8 Radiologic Anatomy of the Neck
Computed tomography (CT) is the most commonly used imaging modality for demonstration of the neck structures. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exhibits superior soft-tissue contrast. However, the quality of the MR image can be compromised by motion artifacts as a result of breathing, swallowing, and vascular pulsations.
At present, conventional radiography is still used for evaluation of swallowing disorders as well as detection of radiopaque foreign bodies. The swallowing action is discussed in a separate section at the end of this chapter.
Evaluation Points in CT of the Neck
• Asymmetry is an important point to note.
• Nasopharyngeal structures and surrounding skull base.
• Parapharyngeal space.
• Prevertebral space and fascia.
• Masticator space.
• Tongue, oral cavity.
• Salivary glands: parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
• Large vessels: carotid arteries and jugular veins.
• Hypopharynx, epiglottis, vallecula, piriform sinus.
• Hypertrophic or infected lymph nodes.
• Presence of solid or cystic structures.
• Thyroid, cricoid, and true/false vocal cords.
• Trachea, esophagus, thyroid glands.
• Cervical spine.
Evaluation of the Neck Structures on Axial CT slices in a Craniocaudal Sequence
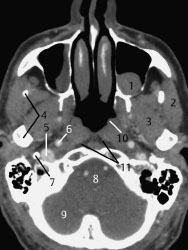
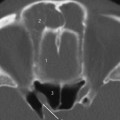
Fig.8.1 Axial CT slice.
1 Retention cyst in left maxillary sinus
2 Masseter
3 Lateral pterygoid
4 Mandible
5 Internal jugular vein
6 Internal carotid artery
7 Styloid process
8 Pons
9 Cerebellum
10 Torus tubarius
11 Retropharyngeal space (fat)
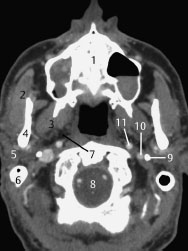
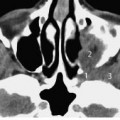
Fig.8.2 Axial CT slice.
1 Maxilla with anterior nasal spine (*)
2 Masseter
3 Lateral pterygoid
4 Mandible
5 Parotid gland
6 Mastoid apex/process
7 Parapharyngeal space
8 Medulla
9 Styloid process
10 Internal jugular vein (right-sided dominance)
11 Internal carotid artery
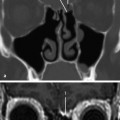
Fig.8.3 Axial CT slice.
1 Intrinsic tongue musculature
2 Parapharyngeal space
3 Medial pterygoid
4 Masseter
5 Parotid gland
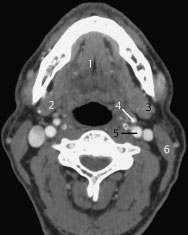
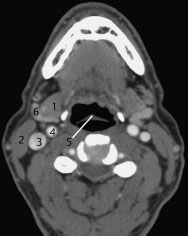
Fig.8.4 Axial CT slice.
1 Genioglossus or geniohyoid muscle; may be differentiated on consecutive slices by their attachments
2 Submandibular gland
3 Internal jugular vein
4 External carotid artery
5 Internal carotid artery
6 Sternocleidomastoid
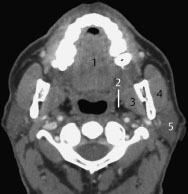
Fig.8.5 Axial CT slice.
1 Submandibular gland
2 Sternocleidomastoid
3 Internal jugular vein
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree