• This exploits the presence of random (Brownian) motion of water molecules • It relies on modification of a standard T2WI sequence: a pair of diffusion sensitizing gradients are applied symmetrically around a 180° refocusing RF pulse • DWI: stationary water molecules appear much brighter than areas with higher molecular diffusion • The degree of phase shift or signal loss depends upon the strength and duration of the diffusion sensitizing gradients – this is expressed by the ‘b-value’ • Quantitative analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) requires sequences with at least two different b-values • This exploits magnetic susceptibility effects within brain tissue during the first pass of an IV gadolinium-based contrast agent • Sequential changes in signal intensity can be plotted as a time–signal intensity curve of a chosen region of interest (or as a pixel-based colour map) • This is a non-invasive in vivo method allowing the investigation of biochemical changes • An example of a high-grade neurological malignancy:
Radiology techniques
SPECIALIZED MRI TECHNIQUES IN NEUROIMAGING
MAGNETIC RESONANCE DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING (DWI)
‘b-value’
 water molecules that do not easily diffuse will only demonstrate signal loss with high b-values
water molecules that do not easily diffuse will only demonstrate signal loss with high b-values
 tissue characterization is possible by observing the signal loss recorded at different b-values – there is increased signal loss within the more cystic components with higher b-values (relative to the more cellular components that demonstrate reduced diffusion)
tissue characterization is possible by observing the signal loss recorded at different b-values – there is increased signal loss within the more cystic components with higher b-values (relative to the more cellular components that demonstrate reduced diffusion)
 For an individual pixel, the gradient of the line plotted for the logarithm of the relative signal intensity of the tissue (y-axis) vs the b-values applied (x-axis) represents the ADC
For an individual pixel, the gradient of the line plotted for the logarithm of the relative signal intensity of the tissue (y-axis) vs the b-values applied (x-axis) represents the ADC
 All the pixel data can be combined to visually produce an ‘ADC map’
All the pixel data can be combined to visually produce an ‘ADC map’
 Areas with a decreased ADC appear dark on ADC maps (this is converse to DWI, where areas of decreased diffusion appear bright)
Areas with a decreased ADC appear dark on ADC maps (this is converse to DWI, where areas of decreased diffusion appear bright)
 ADC maps are independent of any magnetic fields and can therefore overcome ‘T2-shine through’
ADC maps are independent of any magnetic fields and can therefore overcome ‘T2-shine through’
MAGNETIC RESONANCE PERFUSION IMAGING
 During the first pass there is a transient SI drop on T2*-weighted (susceptibility-weighted) imaging
During the first pass there is a transient SI drop on T2*-weighted (susceptibility-weighted) imaging
 Images are acquired every 1–2 s
Images are acquired every 1–2 s
 Arterial spin labelling is a new MR perfusion technique that does not require exogenous contrast medium (but is not currently in clinical use)
Arterial spin labelling is a new MR perfusion technique that does not require exogenous contrast medium (but is not currently in clinical use)
MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY
 it measures the change in resonance intensity of marker compounds:
it measures the change in resonance intensity of marker compounds:
 N-acetylaspartate (NAA): this acts as a neuronal marker as it is almost exclusively found within axons and nerve processes
N-acetylaspartate (NAA): this acts as a neuronal marker as it is almost exclusively found within axons and nerve processes
 Creatine (Cr/PCr): this arises from both phosphocreatine- and creatine-containing substances within the cell
Creatine (Cr/PCr): this arises from both phosphocreatine- and creatine-containing substances within the cell
 Choline (Cho): this arises from choline-containing substances within the cell membrane
Choline (Cho): this arises from choline-containing substances within the cell membrane
Radiology techniques

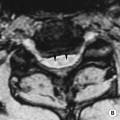
 DWI: high signal
DWI: high signal  ADC: low signal
ADC: low signal it allows for the mapping of the white matter tracts
it allows for the mapping of the white matter tracts

 time to peak (Tp)
time to peak (Tp)  mean transit time (MTT)
mean transit time (MTT)  the rCBF can be estimated by dividing the relative blood volume by the mean transit time
the rCBF can be estimated by dividing the relative blood volume by the mean transit time