CPT code
Description
Medicare allowable – nonfacility
Medicare allowable – facility
Total
64505
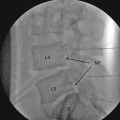
Injection, anesthetic agent; sphenopalatine ganglion
$113.59
$92.39
$205.98
64510
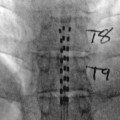
Injection, anesthetic agent; stellate ganglion (cervical sympathetic)
$165.05
$75.59
$240.64
64400
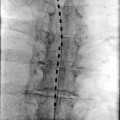
Injection, anesthetic agent; trigeminal nerve, any division or branch
$129.45
$71.02
$200.47
Summary
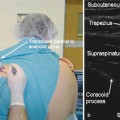
The sphenopalatine ganglion is located in the upper reaches of the nasopharynx and represents the most superior contribution of the superior sympathetic ganglion. Blockade of the sphenopalatine ganglion is easily achieved by a variety of techniques of increasing complexity, and it is deemed useful in the management of various pain syndromes of the head particularly migraine headache. Case series and observational studies have demonstrated its utility for treatment of painful syndromes, with the based designed study reaching 1C level of utility. While future studies should indeed be conducted to determine the exact indications and patient characteristics specific utility of the block, current practice provides a relatively safe and putatively effective treatment strategy for headache and facial pain. Local anesthetic blockade of the ganglion via the anterior nares approach is readily accomplished and serves as a therapeutic trial to determine whether more invasive and perhaps longer lasting treatment such as radiofrequency lesioning should be considered. The magnitude of patient suffering from migraine and facial pain and its societal implications with regard to economics and overall productivity should be a strong impetus to utilize sphenopalatine blockade via the multiple approaches until the definitive studies demonstrate the best algorithm for treatment.
References
1.
Sluder G. The role of the sphenopalatine (or Meckel’s) ganglion in nasal headaches. N Y Med J. 1908;87:989–90.
2.
Saade E, Paige GB. Patient-administered sphenopalatine ganglion block. Reg Anesth. 1996;21(1):68–70.PubMed
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.