Here you will find the most commonly used normal dictations (“macros”) at my hospital. They are only provided as guidelines and should be adjusted to different practices and institutions and many times also vetted by the clinical services. In between brackets, the reader will find spaces that need to be filled out according to the specific circumstances of the dictations. The materials stated—such as types of contrast, needless, catheter and others—are the ones we routinely use, and they vary from institution to institution. The fact that their names are found here does not represent an endorsement of a specific product or products.
Additionally, the entire structure of the report is not detailed for each entry. At our hospital, the structure of all neuroimaging reports is as follows:
Name and type of examination.
Dictated by whom and date.
Clinical indication (including patient demographics and symptoms).
Comparison studies.
Technique.
Findings.
Impression.
 MR BRAIN, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
MR BRAIN, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar, multisequence magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain was performed without and with intravenous (IV) contrast.
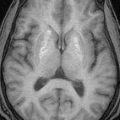
FINDINGS: There is no focal parenchymal signal abnormality. There is no midline shift or mass lesion. There is no evidence of intracranial hemorrhage or acute infarct. There are no extra-axial fluid collections present. No diffusion-weighted signal abnormality is identified. There is no abnormal enhancement.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the brain.
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar, multisequence MRI of the brain was performed without IV contrast.
FINDINGS: There is no focal parenchymal signal abnormality. There is no midline shift or mass lesion. There is no evidence of intracranial hemorrhage or acute infarct. There are no extra-axial fluid collections present. No diffusion-weighted signal abnormality is identified.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the brain.
 MR BRAIN, PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
MR BRAIN, PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar, multisequence MRI of the brain was performed with and without IV contrast following our MS protocol.
FINDINGS: There are multiple white matter foci of abnormal increased T2/FLAIR signal. There are [greater than nine lesions], at least three of which are in the periventricular white matter oriented perpendicular to the lateral ventricles. There are [ ] subcortical lesions. There are [ ] infratentorial lesions. [ ] enhancing lesions are seen. The optic nerves are normal in appearance. There is [ ] evidence of [intracranial hemorrhage, acute infarct, mass effect, or extra-axial fluid collection.]
IMPRESSION: Multiple white matter lesions in a distribution most consistent with multiple sclerosis.
TECHNIQUE: Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of intracranial arterial circulation was also performed.
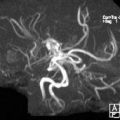
FINDINGS: Circle of Willis MRA does not demonstrate any aneurysms, stenoses, or occlusions. The anatomy is normal, and there are no significant variants that may be associated with disease.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRA of the brain.
TECHNIQUE: Multivoxel short and long echo time MR spectroscopy was obtained at the level of________. The data were postprocessed and baseline correction was applied. Metabolite ratios were automatically generated as the manufacturer program and also displayed as color-graded maps overlying the area studied.
FINDINGS: The ratios between choline, creatine, and n-acetyl aspartate are normal. No abnormal lipids and/or lactate are present.
IMPRESSION: Normal MR spectroscopy.
 MR PITUITARY GLAND, NORMAL (REMEMBER TO DICTATE THE REST OF BRAIN IF INCLUDED AS PART OF THE EXAMINATION)
MR PITUITARY GLAND, NORMAL (REMEMBER TO DICTATE THE REST OF BRAIN IF INCLUDED AS PART OF THE EXAMINATION)
TECHNIQUE: Imaging of the pituitary gland including dynamic and thin section coronal and sagittal images was performed.
FINDINGS: The pituitary stalk is midline. There is no enlargement of the pituitary gland or sella. There is no intrasellar or suprasellar mass. The optic chiasm and cavernous sinuses are normal. Postcontrast imaging shows no abnormal areas of contrast enhancement within the pituitary gland.
IMPRESSION: Normal precontrast and postcontrast MRI of the pituitary gland.
 MR, POST DEEP BRAIN STIMULATOR PLACEMENT, NORMAL
MR, POST DEEP BRAIN STIMULATOR PLACEMENT, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Limited multiplanar, multisequence MRI of the brain was performed without IV contrast.
FINDINGS: There has been placement of bilateral deep brain stimulators that course to the level of the______. No intracranial hemorrhage is identified.
IMPRESSION: Placement of deep brain stimulators that course to the level of the_______.
 MR, CRANIAL NERVE VIII, NORMAL
MR, CRANIAL NERVE VIII, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar, multisequence MRI of the brain was performed without and with IV contrast including high-resolution images through the course of both VIII cranial nerves.
FINDINGS: There is no focal parenchymal signal abnormality. The temporal bones, specifically the internal auditory canals and seventh and eighth cranial nerves, are normal bilaterally. The inner ear structures and cerebellopontine angles are unremarkable. There are four cranial nerves within the internal auditory canals bilaterally as seen on the high resolution T2 imaging. There is no abnormal enhancement. IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the brain using the cranial nerve VIII protocol.
 MRA, NECK, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
MRA, NECK, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: MRA of the extracranial arterial circulation in the neck was performed using 2D Time of Flight and followed by a second MRA after IV contrast administration covering from the aortic arch to the base of the skull.
FINDINGS: The visualized portions of the common, external and internal carotid arteries are of normal caliber. There is no high-grade stenosis. No aneurysm or asymmetry to the branching patterns is identified. The vertebral arteries are patent with antegrade flow. In this report, a stenosis of the internal carotid artery as reported is calculated based on the NASCET method: [1 – (minimal residual diameter/normal diameter of distal ICA)].
IMPRESSION: Normal MRA of the neck.
 MRA, NECK, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
MRA, NECK, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: MRA of the extracranial arterial circulation in the neck was performed using 2D Time of Flight MRA
FINDINGS: The visualized portions of the common, external and internal carotid arteries are of normal caliber. There is no high-grade stenosis. No aneurysm or asymmetry to the branching patterns is identified. The vertebral arteries are patent with antegrade flow. In this report, stenosis of the internal carotid artery as reported is calculated based on the NASCET method: [1 – (minimal residual diameter/normal diameter of distal ICA)].
IMPRESSION: Normal MRA of the neck.
 MR, CERVICAL SPINE, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
MR, CERVICAL SPINE, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar multisequence MRI was performed through the cervical spine without IV contrast.
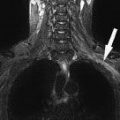
FINDINGS: The vertebral bodies are normally aligned. The signal intensity from the vertebral body bone marrow and spinal cord is normal. There is no significant spinal canal or neural foraminal stenosis.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the cervical spine.
 MR, CERVICAL SPINE, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
MR, CERVICAL SPINE, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar MRI was performed through the cervical spine without and with IV contrast.
FINDINGS: The vertebral bodies are normally aligned. The signal intensity from the vertebral body bone marrow and spinal cord is normal. There is no significant spinal canal or neural foraminal stenosis. No abnormal enhancement is seen.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the cervical spine.
 MR, THORACIC SPINE, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
MR, THORACIC SPINE, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar MRI was performed through the thoracic spine without contrast administration.
FINDINGS: The vertebral bodies are normally aligned. The vertebral body heights and disc spaces are well preserved. The signal intensity from the vertebral body bone marrow and spinal cord is normal. There is no significant spinal canal or neural foramina! stenosis. The conus medullaris ends at a normal level.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the thoracic spine.
 MR, THORACIC SPINE, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
MR, THORACIC SPINE, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar MRI was performed through the thoracic spine prior to and following IV contrast administration.
FINDINGS: The vertebral bodies are normally aligned. The vertebral body heights and disc spaces are well preserved. The signal intensity from the vertebral body bone marrow and spinal cord is normal. There is no significant spinal canal or neural foraminal stenosis. The conus medullaris ends at a normal level. No abnormal enhancement is seen.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the thoracic spine.
 MR, LUMBAR SPINE, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
MR, LUMBAR SPINE, NO CONTRAST, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar MRI was performed through the lumbar spine without IV contrast.
FINDINGS: For the purposes of this dictation, the lowest well-formed intervertebral disc space is assumed to be the L5-S1 level, and there are presumed to be five lumbar-type vertebral bodies. The vertebral bodies are normally aligned. The vertebral body heights and disc spaces are well preserved. The signal intensity from the vertebral body bone marrow and spinal cord is normal. There is no significant spinal canal or neural foraminal stenosis. The conus medullaris ends at a normal level.
IMPRESSION: Normal MRI of the lumbar spine.
 MR, LUMBAR SPINE, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
MR, LUMBAR SPINE, CONTRAST ENHANCED, NORMAL
TECHNIQUE: Multiplanar MRI was performed through the lumbar spine [prior to and following] IV contrast administration.
FINDINGS: For the purposes of this dictation, the lowest well-formed intervertebral disc space is assumed to be the L5-S1 level, and there are presumed to be five lumbar-type vertebral bodies. The vertebral bodies are normally aligned. The vertebral body heights and disc spaces are well preserved. The signal intensity from the vertebral body bone marrow and spinal cord is normal. There is no significant spinal canal or neural foraminal stenosis. The conus medullaris ends at a normal level. No abnormal enhancement is seen.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree