Saline Infusion Sonohysterography
Laura Amodei
Saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS) is known by several other names, including sonohysterosalpingography and hysterosonography. SIS involves the acquisition of multiple endovaginal ultrasonographic (EVS) images of the uterus and endometrial cavity during the infusion of sterile saline.
SIS is most commonly used in one of two ways. The first is for the evaluation of endometrial abnormalities. In this case, patients are often peri- or postmenopausal and may have postmenopausal or other abnormal uterine bleeding. These patients should always have an EVS before SIS. Other patients will have undergone pelvic ultrasonography for another indication and will have been found to have an abnormal endometrium. Endometrial abnormalities on EVS include thickening (normal endometrium: premenopausal ≤15 mm; postmenopausal asymptomatic, on HRT ≤8 mm; and postmenopausal with symptoms ≤5 mm), endometrial distortion, suspected mass/focal abnormality, and poor visualization. The role of SIS in the evaluation of endometrial abnormalities is presented in Figure 62-1. The second application of SIS is in the evaluation of suspected congenital anomalies or variants (e.g., bicornuate uterus) or acquired abnormalities (e.g., uterine synechiae). These patients are younger and are usually being evaluated for infertility or repeated spontaneous abortions.
Evaluation of Endometrial Abnormalities
EVS is very sensitive for endometrial thickening, but is often nonspecific. Occasionally, on EVS, findings are sufficiently specific to warrant proceeding directly to hysteroscopy without SIS (Fig. 62-1).
Hysteroscopy is performed by gynecologists; it allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity and targeted biopsy or resection of abnormalities, but is invasive and requires anesthesia.
Blind endometrial biopsy and dilatation and curettage (D&C) are also performed by gynecologists; they provides tissue for pathologic diagnosis, but can be prone to sampling error and false negatives, particularly in the case of focal abnormalities.
Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is occasionally used to evaluate causes of abnormal uterine bleeding or pelvic pain.
Evaluation of Congenital Variants/Anomalies or Acquired Abnormalities
Hysterosalpingography is an older technique in which contrast material is introduced into the uterine cavity and x-ray images are obtained for evaluation of the morphology or the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. It is particularly useful in the evaluation of fallopian tube patency.
Pelvic MRI can be used to evaluate suspected congenital anomalies or variants.
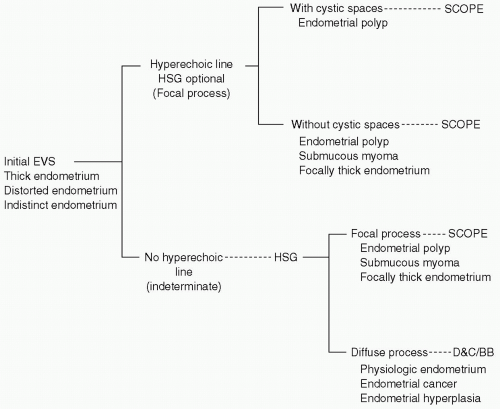 Figure 62-1. Diagram illustrates a method of triage for patients with suspected endometrial pathology. In this flowchart, hysterosonography (HSG) is used only selectively and as a complement to the initial endovaginal ultrasonography. SCOPE, hysteroscopy; EVS, endovaginal ultrasonography; D&C, dilatation and curettage; BB, blind endometrial biopsy. (Reprinted with permission from Dudiak KM. Hysterosonography: a key to what is inside the uterus. Ultrasound Q 2001;17(2):73-86.) |
Pregnancy or possible pregnancy. SIS. should be performed in the follicular portion of cycle after menstruation has ended, but before ovulation, and should generally not be performed after the 10th day of the menstrual cycle.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Patients should be assessed for unexplained pelvic or cervical motion tenderness, which could be a sign of PID during the manual examination described in the subsequent text.
The theoretic risk of spread of endometrial cancer through the fallopian tubes into the abdomen during SIS has not been supported by the literature.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree