Silicosis, Simple
Melinda Z. Rixey, MD
Aqeel A. Chowdhry, MD
Tan-Lucien H. Mohammed, MD, FCCP
Key Facts
Terminology
Simple pneumoconiosis: Micronodules < 1 cm develop more than 10 years after long-term occupational exposure
Acute silicoproteinosis
Rare fulminant respiratory complication of intense exposure to silica dust (typically sandblasting)
Appears within 6 months to 3 years after initial exposure
Caplan syndrome
Seropositive rheumatoid arthritis associated with pneumoconiosis (coal, silica, or asbestos)
Imaging Findings
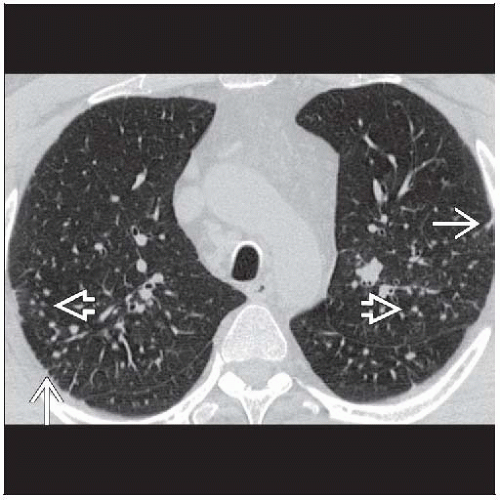
Micronodules < 10 mm in centrilobular and subpleural distribution
More profuse in dorsal aspect of upper lobes, right side more severely involved than left
Silicoproteinosis: May have “crazy-paving” pattern (identical to alveolar proteinosis)
Symmetric enlargement (75%) of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes, generally < 3 cm in diameter
Patterns of calcification: Punctate > diffuse > “eggshell”
Caplan syndrome
Multiple large nodules usually < 5 cm in diameter (may cavitate or calcify)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Sarcoidosis
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Talcosis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Simple pneumoconiosis, anthracosis, anthracosilicosis
Definitions
Lung disease due to inhalation of inorganic mineral dusts containing crystalline silicone dioxide (quartz)
Simple pneumoconiosis: Micronodules < 1 cm develop more than 10 years after long-term occupational exposure
Acute silicoproteinosis
Rare fulminant respiratory complication of intense exposure to silica dust (typically sandblasting)
Appears within 6 months to 3 years after initial exposure
Caplan syndrome
Seropositive rheumatoid arthritis associated with pneumoconiosis (coal, silica, or asbestos)
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Centrilobular and subpleural nodules in upper lung zones
Patient position/location
Rounded dusts like silica and coal predominantly affect dorsal aspect of upper lung zones
Silica accumulates along lymphatics in centriacinar portion of lobule and lobule periphery
Size: Micronodules (< 10 mm in diameter)
CT Findings
More sensitive than chest radiography for detection of nodules
Lung
Micronodules < 10 mm in centrilobular and subpleural distribution
More profuse in dorsal aspect of upper lobes, right side more severely involved than left
Distribution due to accumulation of silicotic nodules in pulmonary lymphatics
Silicotic nodules tend to be more sharply defined than in coal worker’s pneumoconiosis (CWP)
Calcification of nodules (3%)
Chains of subpleural nodules produce pseudoplaques
Subpleural nodules rounded or triangular in configuration
Caplan nodules larger, up to 5 cm in diameter
May cavitate or calcify
Nodules peripheral and subpleural in location; cavitation may produce pneumothorax
May evolve quickly, occasionally disappear
Small branching centrilobular structures
May be early sign of disease
Due to reaction to deposited silica in small airways (mineral dust airways disease)
Pathologically represents fibrosis around respiratory bronchioles
May have air-trapping with expiratory scanning
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree