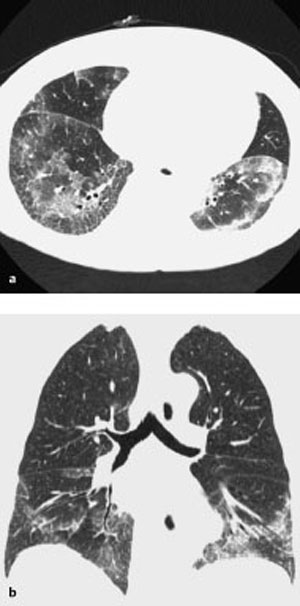
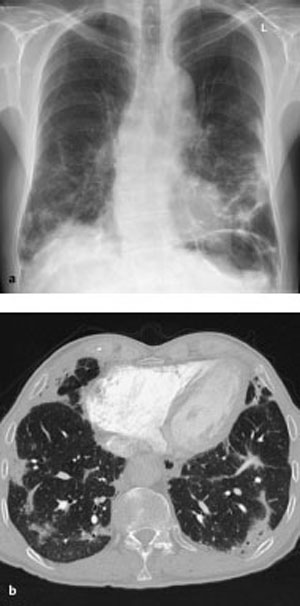
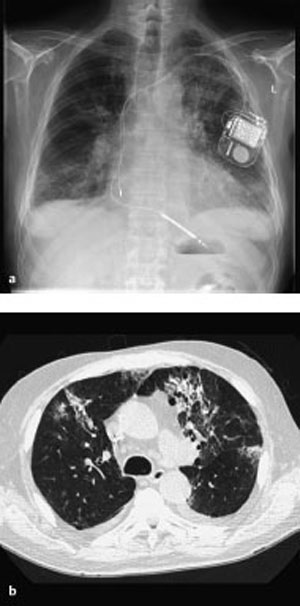
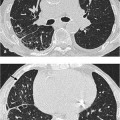
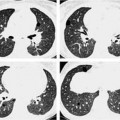
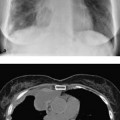
13 Sequelae of Therapy Occurs primarily with chemotherapy agents (in up to 10% of cases), antiarrhythmic agents (amiodarone), and antiseptic agents (nitrofurantoin), etc. Purely toxic or immunologic reaction with variable, unspecific manifestation: Diffuse alveolar damage CT is preferable to plain radiography. – Diffuse alveolar damage: Bilateral ground-glass opacification that may include consolidations – Nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis: Disseminated nodular ground-glass opacities and consolidations in addition to reticular changes, predominantly basal – Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia: Nodular ground-glass opacities and consolidations, predominantly peripheral – Eosinophilic pneumonia: Nodular ground-glass opacities and consolidations, predominantly in the peripheral upper lobes Nonspecific findings Nonspecific symptoms such as fever, malaise, nonproductive cough, and dyspnea of variable severity Alternative treatment. Variable. Tentative diagnosis in conjunction with a suggestive constellation of findings. Fig. 13.1 Sirolimus reaction in a 71-year-old man receiving immunosuppressant macrolide therapy after kidney transplantation. CT shows predominantly basal ground-glass opacities with predominantly interstitial structures similar to findings in nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis. Fig. 13.2 Pulmonary nitrofurantoin reaction in a 73-year-old man. Both the plain chest radiograph (a) and CT (b) show predominantly basal and peripheral nodular consolidations along with streaky densities similar to findings in bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia. Fig. 13.3 Pulmonary amiodarone reaction in a 70-year-old man. a The plain chest radiograph shows heterogeneous interstitial shadowing (mixed pattern of streaky reticular shadows and ground-glass confluent opacities) in the right middle and upper lung fields and in the left upper lung field. b CT also shows a mixed picture—most closely resembling nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis. Areas of normal parenchyma alternate with affected areas. Slight bilateral pleural effusion.
Drug Reaction
Definition
 Epidemiology
Epidemiology
 Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis
Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis
 Unspecific pneumonitis
Unspecific pneumonitis  Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia
Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia  Eosinophilic pneumonia.
Eosinophilic pneumonia.
Imaging Signs
 Modality of choice
Modality of choice
 Radiographic and CT findings
Radiographic and CT findings
 Especially busulfan.
Especially busulfan.
 Especially amiodarone, methotrexate, and carmustine.
Especially amiodarone, methotrexate, and carmustine.
 Especially bleomycin, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, amiodarone, nitrofurantoin, etc.
Especially bleomycin, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, amiodarone, nitrofurantoin, etc.
 Especially nitrofurantoin, penicillamine, antiinflammatory agents, and paraaminosalicylic acid.
Especially nitrofurantoin, penicillamine, antiinflammatory agents, and paraaminosalicylic acid.
 Pathognomonic findings
Pathognomonic findings
 Occurrence of symptoms concurrently with therapy is an important diagnostic criterion.
Occurrence of symptoms concurrently with therapy is an important diagnostic criterion.
Clinical Aspects
 Typical presentation
Typical presentation
 Restrictive ventilation defect.
Restrictive ventilation defect.
 Therapeutic options
Therapeutic options
 Course and prognosis
Course and prognosis
 What does the clinician want to know?
What does the clinician want to know?
Differential Diagnosis
Pneumonic infiltrates | – Morphologically indistinguishable – Clinical findings are crucial to the diagnosis – Biopsy may be indicated |
Pneumonitis, radiation reaction | – Limited to the irradiated field |
Various forms of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia | – Morphologically indistinguishable – An initial clinical situation with no history of medication is crucial to the diagnosis |
Tips and Pitfalls
Pulmonary changes can be misinterpreted as attributable to causes other than medication, especially when they do not occur concurrently with therapy.
Selected References
Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Rossi SE. Drug-induced lung injury. Seminars Roentgenol 2002; 37: 72–81
Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Rossi SE. High-resolution CT of drug-induced lung disease. Radiol Clin North Am 2002; 40: 61–72
Radiation Reaction
Definition
 Epidemiology
Epidemiology
Affects 5–10% of patients receiving radiation therapy in the chest  Depends on the irradiated volume, radiation dose and fractionation, and concurrent chemotherapy
Depends on the irradiated volume, radiation dose and fractionation, and concurrent chemotherapy  Rarely occurs at doses < 30 Gy, nearly invariably at doses > 40 Gy.
Rarely occurs at doses < 30 Gy, nearly invariably at doses > 40 Gy.
 Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis
Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis
Early reaction consists of radiation pneumonitis 1–3 months after therapy and diffuse alveolar damage with an intraalveolar exudate and formation of hyaline membranes  Late reaction consists of radiation fibrosis 6–12 months after therapy or complete recovery.
Late reaction consists of radiation fibrosis 6–12 months after therapy or complete recovery.
Imaging Signs
 Modality of choice
Modality of choice
CT is preferable to plain radiography.
 Radiographic and CT findings
Radiographic and CT findings
Changes are essentially limited to the irradiated volume  Early reaction consists
Early reaction consists  Late reaction occasionally consists of fibrosis with signs of volume loss and development of traction bronchiectasis.
Late reaction occasionally consists of fibrosis with signs of volume loss and development of traction bronchiectasis.
 Pathognomonic findings
Pathognomonic findings
Changes not correlating with specific anatomy and limited to the irradiated field occurring in a time frame consistent with sequelae of radiation therapy.
Clinical Aspects
 Typical presentation
Typical presentation
Often asymptomatic  Symptoms may otherwise include cough, subfebrile temperatures, dyspnea with restrictive ventilation defect, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and leukocytosis.
Symptoms may otherwise include cough, subfebrile temperatures, dyspnea with restrictive ventilation defect, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and leukocytosis.
 Therapeutic options
Therapeutic options
Steroids.
 Course and prognosis
Course and prognosis
Good.
 What does the clinician want to know?
What does the clinician want to know?
Confirmation of the tentative diagnosis.  Follow-up examination in symptomatic patients.
Follow-up examination in symptomatic patients.
Differential Diagnosis
Superinfection | – Not limited to the irradiated field – Clinical aspects – Course under therapy |
Recurrent tumor | – Volume increase – New focal lesions – Peritumoral lymphangitis (can be difficult to distinguish; clinical course is important) |
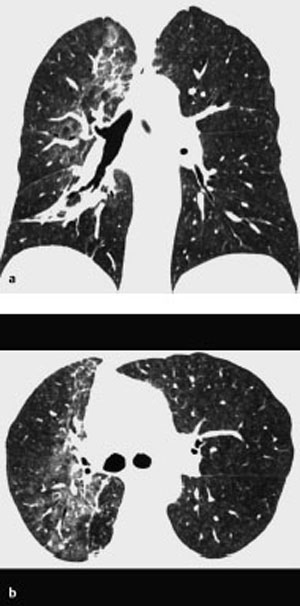
Fig. 13.4 Radiation pneumonitis in a 68-year-old man with bronchial carcinoma in the right lung. CT shows relatively sharply demarcated bandlike ground-glass opacity extending from anterior to posterior. The opacity includes the hilar region and does not respect anatomic boundaries.
Selected References
Choi YW et al. Effects of radiation therapy on the lung: radiologic appearances and differential diagnosis. Radiographics 2004; 24: 985–997
Libshitz HI. Radiation changes in the lung. Semin Roentgenol 1993; 28: 303–320
Reperfusion Edema
Definition
 Epidemiology
Epidemiology
Direct sequela of lung transplantation, occurring in about 50% of cases.
 Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis
Etiology, pathophysiology, pathogenesis
Occurs within 48 hours of transplantation  Sequela of increased capillary permeability because of ischemia, impaired lymph drainage, and surfactant deficiency
Sequela of increased capillary permeability because of ischemia, impaired lymph drainage, and surfactant deficiency  Leads to interstitial and alveolar edema.
Leads to interstitial and alveolar edema.
Imaging Signs
 Modality of choice
Modality of choice
Radiographs  CT is not indicated as primary modality.
CT is not indicated as primary modality.
 Radiographic and CT findings
Radiographic and CT findings
Canges due to edema include: Increased reticular shadowing  Bronchial wall
Bronchial wall  Ground-glass opacity.
Ground-glass opacity.
 Pathognomonic findings
Pathognomonic findings
Findings are nonspecific and are distinguishable from acute rejection or infection only by the time of their occurrence and their clinical course (see below).
Clinical Aspects
 Typical presentation
Typical presentation
Hypoxemia.
 Therapeutic options
Therapeutic options
Oxygen administration  Avoid excessive hydration.
Avoid excessive hydration.
 Course and prognosis
Course and prognosis
Resolves within a week  Persistent or progressive findings suggest complications (acute transplant failure, rejection, infection).
Persistent or progressive findings suggest complications (acute transplant failure, rejection, infection).
 What does the clinician want to know?
What does the clinician want to know?
Detection, localization, and extent of findings  Exclude pulmonary venous obstruction.
Exclude pulmonary venous obstruction.
Differential Diagnosis
Early transplant failure | – Radiographically indistinguishable – Progressive hypoxia |
Acute rejection | – Manifests later, with a different course: new or progressive shadows 5–6 days after lung transplantation – Fever – Dyspnea – Hypoxia – Diagnosis by biopsy |
Infection | – Manifests later, with a different course Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|