Pulmonary Capillary Hemangiomatosis
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Rare cause of pulmonary hypertension due to proliferation of alveolar capillaries within lung
Imaging Findings
Enlarged pulmonary arteries + centrilobular ground-glass opacities
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pulmonary Venoocclusive Disease (PVOD)
Primary Pulmonary Hypertension (PPH)
Chronic Pulmonary Thromboemboli
Pathology
Some evidence that proliferation of thin-walled capillaries in PCH is histologic reaction to PVOD
Clinical Issues
Normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Prognosis poor: Most patients die within 2 years of diagnosis
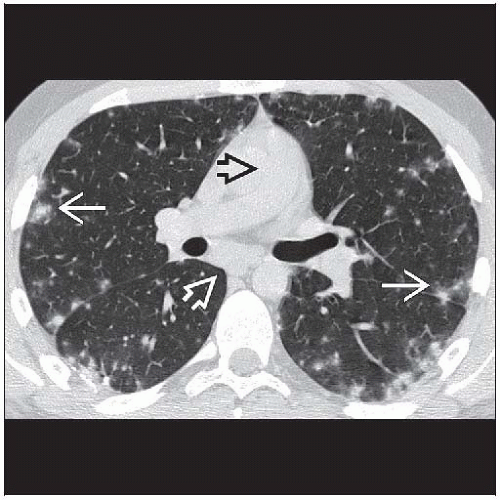
 Axial NECT shows marked enlargement of the central pulmonary arteries
 and faint ground-glass opacities and faint ground-glass opacities 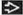 in pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis. in pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|