14 The Sono Consultant
The tables in this chapter serve as a “sono consultant”—a systematic framework for helping the examiner to evaluate specific ultrasound findings and make a differential diagnosis.
The chapter consists of two parts, which represent the situations that beginners will most often encounter in ultrasound examinations:
Part I: The examiner sees an abnormality at ultrasound and wants to analyze it in a systematic way.
Part II: The examiner is consulted for the ultrasound evaluation of a specific clinical situation.
Part I, Ultrasound Findings, provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach for systematically analyzing an abnormality that is noted during an ultrasound examination.
Part II, Clinical Presentation, offers guidelines for interpreting findings and extracting the maximum amount of information that ultrasonography can supply in a given clinical situation.
Both parts deal with the most common sonographic findings and clinical situations that arise in diagnostic ultrasonography. Of course, the exact sequence of steps for interpreting ultrasound findings will vary considerably from one examiner to the next. The goal of this chapter is to provide the beginner with a logical, structured routine that will train and reinforce a complete, systematic ultrasound examination.
I Ultrasound Findings
1. Aorta: Widening
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify, measure in two dimensions | |
| < 25mm | Normal |
| 25–30mm | Ectasia |
| > 30mm | Aneurysm |
| > 50mm | High risk of rupture |
| Full-length visualization of the aorta | |
| Longitudinal shape
|
Kinked? |
| Wall
|
Aortic sclerosis? |
| Lumen
|
Thrombus?
Dissecting aneurysm |
| Location
– Suprarenal – Infrarenal? |
|
| Aortic branches
|
|
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify, measure | |
| < 20mm in late inspiration and end expiration | Normal |
| > 20mm | Suspicious for abnormal dilatation Stasis? |
| Pulsation, respiration, lumen | |
| Double-beat pattern synchronous with the pulse
|
Physiologic dilation? Young, thin patient? Stasis? |
Luminal change with respirations Present Present Not present Not present |
Physiologic dilation? Stasis? |
Lumen Echo-free Echo-free Echogenic Echogenic |
Stasis? Thrombus? |
| Other signs of congestive failure | |
Visualization of all vena cava tributaries Hepatic veins Hepatic veins Renal veins Renal veins Iliac vessels Iliac vessels |
|
Liver Echo pattern Echo pattern Borders Borders Size Size |
|
| Ascites? | |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify enlargement, measure | |
| Measure in medioclavicular line (MCL), left lobe Caudate lobe |
Liver enlarged? Thoracic emphysema? Riedel lobe? |
| Shape of liver, borders | |
| Rounded inferior border | Fatty liver? |
| Increased inferior angle | Liver fibrosis? Hepatic cirrhosis? |
| Echo pattern | |
| Hyperechoic | Fatty liver? Fibrosis? Alcoholic cirrhosis? Chronic hepatitis? |
| Hypoechoic | Acute hepatitis? Congested liver? |
| Inhomogeneous | Disseminated metastasis? |
| Hepatic veins | |
| Narrowed | Fatty liver? Fibrosis? Alcoholic cirrhosis? |
| Dilated | Congested liver? |
| Associated findings | |
| Ascites | |
| Pleural effusion | Congested liver? |
| Splenomegaly | |
| Prominent vena cava | |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify, measure | |
| Liver 15–16 cm in MCL, normal size | Elevation of the diaphragm? |
| Liver small | Cirrhosis? |
| Shape of liver | |
| Posterior surface wavy, nodulated | Posthepatic cirrhosis? |
| Rounded inferior border | Alcoholic cirrhosis? |
| Echogenicity | |
| Hyperechoic | Alcoholic cirrhosis? |
| Coarsely granular, speckled | Hepatitis? |
| Vessels | |
| Portal vein: pruning Hepatic veins: narrowed or irregular |
Hepatic cirrhosis? |
| Circumscribed changes | |
| Masses | Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)? |
| Additional or associated findings | |
| Ascites? Widening or portal vein or splenic vein? Large spleen? Recanalized umbilical vein? Thickening of gallbladder wall? Pleural effusion? |
|
5. Liver: Increased echogenicity
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify | |
| Hyperechoic to kidney | Increased density |
| Posterior acoustic shadowing | Increased density |
| Size of liver | |
| Large or normal | Fatty liver? Fibrosis? Cirrhosis? Congested liver? Disseminated metastasis? Disseminated HCC? Lymphoma? |
| Small | Cirrhosis? Disseminated HCC? |
| 5.1 Liver: Increased echogenicity, liver large | |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Echo pattern | |
| Homogeneous | Fatty liver? (alcohol, diabetes mellitus, hypertriglyceridemia, obesity, drugs, pregnancy) Fibrosis? Cirrhosis? |
| Inhomogeneous | Disseminated metastasis? Disseminated HCC? Lymphoma? Fatty infiltration or sparing? Congested liver? |
| Shape | |
| Inferior angle rounded, blunted, irregular, nodular | Alcoholic cirrhosis? Disseminated metastasis? |
| Hepatic veins | |
| Narrow | Fibrosis? Cirrhosis? |
| Broad | Congested liver? |
| 5.2 Increased echogenicity, liver small | |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Echo pattern | |
| Homogeneous | Cirrhosis? |
| Inhomogeneous | Disseminated metastasis? |
| Hepatic veins | |
| Narrow | Cirrhosis? |
6. Liver: Hepatic veins dilated
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify | |
| < 5 mm before termination at vena cava | Normal? |
| > 5 mm before termination at vena cava | Dilated? |
| Position-dependent lumen changes | |
| Present | Physiologically large hepatic veins (young patients) |
| Not present | Congestion? |
| Liver size | |
| Large | Acute congestion? |
| Normal size | Chronic congestion? |
| Small | Chronic congestion? Cardiac cirrhosis? |
| Echo pattern | |
| Slightly echogenic | Acute congestion? |
| Moderately echogenic | Chronic congestion? |
| Very echogenic | Chronic congestion? |
| Other findings | |
| Ascites, pleural effusion, splenomegaly | Congestive failure? |
7. Liver: Circumscribed mass
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Echogenicity | |
| Echo-free | See below |
| Hypoechoic | See p. 255 |
| Isoechoic | See p. 256 |
| Hyperechoic | See p. 257 |
| Hyperechoic with acoustic shadow | See p. 257 |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify, check cystic criteria | |
| No internal echoes, posterior enhancement, edge shadows | Fluid-filled mass, cyst |
| Shape | |
| Rounded | Simple cyst? |
| Scalloped | Hydatid cyst? |
| Irregular | Abscess? Necrotic tumor? |
| Margins | |
| Sharp, thin | Simple cyst |
| Sharp, echogenic, calcifications | Hydatid cyst? |
| Indistinct, blurry | Abscess? |
| Irregular | Hematoma? |
| Internal echoes | |
| Septa | Hydatid cyst? |
| Inhomogeneous areas | Abscess? |
| Echo-free | Simple cyst? |
| Location | |
| Intrahepatic | Hepatic cyst? |
| Inferior hepatic border | Gallbladder? Choledochal cyst? Cavernous transformation? |
| Other findings: number, size | |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Shape | |
| Rounded | Lymphoma? |
| Adenoma? | |
| Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)? | |
| Metastasis? | |
| HCC? | |
| Scalloped | Metastasis? |
| HCC? | |
| FNH? | |
| Irregular | Abscess? |
| Hematoma? | |
| Infarction? | |
| Focal fatty sparing? | |
| Echo pattern | |
| Homogeneous | Hemangioma? Lymphoma? |
| Inhomogeneous | Metastasis? HCC? Lymphoma? |
| Hypoechoic rim | Metastasis? HCC? |
| Margins, outline | |
| Smooth, sharp | Adenoma? FNH? HCC? |
| Lymphoma? Metastasis? | |
| Focal fatty sparing? | |
| Indistinct | Infarction? Hematoma? Abscess? |
| Number | |
| Solitary | Infarction? Abscess? Adenoma? FNH? HCC? |
| Hematoma? | |
| Multiple | Metastases? |
| Numerous | Metastases? Lymphomas? |
| Other findings | |
| Signs of cirrhosis, search for primary tumor (pancreas, kidney, gallbladder, bowel, gynecologic tumor, ascites) |
|
10. Liver: Isoechoic or hyperechoic mass
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Shape | |
| Rounded | FNH? HCC? Metastasis? Hemangioma? |
| Irregular, polygonal | HCC? Zonal fatty infiltration? Round ligament? |
| Echo pattern | |
| Homogeneous | Hemangioma? |
| Inhomogeneous | Hemangioma? Metastasis? HCC? |
| Margins | |
| Smooth, sharp | Hemangioma? Adenoma? HCC? Lymphoma? Metastasis? Zonal fatty infiltration? |
| Number | |
| Solitary | HCC? Adenoma? FNH? |
| Multiple | Metastases? |
11. Liver: Hyperechoic mass with an acoustic shadow
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Shape | |
| Rounded | Metastasis? Hemangioma? Calcification? |
| Irregular, polygonal | Metastasis? Round ligament? |
| Echo pattern | |
| Homogeneous | Round ligament? Hemangioma? Calcification? |
| Inhomogeneous | Metastasis? |
| Number | |
| Solitary | Hemangioma? Round ligament? |
| Multiple | Metastases? Calcifications? Hemangiomas? |
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify | |
| Floating bowel loops | Ascites? |
| Absence of floating bowel loops | Ovarian cyst? Cystic ovarian tumor? |
| Check sites of predilection | |
| Morrison’s pouch Perihepatic Perisplenic Retrovesical |
Ascites? |
| Sites of predilection are clear | Ovarian cysts? Cystic ovarian tumor? |
| Investigate cause | |
| Signs of cirrhosis Portal vein dilated Splenic vein dilated Splenomegaly |
Hepatic cirrhosis? |
| Hepatic veins dilated | Congestive failure? Budd–Chiari syndrome? |
| Signs of pancreatitis | Pancreatitis? |
| Signs of peritonitis | Bowel obstruction? Peritonitis? |
Mass in Liver Liver Gallbladder Gallbladder Pancreas Pancreas Bowel Bowel Lymph nodes Lymph nodes |
Malignant tumor? |
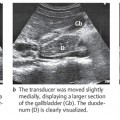
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify | |
| Hard echo | Stone? Air in duodenum? |
| Acoustic shadow: no | Cholesterol polyp? |
| Acoustic shadow: yes | Cystic edge shadow? Artifact in gallbladder neck? Kinked gallbladder? |
| Mobility | Gravel? Stone? |
| Stone characterization Size, number, location, ultrasound appearance |
|
| Hard, crescent-shaped echo | Heavy calcification |
| Hard entry echo, moderate internal echoes | Moderately heavy calcification |
| Soft entry echo, marked internal echoes | Slight calcification Cholesterol stone? |
| Inhomogeneous with some hard internal echoes, irregular outline | Pigment stone? |
| Gallbladder size | |
| Small | Shrunken gallbladder? Contraction? |
| Normal | Uncomplicated stone? |
| Enlarged (see p. 262) | Hydrops? Empyema? |
| Gallbladder wall | |
| Normal | Uncomplicated stone |
| Thickened (see p. 261) | Cholecystitis? Neoplasm? |
| Compressibility | |
| Compressible, painless | Uncomplicated stone |
| Poorly compressible, painful | Hydrops? Empyema? |
| Biliary tract | |
| Stone in the gallbladder neck | Stone with check-valve mechanism? |
| Stone in common duct, dilated commonduct | Choledocholithiasis? |
| Gallbladder function | |
| Fluid-filled lumen | Uncomplicated stone? |
| No detectable residual lumen | Contraction? Shrunken gallbladder? Completely filled with stones? |
| Contracts in response to stimulus | Functional gallbladder? |
| No contractions | Nonfunctioning gallbladder |
| Other findings | |
| Signs of pancreatitis? | Chologenic pancreatitis? |
14. Gallbladder: Circumscribed wall changes
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Visualize in two planes | |
| Patchy | Crease due to fold? Septum? Heister valve? |
| Spherical structure | True mural lesion? |
| Mobility | |
| Yes | Stone? (see p. 259) Polypoid sludge? |
| No | Mural lesion |
| Size | |
| <5mm | |
| >5mm | |
| >10mm | Cholesterol polyp? Adenoma? Adenoma? Carcinoma? |
| Contact with wall | |
| Pedunculated | Cholesterol polyp? |
| Sessile | Adenoma? Carcinoma? |
| Echogenicity | |
| Hyperechoic | Cholesterol polyp? Incrusted stone? |
| Hypoechoic | Adenoma? Carcinoma? |
| Number | |
| Multiple | Cholesterol polyp? |
| Solitary | Adenoma? Carcinoma? |
| Shape | |
| Irregular | Cholesterol polyp? Carcinoma? |
| Rounded | Adenoma? Carcinoma? |
| Other causes | |
| Adenomyomatosis (rare) Metastasis (rare) |
|
15. Gallbladder: Thickened wall
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify | |
| >4mm in fasted state | Thickening? |
| Echo pattern | |
| Homogeneous, hyperechoic | Chronic cholecystitis? Echogenic fat on gallbladder wall? |
| Homogeneous, hypoechoic | Wall thickening due to ascites? Acute hepatitis? Congestive failure? |
| Inhomogeneous, hyperechoic | Chronic cholecystitis? |
| Inhomogeneous, hypoechoic | Acute cholecystitis? Tumor? |
| Gallbladder contents | |
| Stone | Stony gallbladder? |
| Echogenic material | Acute cholecystitis? |
| Obliterated lumen | Shrunken gallbladder? Tumor? |
| Gallbladder surroundings | |
| Edema | Acute cholecystitis? |
| Pain on compression | Acute cholecystitis? |
| Signs of cirrhosis, ascites | Wall thickening due to cirrhosis? |
| Signs of congestive failure | Wall thickening due to congestive failure? |
| Rare causes | |
| Dysproteinemia Lymphoma Adenomyomatosis |
|
| Finding | Interpretation |
| Verify organ identity | |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


 Straight
Straight Curved
Curved Circumscribed plaques, diffuse thickening
Circumscribed plaques, diffuse thickening Echo-free
Echo-free Echogenic
Echogenic Floating membrane
Floating membrane Start and end of the dilatation
Start and end of the dilatation Relationship to vessels
Relationship to vessels Vessel origins
Vessel origins Iliac vessels
Iliac vessels Present
Present Not present
Not present