and Vincent L. Sorrell2
(1)
Division of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Department of Radiology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, USA
(2)
Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Gill Heart Institute, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, USA
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this chapter (doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25436-4_29) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
29.1 Case Challenge #25
29.1.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 35-year-old female presents with “yellow eyes.”
Images for Review
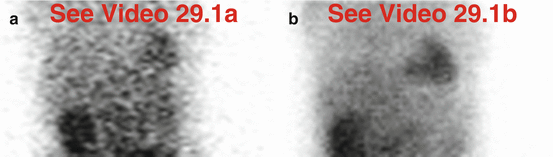
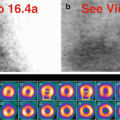
Fig. 29.1
(a) Rest raw projection images (Video 29.1a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b) Stress raw projection images (Video 29.1b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Parathyroid glands: □ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot □ cold
Chest wall: □ hot □ cold
Skeleton: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Mediastinum: □ hot □ cold
Myocardium and pericardium: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
Lymphatic system: □ hot □ cold
Diaphragm: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: □ hot □ cold
Adrenal glands: □ hot □ cold
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ diffuse toxic goiter
Parathyroid glands: □ normal □ adenoma, substernal location
Breasts: □ normal □ lactation
Chest wall: □ normal □ cross talk from another radioactive source
Skeleton: □ normal □ Gaucher disease
Pleura: □ normal □ neoplasm, metastatic
Lungs: □ normal □ postoperative change
Mediastinum: □ normal □ thymoma
Myocardium and pericardium: □ normal □ pericardial mass
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal □ prominent right auricular appendage
Vascular system: □ normal □ retention in central port
Lymphatic system: □ normal □ lymphoma
Diaphragm: □ normal □ eventration, left hemidiaphragm
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ urinary contamination
Peritoneum: □ normal □ malignant metastatic implants
Liver: □ normal □ cirrhosis
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ normal □ cholecystectomy
Spleen: □ normal □ splenomegaly
Stomach: □ normal □ gastropathy with fluid distension
Small intestine and large intestine: □ normal □ diminished bile flow
Adrenal glands: □ normal □ hemorrhagic mass
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ normal □ hyperfunctioning state (hepatic failure)
Vascular system: □ normal □ abdominal aortic aneurysm
29.1.2 Solution
Additional Annotated Images
None.
The Pertinent Findings
Chest
Not applicable
Abdomen
Liver: □ hot ■ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot ■ cold
Spleen: ■ hot □ cold
Stomach: ■ hot ■ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: □ hot ■ cold
Kidneys and female reproductive system: ■ hot □ cold
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Not applicable
Abdomen
Liver: ■ cirrhosis
Biliary system and gallbladder: ■ cholecystectomy
Spleen: ■ splenomegaly
Stomach: ■ gastropathy with fluid distension
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ diminished bile flow
Kidneys and female reproductive system: ■ hyperfunctioning state
Discussion
Chest
There are no significant findings.
Abdomen
The liver and the small intestine are poorly visualized, suggesting severe liver dysfunction and reduced biliary clearance of the radiopharmaceutical (a, b). The patient has known autoimmune hepatitis, awaiting transplant. The gallbladder is surgically absent; however, in patients with such impaired bile flow, differential diagnosis of gallbladder non-visualization would include underlying liver dysfunction and not necessarily acute or chronic cholecystitis. The stomach appears collapsed on rest raw images (a) but appears distended and “cold” on stress raw images (b) after water ingestion. This pattern is characteristic of cirrhosis-related gastropathy. There is markedly greater visualization of the kidneys, the alternate route of biological clearance of the radiopharmaceutical (a, b); renal clearance compensates for liver dysfunction.
29.2 Case Challenge #26
29.2.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 66-year-old female provides a history of diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and previous “heart attack.”
Images for Review
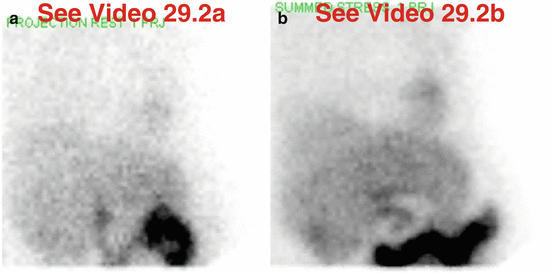
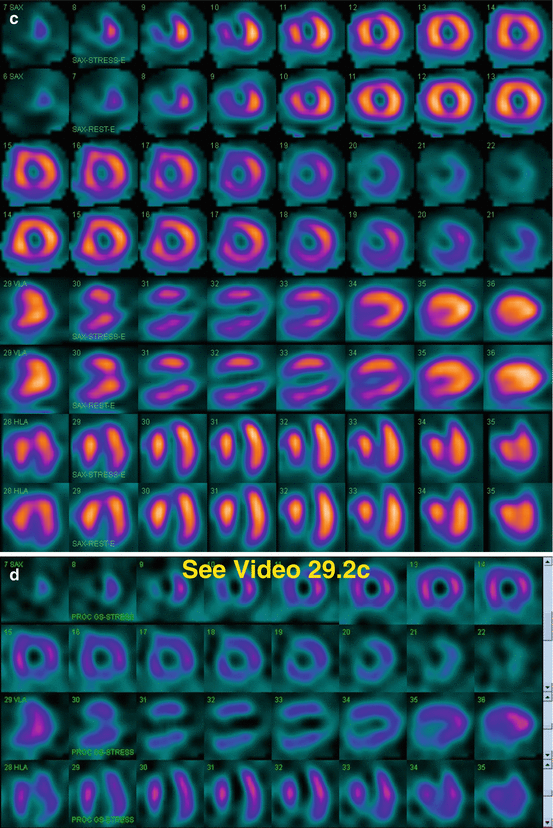
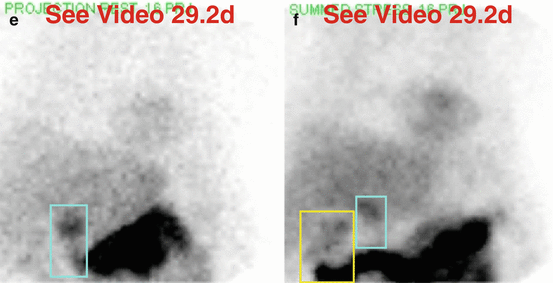
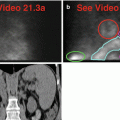
Fig. 29.2
(a) Rest raw projection images (Video 29.2a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b) Stress raw projection images (Video 29.2b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(c) Stress/rest processed SPECT images (SA, VLA, HLA)
(d) Stress gated SPECT images (Video 29.2c, frame 1) (SA, VLA, HLA)
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Parathyroid glands: □ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot □ cold
Chest wall: □ hot □ cold
Skeleton: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Mediastinum: □ hot □ cold
Myocardium and pericardium: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
Lymphatic system: □ hot □ cold
Diaphragm: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: □ hot □ cold
Adrenal glands: □ hot □ cold
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ lymphoma
Parathyroid glands: □ normal □ ectopic hyperplasia
Breasts: □ normal □ soft-tissue attenuation artifact
Chest wall: □ normal □ Holter monitor
Skeleton: □ normal □ multiple metastases
Pleura: □ normal □ mesothelioma
Lungs: □ normal □ posttransplant asymmetry
Mediastinum: □ normal □ lymphoma
Myocardium and pericardium: □ normal □ “hot” mass
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal □ dilatation
Vascular system: □ normal □ chest port injection site
Lymphatic system: □ normal □ necrotic axillary lymph nodes, malignant
Diaphragm: □ normal □ muscular (soft-tissue attenuation)
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ overlying patient’s arms and hands
Peritoneum: □ normal □ ascites
Liver: □ normal □ hepatitis
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ normal □ cholecystectomy
Spleen: □ normal □ infarct
Stomach: □ normal □ duodenogastric reflux and fluid
Small intestine and large intestine: □ normal □ visualization of large intestine
Adrenal glands: □ normal □ cystic neoplasm
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ normal □ left nephrectomy
Vascular system: □ normal □ extravasation
29.2.2 Solution
Additional Annotated Images
(e) Rest raw projection image (Video 29.2d, frame 16),99mTc sestamibi, duodenum (blue box)
(f) Stress raw projection image (Video 29.2e, frame 16),99mTc sestamibi, hepatic flexure of large intestine (yellow box), duodenum (blue box)
The Pertinent Findings
Chest
Breasts: □ hot ■ cold
Abdomen
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot ■ cold
Stomach: ■ hot ■ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ hot □ cold
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Breasts: ■ soft-tissue attenuation artifact
Abdomen
Biliary system and gallbladder: ■ cholecystectomy
Stomach: ■ duodenogastric reflux and fluid
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ visualization of large intestine
Discussion
Chest
The breast tissue creates an attenuation artifact on the heart (a, b, c, d). On processed images (c), there is a medium-size, severe, fixed anteroseptal-apical perfusion defect that represents myocardial scar (her “heart attack”?); there is no ischemia. There is anteroseptal-apical akinesis, but preserved global function with LVEF greater than 60 % (d). Thus, despite the potential for breast attenuation artifact, this perfusion defect is “real” and correlates with “true” coronary artery disease.
Abdomen
The gallbladder is absent (a, b). The rest raw images (a, e) demonstrate duodenal (“C-loop”) activity that could be mistaken for the gallbladder. The first portion of the duodenum is posterior and gravity dependent in the supine position used for imaging. The gallbladder is usually anteriorly situated, whereas the duodenum is posteriorly situated, and should appear focally intense and constant during the acquisition. On later same-day stress raw (b, f) images, large intestinal activity is seen in the right upper quadrant. As is the case for the early duodenal activity, activity in the hepatic flexure of the large intestine could be misconstrued as gallbladder.
On stress raw images (b), the stomach appears “cold” due to water ingestion, but there is no artifactual attenuation effect on the processed images (c).
29.3 Case Challenge #27
29.3.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 62-year-old male presents with chronic disease.
Images for Review
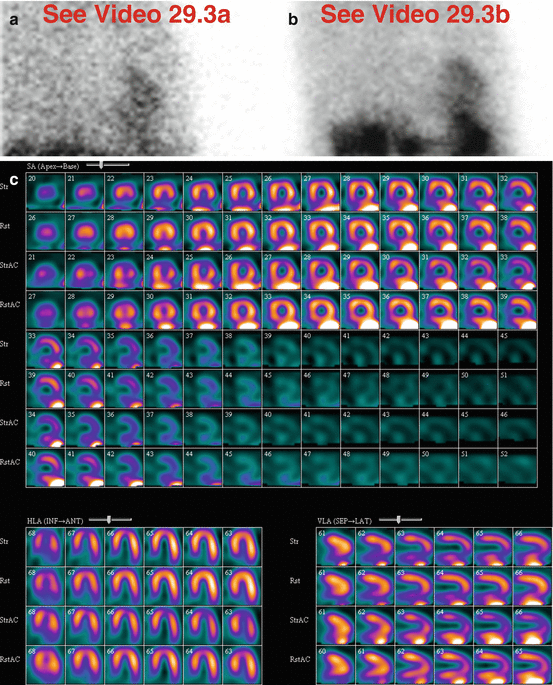
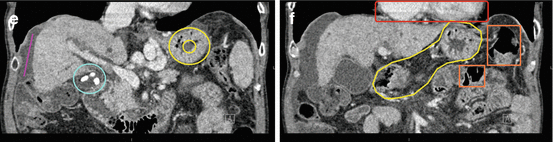
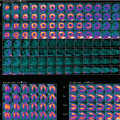
Fig. 29.3
(a) Rest raw projection images (Video 29.3a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b) Stress raw projection images (Video 29.3b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(c) Stress/rest processed SPECT images (SA, HLA, VLA) (without and with AC)
(d) Stress and rest gated SPECT images (Video 29.3c, frame 1) (SA, VLA, HLA)
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Parathyroid glands: □ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot □ cold
Chest wall: □ hot □ cold
Skeleton: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Mediastinum: □ hot □ cold
Myocardium and pericardium: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
Lymphatic system: □ hot □ cold
Diaphragm: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: □ hot □ cold
Adrenal glands: □ hot □ cold
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ multinodular goiter
Parathyroid glands: □ normal □ multiple adenomas
Breasts: □ normal □ gynecomastia
Chest wall: □ normal □ jewelry
Skeleton: □ normal □ myelofibrosis
Pleura: □ normal □ bilateral effusions
Lungs: □ normal □ hyperinflation
Mediastinum: □ normal □ esophageal malignancy
Myocardium and pericardium: □ normal □ effusion
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal □ enlargement
Vascular system: □ normal □ extravasation around chest port during injection
Lymphatic system: □ normal □ metastatic neoplasm
Diaphragm: □ normal □ hiccups
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ umbilical hernia
Peritoneum: □ normal □ ascites
Liver: □ normal □ cirrhosis
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ normal □ calculous cholecystitis, chronic
Spleen: □ normal □ splenomegaly
Stomach: □ normal □ gastropathy
Small intestine and large intestine: □ normal □ visualization of large intestine
Adrenal glands: □ normal □ metastasis
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ normal □ atrophic left kidney
Vascular system: □ normal □ chest port for injection
29.3.2 Solution
Additional Annotated Images
(e) Coronal CT most anterior through the liver, gallbladder with gallstones (blue circle), and stomach (yellow circles, outer wall and inner lumen), perihepatic ascites (pink line)
(f) Coronal CT most posterior through the stomach (yellow outline) and splenic flexure (orange boxes), heart for reference (red box)
The Pertinent Findings
Chest
Not applicable
Abdomen
Peritoneum: □ hot ■ cold
Liver: □ hot ■ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot ■ cold
Stomach: ■ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ hot □ cold
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Not applicable
Abdomen
Peritoneum: ■ ascites
Liver: ■ cirrhosis
Biliary system and gallbladder: ■ calculous cholecystitis, chronic
Stomach: ■ gastropathy
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ visualization of large intestine
Discussion
Chest
There are no abnormal findings.
Abdomen
There is ascites and poor visualization of the liver (a, b, e), consistent with cirrhosis. There might be visualization of the gallbladder on stress raw images (b), but it is difficult to separate from the “hot” large intestine. On the rest raw images (a), the gallbladder is out of the field-of-view and cannot be evaluated. There are multiple large calcified gallstones (e).
Marked gastric activity appears on the rest raw images (a). On the stress raw images (b), the gastric activity is even more marked; this likely represents gastropathy. There is also marked activity in the large intestine (splenic flexure) that overlaps the stomach on the raw images (a, b); their anatomic relationships are correlated on CT images (f). The gastric activity and large intestinal activity are problematic because they create a significant processing artifact affecting the adjacent inferior myocardial wall where there is a fixed perfusion defect (c). This is almost certainly an artifactual defect because the gated SPECT images demonstrate normal wall motion and thickening (d).
29.4 Case Challenge #28
29.4.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 56-year-female presents with three-vessel coronary calcifications on chest CT and a long history of hypertension.
Images for Review
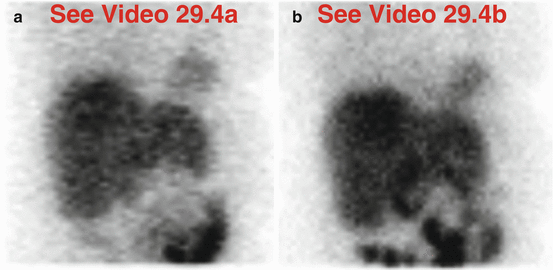
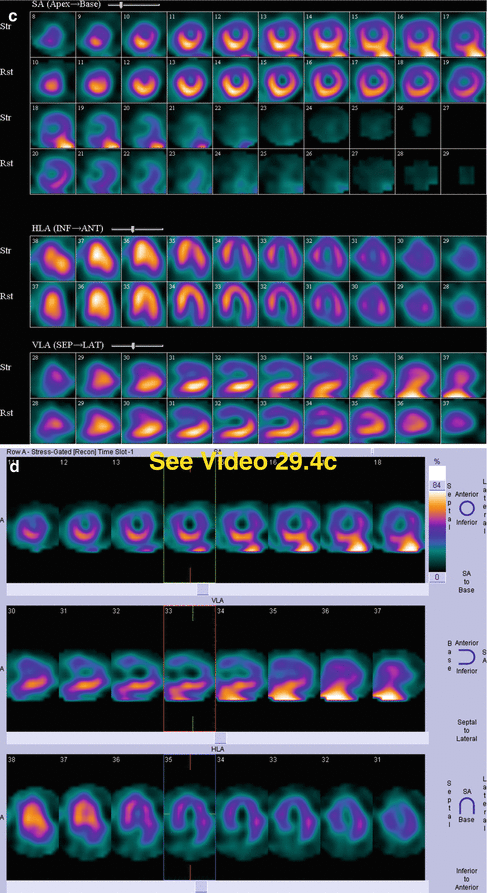
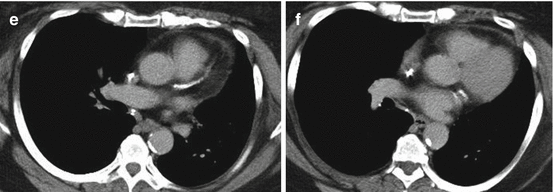
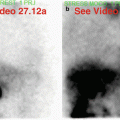
Fig. 29.4
(a) Rest raw projection images (Video 29.4a, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(b) Stress raw projection images (Video 29.4b, frame 1),99mTc sestamibi
(c) Stress/rest processed SPECT images (SA, HLA, VLA)
(d) Stress gated SPECT images (Video 29.4c, frame 1) (SA, VLA, HLA)
Characterize the Pertinent Finding(s)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ hot □ cold
Parathyroid glands: □ hot □ cold
Breasts: □ hot □ cold
Chest wall: □ hot □ cold
Skeleton: □ hot □ cold
Pleura: □ hot □ cold
Lungs: □ hot □ cold
Mediastinum: □ hot □ cold
Myocardium and pericardium: □ hot □ cold
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
Lymphatic system: □ hot □ cold
Diaphragm: □ hot □ cold
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ hot □ cold
Peritoneum: □ hot □ cold
Liver: □ hot □ cold
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot □ cold
Spleen: □ hot □ cold
Stomach: □ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: □ hot □ cold
Adrenal glands: □ hot □ cold
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ hot □ cold
Vascular system: □ hot □ cold
State Your Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Thyroid gland: □ normal □ free99mTc pertechnetate
Parathyroid glands: □ normal □ ectopic adenoma
Breasts: □ normal □ soft-tissue attenuation artifact
Chest wall: □ normal □ photomultiplier tube malfunction
Skeleton: □ normal □ anemia
Pleura: □ normal □ effusion
Lungs: □ normal □ congestive heart failure
Mediastinum: □ normal □ solid mass
Myocardium and pericardium: □ normal □ effusion
Right atrium and right ventricle: □ normal □ hypertrophy
Vascular system: □ normal □ extravasation
Lymphatic system: □ normal □ lymphoma, multifocal
Diaphragm: □ normal □ flattening
Abdomen
Abdominal wall: □ normal □ metallic object
Peritoneum: □ normal □ ascites
Liver: □ normal □ postoperative effect
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ normal □ cholecystectomy
Spleen: □ normal □ enlargement
Stomach: □ normal □ duodenogastric reflux
Small intestine and large intestine: □ normal □ duodenal stasis
Adrenal glands: □ normal □ neoplasm
Kidneys and female reproductive system: □ normal □ large left renal cyst
Vascular system: □ normal □ extravasation
29.4.2 Solution
Additional Images
(e) Axial image from chest CT at level of LAD coronary artery
(f) Axial image from chest CT at level of left circumflex coronary artery
The Pertinent Findings
Chest
Breasts: □ hot ■ cold
Abdomen
Biliary system and gallbladder: □ hot ■ cold
Stomach: ■ hot □ cold
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ hot □ cold
The Relevant Diagnosis(es)
Chest
Breasts: ■ soft-tissue attenuation artifact
Abdomen
Biliary system and gallbladder: ■ cholecystectomy
Stomach: ■ duodenogastric reflux
Small intestine and large intestine: ■ duodenal stasis
Discussion
Chest
Breast attenuation artifact is evident on review of the raw data (a, b). Take note of how the curvilinear edge of the breast overlies most of the heart but spares the inferior wall. This observation permits one to predict (correctly) that there will be an attenuation effect on the anterior wall and that the inferior wall will not be subject to that same effect, thus creating relative differences in the processed perfusion pattern. As predicted, there is a characteristic large, moderately severe, fixed anterior myocardial wall perfusion defect (c). Normal wall thickening and wall motion (d, especially on the VLA images) favor attenuation artifact rather than myocardial scar.
Normal myocardial perfusion in the setting of extensive coronary artery and vascular calcifications, as seen on routine chest CT (e, f), is an important and relatively common clinical situation that confirms that there is coronary atherosclerosis in the absence of significant stenosis.
Abdomen
There is non-visualization of the gallbladder (a, b) (history of cholecystectomy). Prominent duodenal activity (note: posterior location) and marked gastric activity due to duodenogastric reflux are more apparent on stress raw images (b) compared to rest raw images (a). The gastric activity creates a “bleeding in” artifact involving the adjacent inferolateral myocardial wall on the stress processed images (c). There is normal function on gated SPECT images (d).
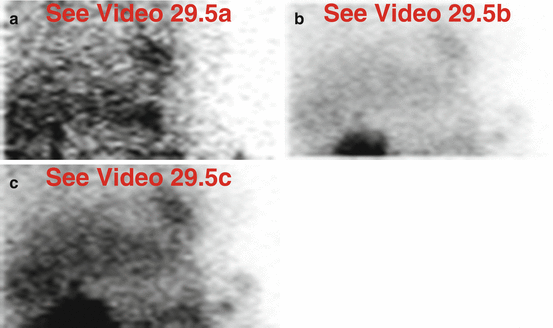
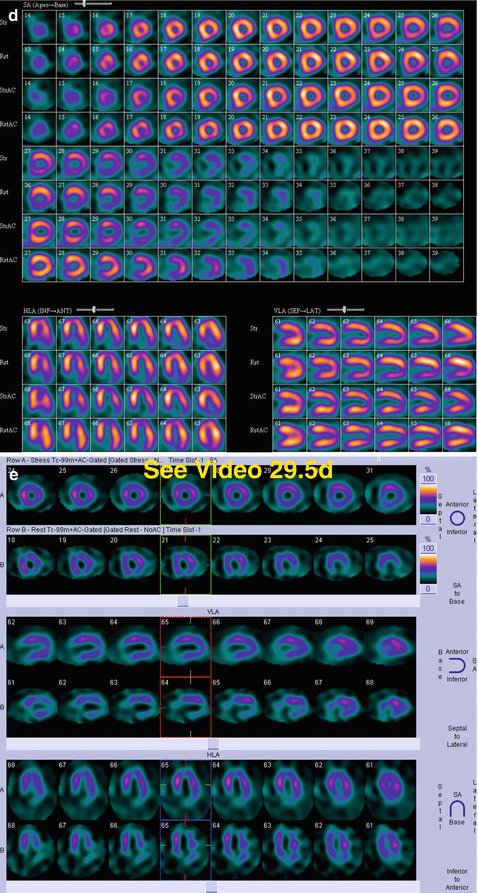
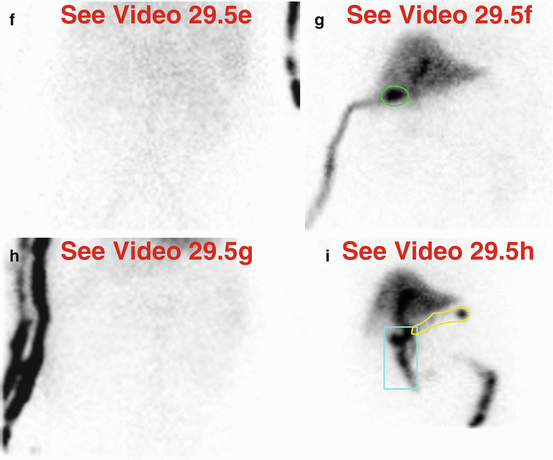
29.5 Case Challenge #29
29.5.1 Problem
Clinical Highlights
A 66-year-old male has a recent abdominal surgical history.