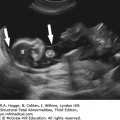
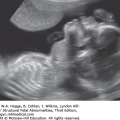
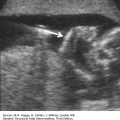
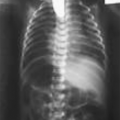
Aarskog syndrome (X-linked recessive)
Hypertelorism
Short nose
Clinodactyly
Brachydactyly
Aase syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Radial hypoplasia
Cleft palate
Ventricular septal defect
Urogenital anomalies
Acrocallosal syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Agenesis of corpus callosum
Intracranial cysts
Hypertelorism
Macrocephaly
Polydactyly—postaxial
Acrofacial dysostosis, Miller syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Malformed ears
Micrognathia
Cleft lip/palate
Absent digits, usually the fifth digits
Radial hypoplasia
Acromesomelic dysplasia (autosomal recessive)
Mesomelic (forearm/lower leg) shortness
Bowed radius
Adams-Oliver syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Absent digits
Encephalocele
Microcephaly
Cardiac defects
Clubfoot
Intrauterine growth restriction
Aicardi syndrome (X-linked dominant)
Agenesis of corpus callosum
Arachnoid cyst
Dandy-Walker malformation
Ventriculomegaly
Microcephaly
Microphthalmia
Amyloplasia congenita (sporadic)
Gastroschisis
Micrognathia
Clubfoot
Joint contractures
Decreased fetal movement
Atelosteogenesis (autosomal dominant)
Small chest
Eleven pairs of ribs
Hypertelorism
Cleft lip and palate
Micrognathia
Absent humeri
Absent fibula
Bowed tibia
Clubfoot
Rhizomelic (proximal) shortening
Intrauterine growth restriction
Polyhydramnios
Baller-Gerold syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Malformed kidney
Mild ventriculomegaly
Hypotelorism
Micrognathia
Absent digits
Abnormal or absent thumb
Radial hypoplasia
Intrauterine growth restriction
Renal abnormalities
Basal cell nevus (Gorlin) syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Macrocephaly
Calcifications in falx cerebri
Ventriculomegaly—mild
Beals syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Joint contractures
Cardiac defects
Boomerang dysplasia (autosomal dominant)
Bowing
Severe micromelia
Hypertelorism
Clubfeet
Polyhydramnios
Branchio-oto-renal (Melnick-Fraser) syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Malformed ears
Renal abnormalities
CHARGE association (autosomal dominant)
Esophageal atresia
Cardiac abnormality
Anophthalmia
Holoprosencephaly
Cleft palate
Micrognathia
Genital hypoplasia
Chondrodysplasia punctata (X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive, autosomal recessive)
Small chest
Joint contractures
Rhizomelic shortening
Hydrops
Stippled epiphyses
Chromosome: 18p-
Holoprosencephaly
Hypotelorism
Clubfoot
Cardiac abnormalities
Chromosome: 18q-
Microphthalmia/anophthalmia
Microcephaly
Chromosome: 47,XXY
Increased nuchal translucency
Chromosome: 4p- (Wolf-Hirschhorn)
Hypertelorism
Cardiac abnormality
Cleft lip/palate
Micrognathia
Malformed ears (tags)
Intrauterine growth restriction
Microcephaly
Cleidocranial dysplasia (autosomal dominant)
Partial or total aplasia of the clavicles
Brachycephaly
Hypertelorism
Congenital muscular dystrophy (autosomal recessive)
Clenched hands
Muscle wasting
Congenital nephrotic syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Polyhydramnios
Hydrops
Placentomegaly
Cornelia de Lange syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Cardiac abnormality
Dandy-Walker malformation
Microcephaly
Short nose
Midface hypoplasia
Abnormal thumb
Absent digits
Absent limbs
Clinodactyly
Radial hypoplasia
Short limbs
Hydrops
Intrauterine growth restriction
Cri-du-chat (5p deletion) syndrome
Microcephaly
Micrognathia
Cardiac malformation
Facial abnormalities, such as cleft lip and palate
Hypoplastic cerebellum
Increased nuchal translucency
Intrauterine growth restriction
Diabetic embryopathy
Duodenal atresia
Malformed kidney
Renal agenesis
Cardiac abnormality
Holoprosencephaly
Spinal dysraphism
Vertebral defects
Cleft lip/palate
Macrosomia
Polyhydramnios
Dyssegmental dysplasia (autosomal recessive)
Bowing
Severe shortening of all limbs
Vertebral abnormalities
Cleft palate
Ectrodactyly-ectodermal-dysplasia-clefting syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Hydronephrosis
Cleft lip with or without cleft palate
Absent digits
Absent limbs
Clinodactyly
Renal anomalies
Holoprosencephaly
Ectrodactyly–tibial aplasia syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Abnormal thumbs
Absent digits
Tibial aplasia
Bifurcation of femora
Ulna hypoplasia
Ellis–Van Creveld syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Renal agenesis
Cardiac abnormalities
Small chest
Clubfoot
Polydactyly—postaxial
Dandy Walker malformation
Short limbs
Intrauterine growth restriction
Fanconi syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Cardiac abnormality
Thumb hypoplasia/aplasia
Microcephaly
Radial hypoplasia
Renal abnormalities
Absent cavum septum pellucidum
Cardiac defects
Fetal infections
Echogenic bowel
Echogenic brain foci
Hepatic calcifications
Microcephaly
Limb abnormalities (varicella)
Mild ventriculomegaly
Cataracts
Microphthalmia
Hydrops
Intrauterine growth restriction
Thick placenta
Fetal methotrexate embryopathy
Mesomelic shortness
Micrognathia
Intrauterine growth restriction
Clubfeet
Cleft palate
Neural tube defects
Fetal warfarin syndrome
Nasal hypoplasia
Rhizomelic shortening
Intrauterine growth restriction
Stippled epiphyses
Fibrochondrogenesis (autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive)
Small chest
Rhizomelic shortening
Cleft palate
Hydrops
Intrauterine growth restriction
Omphalocele
Fraser syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Microphthalmia or anophthalmia
Syndactyly
Genital abnormalities
Laryngeal atresia
Malformations of the nose and ear
Renal agenesis
Freeman-Sheldon syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Micrognathia
Ulnar deviation of hands
Clenched hands
Clubfoot
Joint contractures
Microcephaly
Frontonasal dysplasia sequence (autosomal recessive in some forms)
Frontal bone defect
Median cleft lip
Hypertelorism
Grebe syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Acromesomelia
Absent limbs
Polydactyly—preaxial
Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Macrocephaly
Hypertelorism
Abnormal thumb
Hands: polydactyly—postaxial
Feet: polydactyly—preaxial
Absence of the corpus callosum
Ventriculomegaly
Harlequin icthyosis (autosomal recessive)
Open mouth with large tongue
Clenched or fixed hands
Limbs in fixed positions
Holt-Oram syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Cardiac abnormality
Abnormal thumb
Absent digits
Absent limbs
Clinodactyly
Radial hypoplasia
Hydrolethalus (autosomal recessive)
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Microphthalmia or anophthalmia
Polydactyly—postaxial
Ventriculomegaly
Polyhydramnios
Micrognathia
Cleft palate
Heart defect
Clubfoot
Hypophosphatasia (autosomal recessive)
Small chest
Easily visualized brain structures
Bowed limbs
Moderate-to-severe bone shortening
Diffuse hypomineralization
Polyhydramnios
Ivemark syndrome (usually sporadic)
Situs inversus
Complex heart defect
Polysplenia
Renal abnormalities
Jackson-Weiss syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Exophthalmos/proptosis/prominent eyes
Facial asymmetry
Jacobsen syndrome (sporadic unless a parent has a balanced translocation)
Trigonocephaly
Microcephaly
Hypertelorism
Micrognathia
Cardiac defects
Jarcho-Levin syndrome, spondylocostal dysostosis (autosomal recessive)
Malaligned and malformed vertebra
Fan-shaped ribs
Severe shortening of the spine
Joubert syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Cerebellar hypoplasia
Dandy-Walker malformation
Renal abnormalities
Micrognathia
Polydactyly
Klippel-Feil sequence (sporadic)
Vertebral defects
Congenital heart defects
Cleft palate
Kniest syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Short limbs
Kyphoscoliosis
Platyspondyly
Hypoplastic pelvic bones
Cleft palate
Larsen syndrome (autosomal dominant and recessive)
Clubfoot
Abnormal vertebral segmentation with kyphoscoliosis
Hypertelorism
Micrognathia
Joint dislocation
Cleft palate (autosomal dominant form)
Lenz syndrome (X-linked recessive)
Microcephaly
Renal aplasia/hypoplasia
Microphthalmia
Marden-Walker syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Microcephaly
Micrognathia
Cleft palate
Clubfeet
Joint contractures
Renal cysts
Intrauterine growth restriction
Maternal phenylketonuria
Cardiac abnormality
Microcephaly
Intrauterine growth restriction
McKusick-Kaufman syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Hydronephrosis
Cardiac abnormality
Polydactyly—postaxial
Hydrometrocolpos (midline lower abdominal mass containing echogenic debris that is due to vaginal atresia/stenosis)
Other genitourinary anomalies
Anorectal atresia
Megacystis megaureter (sporadic)
Hydronephrosis
Large thick-walled bladder
Dilated ureters
Mostly male
Megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome (possibly autosomal recessive)
Large bladder without wall thickening
Polyhydramnios
Dilated small bowel
Mostly female
Melnick-Needles syndrome (X-linked dominant)
Exophthalmos
Micrognathia
Bowing of humerus, radius, ulna, tibia
Small chest
Miller-Dieker syndrome (17p13.3 deletion may be de novo or inherited from a parent with a balanced translocation)
Micrognathia
Clinodactyly
Absent parieto-occipital fissure
Abnormal sylvian fissure
Lissencephaly-only complete agyria can be diagnosed in utero (should not be considered until after 20 weeks’ gestation)
Ventriculomegaly
Microcephaly
Intrauterine growth restriction
Polyhydramnios
Absence of the corpus callosum
MURCS (müllerian duct aplasia, renal aplasia, cervicothoracic somite dysplasia) association (sporadic)
Upper spine vertebral deformities
Absence or hypoplasia of uterus
Enlarged fetal bladder
Renal agenesis/ectopy
Cystic umbilical cord due to patent urachus
Oligohydramnios
Female fetus
Nager acrofacial dysostosis (autosomal dominant)
Micrognathia
Cleft palate
Deformed ears
Absent or hypoplastic thumb
Neu-Laxova syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Intrauterine growth restriction
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Cerebellar hypoplasia
Lissencephaly
Microcephaly with sloping forehead
Cataract
Exophthalmos/proptosis/prominent eyes with hypertelorism
Extreme puffiness of hands and feet
Clenched hands
Joint contractures
Rocker-bottom feet
Micrognathia with flat nose
Malformed ears
Congenial heart disease
Noonan syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Cardiac abnormality—pulmonary stenosis
Other cardiac defects
Cystic hygroma
Hypertelorism
Hemivertebrae
Oculodentodigital syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Microphthalmia or anophthalmia
Aplasia of one or more fingers or toes
Opitz G/BBB syndrome (autosomal dominant, X-linked recessive)
Hypertelorism
Hypospadias
Cleft lip with or without cleft palate
Micrognathia
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Genital abnormality
Oral-facial-digital syndrome type I (X-linked dominant)
Renal cystic disease
Median cleft lip and palate
Abnormal digits
Clinodactyly
Polydactyly—preaxial of feet
Oromandibular limb hypogenesis spectrum (sporadic)
Absent digits
Absent limbs
Micrognathia
Cleft palate
Syndactyly
Otocephaly (likely sporadic)
Hypoplasia or absence of the mandible and tongue
Agnathia
Cleft palate
Polyhydramnios
Otopalatodigital syndrome (X-linked with intermediate expression in females)
Hypertelorism
Cleft palate
Small thorax
Bowed tibia
Pallister-Hall syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Intracranial tumor—hypothalamic hamartoblastoma
Polydactyly—postaxial
Imperforate anus
Poland sequence (sporadic)
Absent digits
Absent or hypoplastic upper limb
Syndactyly
Proteus syndrome (sporadic)
Macrodactyly
Soft tissue masses
Variable-size limbs
Macrocephaly
Nephromegaly
Retinoic acid embryopathy
Cardiac abnormalities
Cerebellar hypoplasia
Microcephaly
Ventriculomegaly
Microtia
Micrognathia
Hypertelorism
Roberts syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Hypomelia, more severe in upper extremities
Phocomelia
Absent digits
Absent limbs
Cleft lip with or without cleft palate
Hypertelorism
Cardiac abnormality
Encephalocele
Cataract
Clinodactyly
Severe intrauterine growth restriction
Genitourinary anomaly
Robinow syndrome (autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant)
Hypertelorism
Cleft lip with or without cleft palate
Micrognathia
Midface hypoplasia
Macrocephaly
Hemivertebrae
Fused/missing ribs
Genital abnormalities
Shortened long bones
Cardiac defects
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (sporadic)
Broad thumbs with radial angulation
Microcephaly
Renal abnormalities
Cardiac defects
Russell-Silver syndrome (sporadic)
Asymmetrical intrauterine growth restriction with normal-size head
Asymmetric short long bones
Micrognathia
Clinodactyly
Saethre-Chotzen syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Exophthalmos/proptosis/prominent eyes
Hypertelorism
Facial asymmetry
Craniosynostosis
Frontal bossing
Small ears
Syndactyly
Broad/duplicated large toe
Seckel syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Microcephaly
Micrognathia
Clinodactyly
Intrauterine growth restriction
Simpson-Golabi-Behnel syndrome (X-linked recessive)
Macrosomia
Polyhydramnios
Macrocephaly
Macroglossia
Polydactyly—postaxial
Sotos syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Dolichocephaly
Macrocephaly
Frontal bossing
Macrosomia
Ventriculomegaly
Absence of the corpus callosum
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita (autosomal dominant)
Small chest
Cleft palate
Short limbs
Short spine with vertebral abnormalities
Kyphoscoliosis
Platyspondyly
Clubfeet
Intrauterine growth restriction
Stickler syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Cleft palate
Micrognathia
Cataracts
Scoliosis
Clubfoot
Thalidomide embryopathy
Absent limbs
Phocomelia
Cardiac defects
Microtia
Renal abnormalities
Gastrointestinal atresias
α-Thalassemia
Hydrops
Thrombocytopenia—absent radius (TAR) syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Absent radius bilaterally
Ulnar abnormalities
Cardiac abnormality
Absent limbs
Clubfoot
Renal abnormalities
Townes-Brock syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Facial asymmetry
Malformed ears
Abnormal thumb
Absent digits
Polydactyly—preaxial
Renal agenesis
Multicystic dysplastic kidneys
Duodenal atresia
Walker-Warburg syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Absent cavum septum pellucidum
Dandy-Walker malformation
Encephalocele
Lissencephaly
Mild ventriculomegaly
Cataracts
Microphthalmia or anophthalmia
Weaver syndrome (autosomal dominant)
Macrosomia
Micrognathia
Camptodactyly
Clubfoot
Cardiac defects
Williams syndrome (usually sporadic but transmitted from parent to child)
Cardiac defects—supravalvular aortic stenosis
Other cardiac defects
Renal abnormalities
Mild intrauterine growth restriction
Zellweger syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Renal cystic disease
Cataracts
Clubfoot
Joint contractures
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Cardiac defects-septal defects
Decreased fetal movement
Stippled epiphyses
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree