Institute (year)
Histology
Modalities
No. of patients
5-year LC
5-year OS
RMH (1944–1988)
Soft tissue sarcoma
R, C
17
21
36
MGH (1972–1993)
Soft tissue sarcoma
R, C
14
55
63
UCSF (1961–1993)
Soft tissue sarcoma
R, C
5
0
9
NCI (1985–1996)
Osteosarcoma
R, C
71
–
22
LBL (1977–1992)
Bone and Soft tissue sarcoma
Helium ion radiotherapy
19
58
71
NIRS (2001–2012)
Bone and Soft tissue sarcoma
Carbon ion radiotherapy
42
73
53
17.6 Case Studies
17.6.1 Case 1
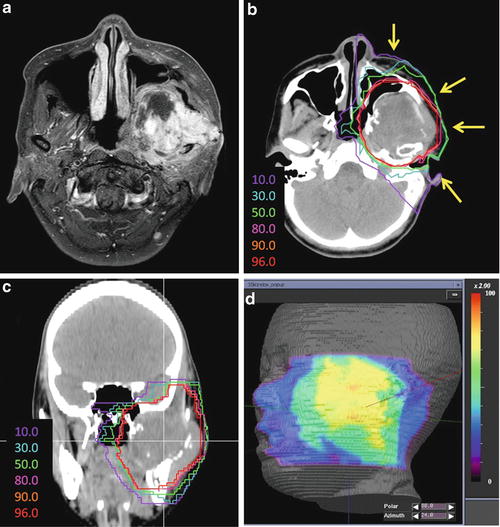
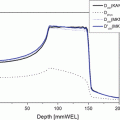
A 32-year-old woman presented with osteosarcoma of the mandible. Imaging examination revealed a tumor in the pterygopalatine fossa with intracranial invasion (Fig. 17.1a). The tumor had a maximum diameter of 66 mm. This patient was deemed inoperable and received chemotherapy. After a cycle of chemotherapy, the tumor did not show any change in size. Then, the patient was referred to our hospital for C-ion RT. Determination of the GTV was based on T1-weighted and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted and T2-weighted MRI obtained using image fusion technique. The CTV had minimum margins of 5–10 mm added to the GTV. The margin for the brain and skin was reduced as much as possible. Four portals were used mainly to avoid severe skin reaction. Because only two fixed beams (horizontal and vertical directions) were available, the patient was immobilized in a supine or oblique position to spare the critical organs. C-ion RT was administered at 70.4 GyE/16 fractions (Fig. 17.1b, c). The maximum dose to the skin was reduced to less than 80 % of the prescribed dose (Fig. 17.1d). The patient developed asymptomatic brain necrosis; however, 6 years later, she is without any disease.