KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Localized collection of pus in liver due to bacterial infectious process with destruction of hepatic parenchyma and stroma
Imaging
- •
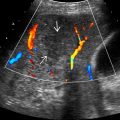
Cluster sign: Cluster of small pyogenic abscesses that coalesce into single large cavity
- •
Early lesions tend to be echogenic and poorly demarcated, evolve into well-demarcated anechoic lesions
- •
May see central gas or fluid level
- •
Nonliquefied abscess may simulate solid tumor
- •
Echogenicity of abscesses
- ○
Anechoic (50%), hyperechoic (25%), hypoechoic (25%)
- ○
- •
Fluid level or debris, internal septa, and posterior acoustic enhancement
- •
CECT: Double target sign
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Metastasis (post treatment)
- •
Cholangiocarcinoma (peripheral mass forming)
- •
Biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- •
Hepatocellular carcinoma (hypovascular)
- •
Amebic abscess
- •
Hemangioma (small)
- •
Hemorrhagic simple cyst
- •
Hydatid cyst (echinococcal cyst)
- •
Hepatic infarction in liver transplantation
Pathology
- •
Development via 5 major routes: Portal vein, biliary tract, hepatic artery, direct extension, trauma
- •
Common organisms: Escherichiacoli , Klebsiella pneumoniae (adult), Staphylococcus aureus (children)
Clinical Issues
- •
Accounts for 88% of all liver abscesses
- •
Typical presentation: Middle-aged/elderly patient with history of fever, right upper quadrant pain, tender hepatomegaly, leukocytosis
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Rule out amebic/fungal liver abscesses, cystic/hypovascular tumors
- •
Check for history of transplantation or ablation/chemotherapy for liver tumor
Scanning Tips
- •
Demonstration of mobile echogenic debris very helpful in diagnosis
- •
Fluid level or debris, internal septa, and posterior acoustic enhancement are also very helpful clues
 coalescing to form a large abscess cavity
coalescing to form a large abscess cavity  .
.