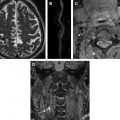
There has been significant progress made in 3-dimensional (3D) carotid plaque MR imaging techniques in recent years. Three-dimensional plaque imaging clearly represents the future in clinical use. With effective flow-suppression techniques, choices of different contrast weighting acquisitions, and time-efficient imaging approaches, 3D plaque imaging offers flexible imaging plane and view angle analysis, large coverage, multivascular beds capability, and even can be used in fast screening.
Information on the condition of carotid atherosclerosis may provide a useful window to understanding system-wide disease burden and assess overall cardiovascular risk.
Information on the condition of carotid atherosclerosis may provide a useful window to understanding system-wide disease burden and assess overall cardiovascular risk.
Summary
In summary, there has been significant progress made in 3D carotid plaque imaging techniques in recent years. Three-dimensional plaque imaging clearly represents the future in clinical use. With effective flow-suppression techniques, choices of different contrast weighting acquisitions, and time-efficient imaging approaches, 3D plaque imaging offers flexible imaging plane and view angle analysis, large coverage, multivascular beds capability, and even can be used in fast screening.
Disclosure Statement: Dr C. Yuan holds grants from the National Institutes of Health and (R21EB017514 & R01HL103609) Philips Medical . He also serves as a Member of Radiology Advisory Network, Philips. Dr D.L. Parker has nothing to disclose.
References
- 1. Virmani R., Kolodgie F.D., Burke A.P., et al: Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: pp. 2054-2061
- 2. Saam T., Hetterich H., Hoffmann V., et al: Meta-analysis and systematic review of the predictive value of carotid plaque hemorrhage on cerebrovascular events by magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62: pp. 1081-1091
- 3. Gupta A., Baradaran H., Schweitzer A.D., et al: Carotid plaque MRI and stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2013; 44: pp. 3071-3077
- 4. O’Leary D.H., and Polak J.F.: Intima-media thickness: a tool for atherosclerosis imaging and event prediction. Am J Cardiol 2002; 90: pp. 18L-21L
- 5. Sillesen H.: Carotid intima-media thickness and/or carotid plaque: what is relevant? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2014; 48: pp. 115-117
- 6. Spence J.D.: Carotid plaque measurement is superior to IMT. Invited editorial comment on: carotid plaque, compared with carotid intima-media thickness, more accurately predicts coronary artery disease events: a meta-analysis-Yoichi Inaba, M.D., Jennifer A. Chen M.D., Steven R. Bergmann M.D., Ph.D. Atherosclerosis 2012; 220: pp. 34-35
- 7. Cai J.M., Hatsukami T.S., Ferguson M.S., et al: Classification of human carotid atherosclerotic lesions with in vivo multicontrast magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 2002; 106: pp. 1368-1373
- 8. Yuan C., and Kerwin W.S.: MRI of atherosclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 2004; 19: pp. 710-719
- 9. Yarnykh V.L., Terashima M., Hayes C.E., et al: Multicontrast black-blood MRI of carotid arteries: comparison between 1.5 and 3 tesla magnetic field strengths. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006; 23: pp. 691-698
- 10. Kerwin W.S., Liu F., Yarnykh V., et al: Signal features of the atherosclerotic plaque at 3.0 Tesla versus 1.5 Tesla: impact on automatic classification. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008; 28: pp. 987-995
- 11. Ota H., Yarnykh V.L., Ferguson M.S., et al: Carotid intraplaque hemorrhage imaging at 3.0-T MR imaging: comparison of the diagnostic performance of three T1-weighted sequences. Radiology 2010; 254: pp. 551-563
- 12. Hayes C.E., Mathis C.M., and Yuan C.: Surface coil phased arrays for high-resolution imaging of the carotid arteries. J Magn Reson Imaging 1996; 6: pp. 109-112
- 13. Tate Q., Kim S.E., Treiman G., et al: Increased vessel depiction of the carotid bifurcation with a specialized 16-channel phased array coil at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2013; 69: pp. 1486-1493
- 14. Edelman R.R., Chien D., and Kim D.: Fast selective black blood MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 181: pp. 655-660
- 15. Yuan C., Kerwin W.S., Ferguson M.S., et al: Contrast-enhanced high resolution MRI for atherosclerotic carotid artery tissue characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 2002; 15: pp. 62-67
- 16. Antiga L., Wasserman B.A., and Steinman D.A.: On the overestimation of early wall thickening at the carotid bulb by black blood MRI, with implications for coronary and vulnerable plaque imaging. Magn Reson Med 2008; 60: pp. 1020-1028
- 17. Balu N., Chu B., Hatsukami T.S., et al: Comparison between 2D and 3D high-resolution black-blood techniques for carotid artery wall imaging in clinically significant atherosclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008; 27: pp. 918-924
- 18. Balu N., Kerwin W.S., Chu B., et al: Serial MRI of carotid plaque burden: influence of subject repositioning on measurement precision. Magn Reson Med 2007; 57: pp. 592-599
- 19. In Balu N., Yarnykh V., and Chu B. (eds): Carotid plaque assessment using fast 3D isotropic-resolution black-blood MRI. International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2009.
- 20. Wang J., Yarnykh V.L., Hatsukami T., et al: Improved suppression of plaque-mimicking artifacts in black-blood carotid atherosclerosis imaging using a multislice motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium (MSDE) turbo spin-echo (TSE) sequence. Magn Reson Med 2007; 58: pp. 973-981
- 21. Zhao H., Wang J., Liu X., et al: Assessment of carotid artery atherosclerotic disease by using three-dimensional fast black-blood MR imaging: comparison with DSA. Radiology 2015; 274: pp. 508-516
- 22. Wang J., Yarnykh V.L., and Yuan C.: Enhanced image quality in black-blood MRI using the improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium (iMSDE) sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010; 31: pp. 1256-1263
- 23. Makhijani M.K., Balu N., Yamada K., et al: Accelerated 3D MERGE carotid imaging using compressed sensing with a hidden Markov tree model. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012; 36: pp. 1194-1202
- 24. Wang J., Gerretsen S.C., Maki J.H., et al: Time-efficient black blood RCA wall imaging at 3T using improved motion sensitized driven equilibrium (iMSDE): feasibility and reproducibility. PLoS One 2011; 6: pp. e26567
- 25. Obara M., Kuroda K., Wang J., et al: Comparison between two types of improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium (iMSDE) for intracranial black-blood imaging at 3.0 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014; 40: pp. 824-831
- 26. Zhu C., Graves M.J., Yuan J., et al: Optimization of improved motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium (iMSDE) blood suppression for carotid artery wall imaging. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2014; 16: pp. 61
- 27. Moody A.R., Murphy R.E., Morgan P.S., et al: Characterization of complicated carotid plaque with magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging in patients with cerebral ischemia. Circulation 2003; 107: pp. 3047-3052
- 28. Murphy R.E., Moody A.R., Morgan P.S., et al: Prevalence of complicated carotid atheroma as detected by magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging in patients with suspected carotid artery stenosis and previous acute cerebral ischemia. Circulation 2003; 107: pp. 3053-3058
- 29. Zhang Z., Fan Z., Carroll T.J., et al: Three-dimensional T2-weighted MRI of the human femoral arterial vessel wall at 3.0 Tesla. Invest Radiol 2009; 44: pp. 619-626
- 30. Fan Z., Zhang Z., Chung Y.C., et al: Carotid arterial wall MRI at 3T using 3D variable-flip-angle turbo spin-echo (TSE) with flow-sensitive dephasing (FSD). J Magn Reson Imaging 2010; 31: pp. 645-654
- 31. Parker D.L., Yuan C., and Blatter D.D.: MR angiography by multiple thin slab 3D acquisition. Magn Reson Med 1991; 17: pp. 434-451
- 32. Yim Y.J., Choe Y.H., Ko Y., et al: High signal intensity halo around the carotid artery on maximum intensity projection images of time-of-flight MR angiography: a new sign for intraplaque hemorrhage. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008; 27: pp. 1341-1346
- 33. Yoshimura S., Yamada K., Kawasaki M., et al: High-intensity signal on time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography indicates carotid plaques at high risk for cerebral embolism during stenting. Stroke 2011; 42: pp. 3132-3137
- 34. Yuan C., Mitsumori L.M., Ferguson M.S., et al: In vivo accuracy of multispectral magnetic resonance imaging for identifying lipid-rich necrotic cores and intraplaque hemorrhage in advanced human carotid plaques. Circulation 2001; 104: pp. 2051-2056
- 35. Chu B., Kampschulte A., Ferguson M.S., et al: Hemorrhage in the atherosclerotic carotid plaque: a high-resolution MRI study. Stroke 2004; 35: pp. 1079-1084
- 36. Kampschulte A., Ferguson M.S., Kerwin W.S., et al: Differentiation of intraplaque versus juxtaluminal hemorrhage/thrombus in advanced human carotid atherosclerotic lesions by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 2004; 110: pp. 3239-3244
- 37. Takaya N., Yuan C., Chu B.C., et al: Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: a high-resolution MRI study. Circulation 2005; 111: pp. 2768-2775
- 38. Yuan C., Zhang S., Polissar N.L., et al: Identification of fibrous cap rupture with magnetic resonance imaging is highly associated with recent TIA or stroke. Circulation 2002; 105: pp. 181-185
- 39. Yamada K., Song Y., Hippe D.S., et al: Quantitative evaluation of high intensity signal on MIP images of carotid atherosclerotic plaques from routine TOF-MRA reveals elevated volumes of intraplaque hemorrhage and lipid rich necrotic core. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2012; 14: pp. 81
- 40. Wang J., Börnert P., Zhao H., et al: Simultaneous noncontrast angiography and intraplaque hemorrhage (SNAP) imaging for carotid atherosclerotic disease evaluation. Magn Reson Med 2013; 69: pp. 337-345
- 41. Balu N, Liu H, Chen S, et al. Dual contrast vessel wall MRI using phase sensitive polarity maps, Proceedings of the 22st Scientific Meeting and Exhibition, International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Milan (Italy), May 10–16, 2014.
- 42. Fan Z., Yu W., Xie Y., et al: Multi-contrast atherosclerosis characterization (MATCH) of carotid plaque with a single 5-min scan: technical development and clinical feasibility. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2014; 16: pp. 53
- 43. Zhu D.C., Vu A.T., Ota H., et al: An optimized 3D spoiled gradient recalled echo pulse sequence for hemorrhage assessment using inversion recovery and multiple echoes (3D SHINE) for carotid plaque imaging. Magn Reson Med 2010; 64: pp. 1341-1351
- 44. Li L., Chai J.T., Biasiolli L., et al: Black-blood multicontrast imaging of carotid arteries with DANTE-prepared 2D and 3D MR imaging. Radiology 2014; 273: pp. 560-569
- 45. Li L., Miller K.L., and Jezzard P.: DANTE-prepared pulse trains: a novel approach to motion-sensitized and motion-suppressed quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 2012; 68: pp. 1423-1438
- 46. Mendes J., Parker D.L., Kim S.E., et al: Reduced blood flow artifact in intraplaque hemorrhage imaging using CineMPRAGE. Magn Reson Med 2013; 69: pp. 1276-1284
- 47. Zhou Z., Li R., Zhao X., et al: Evaluation of 3D multi-contrast joint intra- and extracranial vessel wall cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2015; 17: pp. 41
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree