(C) all patients’ records
(D) surgical and radiography patient records
41. Women who were exposed to diethylstilbestrol (DES) in utero may have
(A) a lower risk for breast cancer
(B) a higher breast cancer risk if they also take HRT
(C) a lower risk for breast cancer if they also take HRT
(D) breast tissue that is extra sensitive to radiation
42. In which of the following modified projections is the superior surface of the breast rolled medially?
(A) medial roll (RM)
(B) lateral roll (RL)
(C) medial (M)
(D) lateromedial (LM)
43. Factors that lower breast cancer risk include
1. having your first child after age 30
2. breast-feeding your child
3. late menarche
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
44. PACS stands for
(A) picture access to communication system
(B) picture archiving and computer systems
(C) picture archiving and communication system
(D) pixel access and computer systems
45. The computer processing or photostimulable phosphor (PSP) reader functions to
(A) focus a beam of infrared light on the PSP
(B) trap excited electrons at a higher energy level
(C) scan, read, and erase the exposed PSP
(D) provide energy to the trapped electrons
46. Gynecomastia defines
(A) a localized abscess
(B) increased breast tissue in the male breast
(C) decreased breast tissue in the female breast
(D) a risk of carcinoma for the male patient
47. Photostimulable luminescence (PSL) is
(A) emission of bluish-purple light from electrons as they transition from higher energy to a lower energy state
(B) conversion of light energy to an electrical signal by the photomultiplier tube (PMT)
(C) conversion the analog signal to a digital signal by the analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
(D) conversion light into an analog signal by the charge-coupled device (CCD)
48. According to Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) regulations, which of the following is not required on the final mammographic image?
(A) date of the examination
(B) technical factors used
(C) mammographer/technologist identification
(D) projection identification
49. The inframammary crease is located at approximately the level of the
(A) second to third rib
(B) third to fourth rib
(C) fourth to fifth rib
(D) sixth to seventh rib
50. Identify Cooper ligament in Figure 7-5.
(A) site A
(B) site B
(C) site C
(D) site D
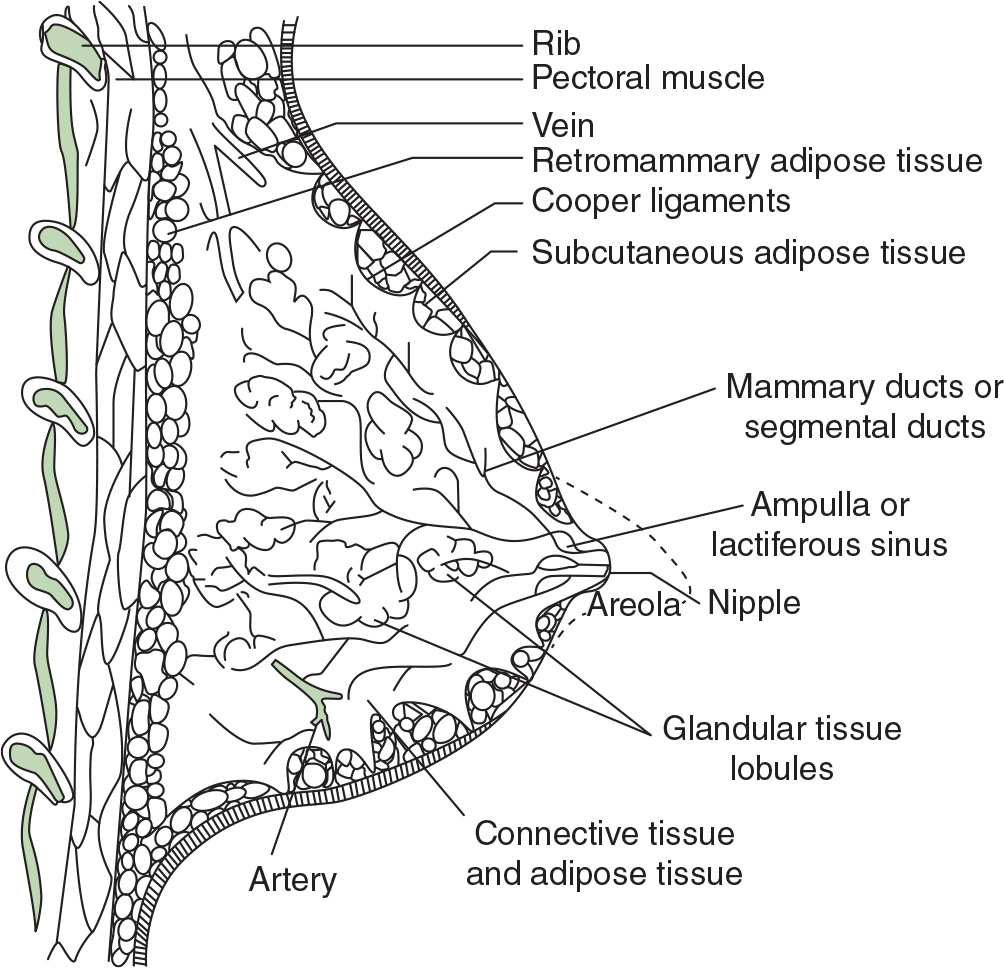
Figure 7-5. (Reproduced with permission from Peart O: Lange Q&A: Mammography Examination, 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2008.)
51. Identify the lactiferous sinus in Figure 7-5.
(A) site A
(B) site B
(C) site C
(D) site D
52. Scattered radiation is reduced during magnification mammography by
(A) using a small focal spot size
(B) using a grid
(C) using the air-gap technique
(D) increasing the source-to-image receptor distance (SID)
53. Ductography can be used to determine
(A) the location of the lesions in the ducts
(B) if a lesion is benign or malignant
(C) changes or abnormalities associated with the ducts
(D) more than 1 of the above
54. When imaging small breasts a useful option is
(A) replacing the craniocaudal (CC) with the exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL)
(B) using the mediolateral (ML) instead of the mediolateral oblique (MLO)
(C) using a spatula to avoid compressing fingers
(D) reducing the angulation to avoid compressing too much pectoral muscle
55. During magnification, positioning the breast away from the detector utilizes which law/principle in scatter reduction?
(A) inverse-square law
(B) reciprocity law
(C) heel effect
(D) line-focus principle
56. A woman who is nulliparous has a lower risk for breast cancer than a woman with
(A) late menopause
(B) late menarche
(C) a personal history of breast cancer
(D) early menarche
57. The primary purpose of the grid in mammography is to
(A) improve image sharpness
(B) reduce the production of scatter
(C) reduce patient dose
(D) increase the subject contrast
58. The implant-displaced (ID) projection is possible on all of the following cases except
(A) implants placed posterior to the pectoral muscle
(B) implants placed anterior to the pectoral muscle
(C) soft implants
(D) encapsulated implants
59. A palpable mass that is not seen on a diagnostic mammogram generally means
(A) breast cancer is ruled out; the mass is probably benign
(B) other diagnostic testing must be considered
(C) the mass is likely breast cancer
(D) the mass is likely caused by fluctuating hormones
60. Which of the following patients has the greatest risk for breast cancer?
(A) a nulliparous woman at age 40
(B) a never married woman
(C) a woman, age 70
(D) a woman, age 30
61. A mammographer using a 0.1-mm focal spot size is most likely performing
(A) routine mammography work
(B) magnification imaging
(C) spot compression imaging
(D) stereotactic work
62. Which of the following patients cannot give consent?
(A) minor who is married
(B) minor serving in the military
(C) competent adult
(D) mentally challenged adult
63. In the photostimulable phosphor (PSP) computer reader the photomultiplier tube
(A) collects the blue/purple light given off by the trapped electrons
(B) scans the PSP with a red laser light
(C) provides energy to the trapped electrons in the phosphor layer
(D) erases the PSP by releasing electrons
64. Which of the following statements is true when imaging the breast?
(A) Fold and or wrinkles should be eliminated by pushing the fold or wrinkle posteriorly.
(B) Skin folds or wrinkles may be impossible to avoid in the elderly.
(C) When imaging the elderly the study will always be compromised by a fold or wrinkle.
(D) Fold and or wrinkles can be eliminated by pulling the fold or wrinkle anteriorly.
65. The base of the breast refers to the
(A) the nipple area of the areola
(B) areas adjacent to the chest wall
(C) axilla area of the breast
(D) lower outer quadrant of the breast
66. Fibrous tissues are presented radiographically as
(A) black or radiolucent areas
(B) gray and less dense areas
(C) white or denser areas
(D) black and less dense areas
67. The calcifications in Figure 7-6 are characteristic of
(A) invasive ductal carcinoma
(B) mammographically malignant calcifications
(C) calcifications due to plasma cell mastitis
(D) numerous oil cysts
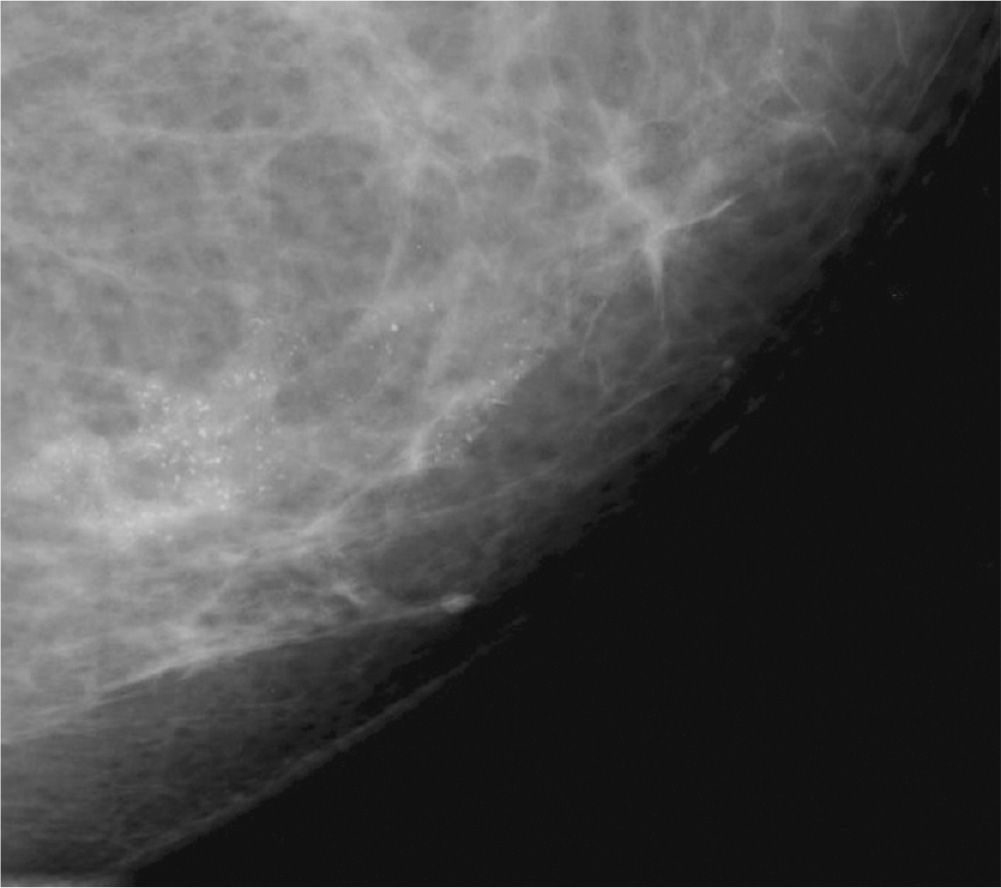
Figure 7-6.
68. The mediolateral oblique (MLO) projection demonstrates a large encapsulated lesion occupying almost the entire breast. The contour is sharp and the lesion is radiolucent. This lesion is most likely to be a (an)
(A) oil cyst
(B) hematoma
(C) fibroadenoma
(D) lipoma
69. The latent image on the photostimulable phosphor (PSP) can last several hours but will lose
(A) 50% of its energy in 4 hours
(B) 50% of its energy in 8 hours
(C) 25% of its energy in 4 hours
(D) 25% of its energy in 8 hours
70. Disadvantages of photostimulable phosphor (PSP) or computed mammography (CM) technology includes
(A) reduced repeats
(B) wide latitude and dynamic range of the system
(C) the PSPs sensitively to radiation
(D) speed of the imaging system
71. In the nonscintillator direct based flat-panel digital mammography (DM) system, the x-ray beam strikes a/an
(A) scintillator
(B) photoconductor
(C) thin-film transistor
(D) photomultiplier
72. Spot compression
1. applies more compression to a localized area
2. can be performed with magnification
3. employs a coned collimated field to limit the area of interest
(A) 1 only
(B) 1 and 2 only
(C) 2 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
73. Identify the minus density structure shown in the middle of the breast on Figure 7-7.
(A) closed inframammary fold
(B) skin fold
(C) pectoralis muscle
(D) vein
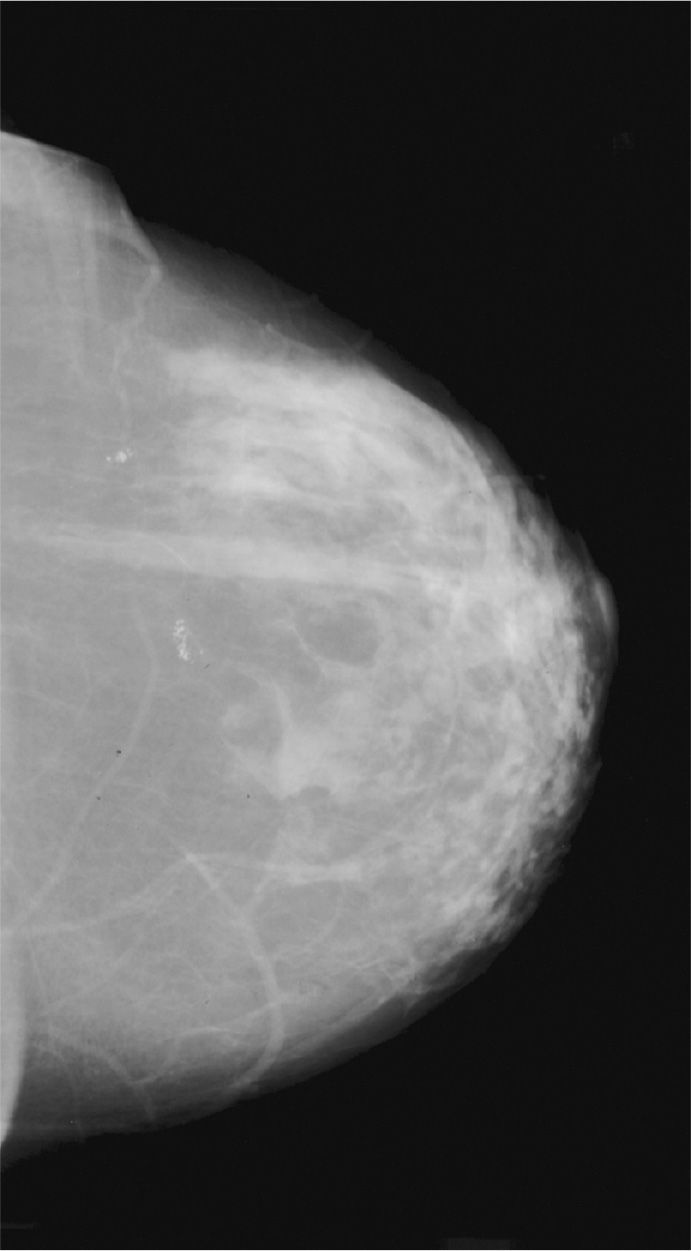
Figure 7-7.
74. To reduce the possibility of projecting the abdomen on the mediolateral oblique (MLO) image, the mammographer could
(A) have the patient stand just at the detector and bend back
(B) have the patient stand away from the detector and bend forward
(C) have the patient turn medially to image the lateral breast on the craniocaudal (CC)
(D) discard the MLO and image the breast in the lateral position instead
75. A 4-projection mammography series shows a solitary tumor, with the halo sign, in the upper-outer quadrant (UOQ) of the left breast. The lesion is partially obscured. The next recommended step is
(A) biopsy
(B) ultrasound
(C) stereotactic localization
(D) aspiration
76. Why is the specimen magnified?
(A) to ensure that the lesion has been completely removed
(B) to visualize the calcifications within the specimen
(C) to compare the magnified and nonmagnified images
(D) to check the number and placement of calcifications
77. In digital mammography, a grossly underexposed image
(A) appears excessively noisy
(B) is too light
(C) is too dark
(D) appears correctly exposed
78. Which of the following patients is likely to be diagnosed with pathological gynecomastia?
(A) lactating woman
(B) elderly man
(C) premenopausal woman
(D) young man
79. Montgomery glands are located on the breast’s
(A) skin
(B) nipple
(C) areola
(D) muscle
80. Aluminum can be used as the filtration material in
(A) digital units when imaging dense breast
(B) digital tomosynthesis units
(C) digital units when imaging fatty breast
(D) analog units with tungsten targets
81. Digital mammography units often use _____ as the target material.
(A) molybdenum
(B) rhodium
(C) aluminum
(D) tungsten
82. Over age 40, it is recommended that women have a clinical breast examination (CBE) every
(A) year
(B) 2 years
(C) 3 years
(D) 4 years
83. When imaging the breast using the craniocaudal (CC) projection, if the detector is too high or too low the inframammary fold (IMF) will be over or under elevated. Over elevation of the IMF will result in
(A) loss of posterior and superior breast tissue
(B) loss of anterior and posterior breast tissue
(C) loss of superior and posterior breast tissue
(D) loss of inferior and posterior breast tissue
84. Capture elements in the flat-panel detector system can include all of the following except
(A) photomultiplier
(B) cesium iodide
(C) gadolinium oxysulfide
(D) amorphous selenium
85. Which of the following involves the use of a small-gauge needle to remove cell samples from a suspected cancerous lesion in the breast for cytological analysis?
(A) core biopsy
(B) excisional biopsy
(C) needle localization
(D) fine-needle biopsy (FNB)
86. A lesion is superimposed by breast tissue in the craniocaudal (CC) projection. A projection/position used to demonstrate the lesion in the same orientation but free of superimposition is the
(A) mediolateral oblique (MLO)
(B) implant-displaced (ID)
(C) exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL)
(D) medial roll (RM)
87. In imaging the breast in the mediolateral oblique (MLO) projection, compression to the lower, anterior portion of the breast is compromised if
(A) the detector is too high
(B) the pectoral muscle extends to the nipple line
(C) too much axilla and shoulder are under compression
(D) the inframammary fold is not horizontal
88. Involution of the breast describes a process by which
(A) milk is removed from the breast by suckling
(B) breast epithelium proliferates during menstruation
(C) the glandular tissue in the breast is replaced by fat
(D) estrogen use causes an overall density decrease in the breast
89. In imaging the breast for the craniocaudal (CC) projection, what technique is used to minimize skin folds in the lateral aspect of the breast?
(A) Lift the posterior lateral aspect of the breast onto the detector.
(B) Drape the contralateral breast over the corners of the detector.
(C) Have the patient’s head turned facing the ipsilateral breast.
(D) On the side being imaged, the patient’s arm hangs relaxed with humerus externally rotated.
90. Phosphor crystals in the flat-panel detector system are classified as ________ phosphors when they are scattered through the phosphor level.
(A) needle
(B) turbid
(C) amorphous
(D) selenium
91. Grid use in magnification mammography is contraindicated because
(A) the use of a grid will increase subject contrast
(B) scatter is already minimized
(C) grid use increase scatter
(D) grids would result in decrease subject contrast
92. The breast can be imaged in the from below (FB) projection
(A) to improve visualization of lesions in uppermost aspect of breast by reducing object-to-image receptor distance (OID)
(B) during needle localization to provide a shorter route to inferior lesions
(C) to maximize the amount of tissue visualized in patients with kyphosis
(D) all of the above
93. Figure 7-8 shows a radiograph of the right mediolateral oblique (RMLO). What major problem makes this radiograph suboptimal? The patient and mammographer’s identification plus the projection has been removed to avoid Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) violations.
(A) The skin marker does not fully cover the skin lesion.
(B) The posterior breast is not imaged.
(C) There is a skin fold in the posterior area of the breast.
(D) The inframammary fold is missing.
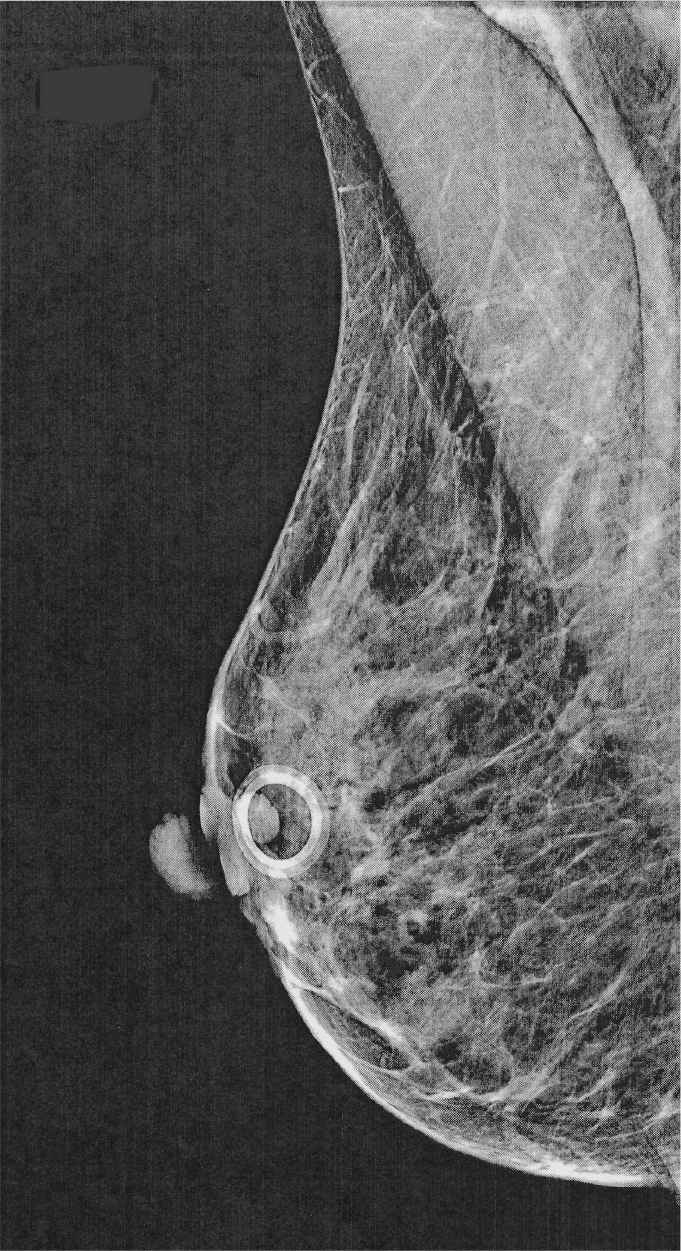
Figure 7-8.
94. Which statement best describes a parallel or linear grid?
(A) Lead strips are aligned adjacent to one another and placed lengthwise in the same direction within the structure of the grid.
(B) Lead strips are aligned at right angles to each other.
(C) Lead strips are designed to take advantage of the divergence of the x-ray beam as it leaves the x-ray tube.
(D) Lead strips are designed to move during the exposure.
95. The charge-coupled device (CCD) serves to convert
(A) x-rays to light
(B) x-rays to electrons
(C) light to electrons
(D) electrons to light
96. The scintillators are used to convert
(A) x-rays to light
(B) x-rays to electrons
(C) light to electrons
(D) electrons to light
97. The photoconductor in the direct digital radiography system is used to convert
(A) x-rays to light
(B) x-rays to electrons
(C) light to electrons
(D) electrons to light
98. The repeat rate should be analyzed if the rate changes from the previous measure rate by more than
(A) ±2% points
(B) ±3% points
(C) ±4% points
(D) ±5% points
99. A magnification image of a breast shows several oval-shaped radiolucent lesions with eggshell-like calcifications. These are most likely to be
(A) ductal papilloma
(B) fibroadenomas
(C) oil cysts
(D) hematomas
100. The thin-film transistor (TFT) in the flat-panel detector systems collects
(A) light
(B) pixels
(C) electrons
(D) x-rays
101. In general, the implant-displaced (ID) series are taken using the
(A) axillary tail (AT) and mediolateral oblique (MLO) projections
(B) craniocaudal (CC) and ML projections
(C) CC and MLO projections
(D) CC and lateromedial (LM) projections
102. Today all mammographers (technologists or radiographers performing mammograms independently) must have
(A) satisfied the final requirements of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
(B) completed at least 20 hours of documented training in mammography
(C) performed at least 75 examinations under direct supervision of a qualified mammographer
(D) none of the above
103. The criteria for a properly positioned mediolateral oblique (MLO) includes
1. a concave pectoral muscle on the anterior border
2. fat visualized posterior to the fibroglandular tissues
3. an open inframammary fold (IMF)
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
104. A benign inflammatory condition of the lactiferous ducts leading to nipple discharge, nipple inversion, or periareolar sepsis is called
(A) ductal ectasia
(B) Paget disease of the breast
(C) peau d’orange
(D) ductal papilloma
105. The cells lining the alveoli in the lobules are called
(A) epithelial cells
(B) myoepithelial cells
(C) basement cells
(D) superficial cells
106. Informed consent implies that the patient
1. has already signed the authorization for treatment
2. was informed of the procedure or operation, its risks, possible consequences and any alternative options
3. the patient was given information about the procedure in their language
(A) 1 and 2 only
(B) 2 and 3 only
(C) 1 and 3 only
(D) 1, 2, and 3
107. A technique describing reshaping of the breast is called
(A) reduction mammoplasty
(B) mammoplasty
(C) breast augmentation
(D) breast biopsy
108. Smaller pixels will result in
(A) lower spatial resolution
(B) lower image resolution
(C) greater spatial resolution
(D) greater image resolution
109. The detector elements (DELs) are located within the
(A) scintillator
(B) thin-film transistor (TFT)
(C) charge-coupled device (CCD)
(D) complementary metal-oxide silicon (CMOS)
110. In positioning for the superoinferior oblique (SIO), the _________ of the breast will rest on the detector.
(A) lateral surface
(B) superior surface
(C) medial surface
(D) inferior aspect
111. Imaging the craniocaudal (CC) projection in males will present the same difficulty as imaging small, firm-breasted females. An added problem may be that
(A) males have more problems with the compression
(B) the male breast is smaller than the smallest female breast
(C) males have more muscular breast tissue
(D) hair on the chest of males makes compression difficult
112. For the superoinferior oblique (SIO) projection, the central ray is directed
(A) inferolateral to superomedial
(B) superomedial to inferolateral
(C) inferomedial to superolateral
(D) superolateral to inferomedial
113. Which of the following are considered agencies granting accreditation under the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulation?
(A) State of California
(B) American College of Radiology (ACR)
(C) NY State Department of Health
(D) State of Florida
114. Which alternative projection could be used, in addition to the craniocaudal (CC), in imaging a patient with a prominent pacemaker?
(A) mediolateral (ML)
(B) lateromedial oblique (LMO)
(C) exaggerated craniocaudal (XCCL)
(D) mediolateral oblique (MLO)
115. The 2 main classifications of breast cancer are
(A) tubular and lobular
(B) lobular and medullary
(C) lobular and ductal
(D) inflammatory and ductal
116. In addition to the patient’s name, all mammographic reports should have the
(A) final assessment of findings
(B) hospital number or additional patient identifier
(C) name of the radiologist
(D) all of the above
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree