13 The Systematic Ultrasound Examination
Now that you have learned the sonographic anatomy and interrelationships of the relevant organs, here are some guidelines on how to conduct a systematic ultrasound examination of the abdomen. Of course, the sequence in which the parts of the examination are performed will vary from one examiner to the next. The main thing for the beginner is to adopt a systematic routine that can be carried out within a certain period of time. In this system the abdomen is divided into seven topographic units:
1 Liver
2 Gallbladder and porta hepatis
3 Right kidney
4 Left kidney and spleen
5 Epigastrium and pancreas
6 Midabdomen
7 Lower abdomen
These units are shown schematically in Fig. 13.1 and are covered individually below.
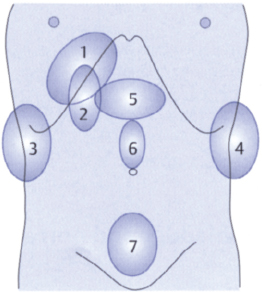
Fig. 13.1 Topographic units of the ultrasound examination.
Topographic Units
Liver
Examination of the liver proceeds in three steps:
1 Survey in longitudinal scans.
2 Survey in transverse/oblique scans.
3 Survey in intercostal scans.
L I V E R
Shape
– Angle of inferior border
– Surface
Size
Structure
– Hyperechoic
– Pattern: coarse/fine
– Distribution
– Masses?
Vessels
– Hepatic veins
Diameter
Course
– Portal vein
Diameter
Course
Biliary tract
Reporting guidelines
The liver is:
 normal in size and shape;
normal in size and shape;
 enlarged, diameter… cm on the mid clavicular line (MCL);
enlarged, diameter… cm on the mid clavicular line (MCL);
 reduced in size.
reduced in size.
The echo pattern:
 is normal,
is normal,
 is homogeneous,
is homogeneous,
 shows slightly/moderately/markedly increased echogenicity.
shows slightly/moderately/markedly increased echogenicity.
The angle of the inferior border is:
 sharp,
sharp,
 slightly rounded,
slightly rounded,
 blunted.
blunted.
The hepatic veins are:
 normal in appearance,
normal in appearance,
 rarefied,
rarefied,
 distorted.
distorted.
No masses are seen.
Gallbladder and porta hepatis
Examination of the gallbladder proceeds in three steps:
1 Survey in longitudinal scans.
2 Survey in transverse/oblique scans.
3 Lateral intercostal scans.
G A L L B L A D D E R
Location
Size
Shape
Contents
Wall
Tenderness
Contracted?
Examination of the porta hepatis proceeds in two steps:
1 Upper abdominal oblique scan (“portal scan”).
2 Subcostal oblique scan.
Reporting guidelines
The gallbladder:
 appears normal in size and shape,
appears normal in size and shape,
 shows postprandial contraction.
shows postprandial contraction.
A lumen is not seen.
The gallbladder is free of stones.
Several stones with acoustic shadows are noted: size … cm.
The gallbladder is folded over at the fundus (“Phrygian cap”).
The gallbladder wall is thickened.
The gallbladder is tender to local pressure.
There is no dilatation of the intra- or extrahepatic bile ducts.
The common bile duct measures… mm.
Right kidney
Examination of the right kidney proceeds in three steps:
1 Survey in longitudinal flank scans.
2 Survey in transverse flank scans.
3 Try to image from the front in longitudinal and transverse scans.
K I D N E Y
Location
Shape
Size
Mobility
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree